Definition: Valuation of Assets or asset valuation is a process of determining the present market value of the assets of the business as shown in the balance sheet of the company based on universally accepted accounting principles. It’s a duty of an auditor to make an appropriate asset valuation along with the verification of such assets, and such valuation is done based on its utility after getting depreciated.
Content: Valuation of Assets
- Methods of Valuation of Assets
- Importance of Valuation of Assets
- Auditors Duty Regarding Asset Valuation
- Problems in the Valuation of Assets
- Conclusion
Methods of Valuation of Assets
A certified valuer can value the assets of the company by several distinctive methods; some of them are as follows:
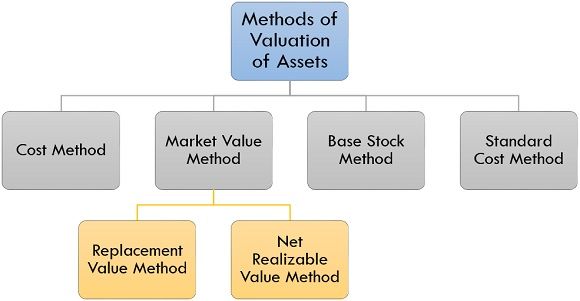
- Cost Method
The purchasing cost of an asset is treated as a base for the asset valuation in this method, the valuer need not do any calculation, the purchase value of the asset is considered as the current value of the asset, and this method of valuation is the simplest method amongst all method.
- Market Value Method
In this method market value of an asset is considered as a base for the asset valuation; however, it becomes troublesome if assets having similar nature is not available in the market, considering the problem two subsequent methods are adopted under this method:
-
- Replacement Value Method: Valuation of an asset will be done on the basis of the similar value the older asset possesses if the new asset purchased is of similar nature.
- Net Realizable Value Method: After deducting the expenses incurred on the sale of an old asset, the remaining amount left over after it is treated as the net realizable value of that asset for sale in the market. This method is generally used only if a similar nature asset is not available in the market.
- Base Stock Method
The company has to maintain a level of inventory up to a certain limit on the basis of which valuation of inventories is done in the base stock method of asset valuation.
- Standard Cost Method
In this method of valuation standard cost of an asset is treated as a base instead of an actual cost of such asset and such standard cost are set by the companies generally on the basis of their previous experiences.
Importance of Valuation of Assets
Valuation of assets plays a significant role in the process of audit as it helps in determining the fair position of the assets in the balance sheet. Along with this, there are a number of motives behind the valuation of assets; some of them are as follows:
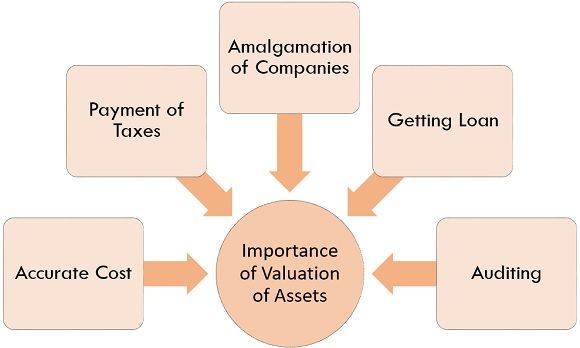
- Accurate Cost
Correct valuation of asset is necessary to identify the accurate cost of the asset so that at the time of selling such assets appropriate value gets received and at the time of purchasing assets also relevant asset value will get paid.
- Payment of Taxes
Company holding assets are required to pay the amount of tax imposed on such assets, and for computing the precise amount of tax to be paid proper valuation of asset is mandatory.
- Amalgamation of companies
At the time of the amalgamation of two company’s valuation of the asset becomes an essential aspect as it helps both the companies to evaluate the business.
- Getting Loan
At the time of need of a loan from the bank or any other financial institution valuation of an asset is required by the bank to ascertain the amount of loan the company can get on a guarantee of their assets.
- Auditing
For auditing, the financial statement of a company an auditor performs the valuation of assets thoroughly so that the assets of the company reflect the true and fair value in the statement.
Auditors Duty Regarding Asset Valuation
However, the auditor does not perform the valuation of assets, yet he is involved with the suitable valuation of assets. It is the auditor’s duty to check thoroughly whether the assets are valued appropriately or not according to the accounting principles because if they are not adequately valued they will not show fair value in the financial statement.
Problems in the Valuation of Assets
The following are the problems that an auditor faces at the time of the asset valuation:
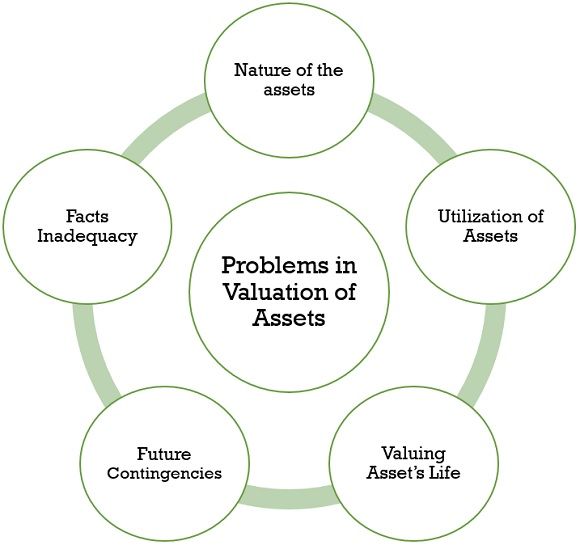
- Nature of the assets
Sometimes it becomes critical to identify the nature of the asset, whether it is a fixed asset or a current asset, and it is necessary to differentiate it because the method of valuation of both differs from each other.
- Utilization of Assets
Valuation of an asset in case of a re-purchased asset also depends upon the nature of the use of such an asset. For example, Old Machinery again purchased and used in the company needs to be valued according to its use which may create confusion if the same machine is getting used for a different purpose.
- Valuing Asset’s Life
Valuing an asset on the basis of its estimated life seems to be difficult as it may vary, one cannot ascertain the actual life of the fixed assets; thus, its valuation is done on the estimated basis only.
- Future Contingencies
An auditor does not consider the effect on the asset after the preparation of the balance sheet. Still, they have an impact on such assets afterwards also, which may act as a problem for fair valuation of assets.
- Facts Inadequacy
Sometimes there is a possibility that an auditor may miss some facts or information due to any reason that can be a reason behind the improper valuation of assets.
Conclusion
Valuation of Assets means determining the monetary value of an asset, and for preparing the fair financial statement, correct asset valuation is a must, as without it one cannot ascertain the correct profit and loss of the company. It’s the duty as well as the responsibility of an auditor to make sure that the assets showing their true value in the financial statement at the end of the year.
talha says
brief and crisp info