Definition: Human resource management (HRM) is a tactical approach which deals with acquisition, training and development, orientation, motivation and retention of personnel in an organisation. It is a powerful tool for any organisation to succeed. It is a continuous and never-ending process.
A human resource refers to the human capital available with the organisation in the form of employees who add value to the business.
It is considered to be the most complex and valuable asset to the growth and success of an organisation.
Content: Human Resource Management (HRM)
Human Resource Manager
A human resource manager is a trained person responsible for the placement of employees in the right position, training and orientation of employees, addressing grievances and solving conflicts, ensuring safety and security of employees, looking after promotions and appraisals of employees, and aiming at the retention of valuable employees in the organisation.
A human resource manager also acts as a link between the management and the employees; he communicates the management’s policies and instructions to employees as well as employee’s grievances and queries to the management.
Nature of Human Resource Management (HRM)
Human resource management (HRM) is an inevitable part of every organisation. It is crucial to have an in-depth knowledge of HRM to realise organisational goals and simultaneously creating a happy and contented workforce.
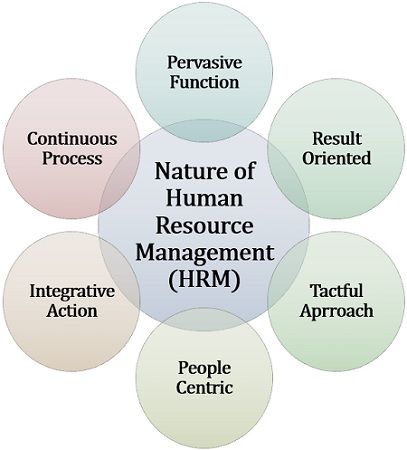 To get a better understanding of the nature of human resource management, we must go through the following points:
To get a better understanding of the nature of human resource management, we must go through the following points:
- Pervasive Function: HRM is practised at all levels of management and applies to all kinds of organisations, even to non-profit organisations.
- Result Oriented: It aims at achieving organisational objectives through the optimum utilisation of human resources.
- Tactful Approach: HRM deals with the people who are distinct from one another; thus the manager needs to apply diverse strategies and tactics at different point of time and in different situations.
- People-Centric: Human resource management is concerned majorly with the employees working in an organisation.
- Integrative Action: It focusses on maintaining cordial relations among the employees at different levels and also addresses employee grievances.
- Continuous Process: HRM is an ongoing process of procurement, development and redirection of personnel towards the organisational goals. It cannot be completed in a day, a week or a month.
Objectives of Human Resource Management (HRM)
The primary aim of human resource management (HRM) is to meet the human capital requirement of an organisation. Further, we will discuss four other vital objectives of HRM:
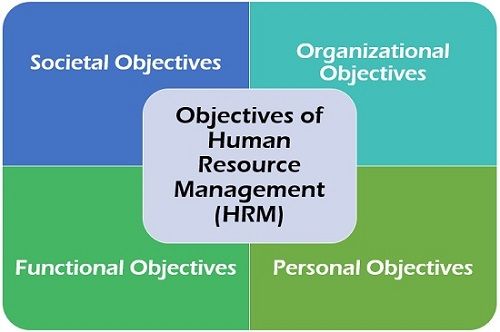
- Societal Objectives: HRM is essential to comply with the laws of the society such as labour law or reservation system. It is obligatory for any organisation to fulfil its ethical and social responsibilities which can be done only through HRM.
- Organisational Objectives: In an organisation, human resource management is not an independent unit, but it is a department which aims at facilitating the other departments of the organisation to function smoothly.
- Functional Objectives: HRM ensures that every department is supplemented with the employees possessing the required set of skills and talent, at the desired cost. It also provides for the optimum utilisation of the human capital.
- Personal Objectives: To ensure employee’s long-term association with the organisation and to enhance employee’s commitment and contribution towards the organisation, HRM helps the employees to reach their personal goals.
Functions of Human Resource Management (HRM)
Human resource management (HRM) is a systematic approach to fill in the gap between the organisation and its employees. To simplify the task of managing the human capital of the organisation, various functions of HRM have been developed. These functions are categorised broadly as:
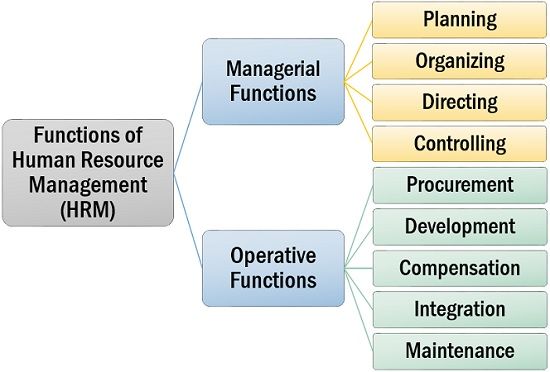
Managerial Functions
Human resource management is essential at all levels of an organisation. The top management is responsible for forming strategies and giving directions for the successful application of such plans. In the process, they perform the following functions:
- Planning: Firstly, the management must be aware of the vacant positions or workforce requirement of the organisation. Then, they need to formulate the strategies for meeting the requirements.
- Organising: The manager has to establish a framework for the operative functions, bringing together the human resources and physical resources available with the organisation.
- Directing: Once the framework is ready, the manager instructs and guides the team to work accordingly, to meet the organisational objective.
- Controlling: The management predefines the standard for performance, and later analyses the results based on such criteria through performance appraisal and job analysis. The management has to take corrective measures if necessary.
Operative Functions
The operative functions are those which are taken on the departmental level or middle level and mainly concerned about the execution of the plans and strategies formulated at the managerial level. To know more about the different operative functions, read below:
- Procurement: The acquisition of human resource is the primary function of a manager. It involves the estimation of personnel requirement, recruitment and selection of suitable candidates, placement and orientation of the workforce in the right position.
- Development: To develop the required skills and talent within the employees, the managers have to use various training techniques.
- Compensation: Compensation in the form of remuneration, given to employees instead of their services to the organisation should be adequate and fair. The employees are liable to get other benefits such as a bonus or incentives.
- Integration: Integration means making the new employees familiar with the organisation and to their task or process. It introduces them to the organisational environment and their colleagues.
- Maintenance: The most important of all is the retention of the employees which requires providing them with various benefits and facilities like PF, life insurance, accidental insurance, health insurance, pension, gratuity, allowances and taking other health and safety measures.
Importance of Human Resource Management (HRM)
Over the years, human resource management (HRM) has gained importance in the business sector, as well as non-profit organisations. Human capital is equally important as the financial capital is to an organisation, since ‘people perform a task’.

To add further to the knowledge about the need for human resource in an organisation, go through the following:
- Fulfil the Human Resource Requirement: Human resource management fills in the gap between the vacancies in the organisation and the suitable candidates for such positions.
- Employee Retention: HRM not only functions to acquire the manpower but also concentrates on the maintenance and retention of the human capital.
- Enhance the Quality of Work Life: It focusses on the continuous enhancement of the job facilities, hence improving the quality of employee’s work life.
- Redressing Grievance and Conflict: HRM addresses the problems among employees or with the management since it is essential for any organisation to resolve its internal conflicts and grievances to ensure a sound and co-operative work environment.
- Achieving Organizational Goals: To reach the set objectives and targets on time, it is necessary to direct the employee’s efforts towards the organisational goals. All this is possible only through the practice of human resource management.
- Long-term Existence in the Market: As we all know that employees are the inevitable part of any organisation, therefore to survive in the competition, it is imperative that the organisation brings HRM into functioning.
- Developing Team Spirit and Feeling of Belongingness: It brings together the different employees as a team to accomplish the goals of the organisation. HRM also make the employees feel valuable to the organisation.
- Employee Satisfaction and Welfare: HRM works for the welfare, safety and security of the organisation. It is majorly concerned about the level of satisfaction derived by an employee from his job.
Challenges of Human Resource Management (HRM)
The human resource managers go through many obstacles in the management and development of the human resource, all due to the emergence of new technology and the changing of political and socio-economic conditions. To get an overview of these challenges, read further:

- Growing Employee Expectations: With the learning of new skills and better qualification, the employee’s expectations keep on increasing, and at times it is difficult for managers to meet such high expectations.
- Growing Size of Workforce: With the growth of any organisation, the workload increases and the number of employees also multiply. This leads to the excessive workload on the human resource manager and the HR team.
- The emergence of New Technology: The technological advancement has though simplified the business process but has emerged as a challenge in front of the managers to either provide training to their old staff or seek for the new talent.
- Internal Politics: Sometimes, the human resource manager has to face situations where employees either mislead or influence other employees to restrict them from performing their task if the problem pertains the organisation may experience employee turnover or resignations.
- Human Psychology: HRM somehow deals with human psychology and its impact on the business which is a complex system and unlike the problems related to other physical resources and assets, have no particular solution.
- Changes in Law and Regulations: To safeguards the interest of employees, government bring in specific rules and regulations which have to be followed by organisations. At times, it is difficult for the HR manager to adhere to such laws.
- Maintenance of Human Relations: A human resource manager not only acts as a mediator between the management and the employees but also tries to maintain a cordial relationship among the two, which requires a lot of tactics and diplomacy.
Conclusion
We humans have a nature of never being content with what we have. They always aspire for more. Also, the problems related to human resource have different solutions each time, this created the need for human resource management.
HRM is a complex process; therefore the human resource managers require a lot of patience, careful approach and a diplomatic attitude to handle the human capital of an organisation effectively.
CCK says
a very comprehensive article
Jaun says
Very lucid and precise. Thanks.
Aakla says
Thanks for sharing this information with us, I learned a lot about human resource management from your blog.
Chimaobi Okemiri says
Thanking you plentifully for the well-educating article. It is simple, and precise. It has enhanced my understanding and knowledge of HRM. Keep on enriching us the more. God bless your team immeasurably.
GODWILL INNO MOSES says
thanks for this article, it has really helped me during my research.