Definition: Financial intermediary is the organization which acts as a link between the investor and the borrower, to meet the financial objectives of both the parties. These can be seen as business entities which accept deposits from the depositors or investors (lenders) by allowing them low interest on their sum. Further, these organizations, lend this amount to the individuals and firms (borrowers) at a comparatively high rate of interest to make their margin.
The two of the significant roles played by the financial intermediary in the economy are the creation of funds and governing the payments system.
Content: Financial Intermediaries
Example
Mrs A. is a housewife and deposits her savings into her account with the XYZ bank every month.
On the other hand, Mr B is a young entrepreneur who is seeking a loan to start his venture. Now, Mr B has two options for availing the loan:
- The first is that he can find and convince the individuals who are looking for investment opportunities, or;
- he can approach the XYZ bank for a loan
We can see that the first option is uncertain, and it will take a lot of time to find the investors. However, the second option is more convenient and quick.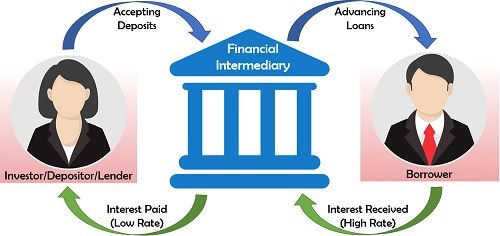
Thus, we can say that with the financial intermediary facilitate the lending and borrowing of funds on a large scale.
Types of Financial Intermediaries
There are several financial intermediaries formed to serve the different aims and objectives of the customers or members or lenders and borrowers. These entities are explained in detail below:
Banks: The central and commercial banks are the most well known financial intermediaries simplifying the lending and borrowing process, along with providing various other services to its customers on a large scale.
Credit Unions: These are the cooperative financial units which facilitate lending and borrowing of funds to provide financial assistance to its members.
Non-Banking Finance Companies: A NBFC is a financial company engaged in activities such as advancing loans to its clients at a very high rate of interest.
Stock Exchanges: The stock exchange facilitate the trading of securities and stocks, and in every trading activity, it charges the brokerage from each party which is its profit.
Mutual Fund Companies: The mutual fund organizations club the amount collected from various investors. These investors have identical investment objectives and risk-taking ability. The funds are then collectively invested in the securities, bonds, and other investment options, to ensure a capital gain in the long run.
Insurance Companies: These companies provide insurance policies to the individuals and business entities to secure them against accident, death, risk, uncertainties and default. For this purpose, they accept deposits in the form of premium, which is pooled into profitable investments to gain returns. The insured person can claim the money in case of any mishap as per the agreement.
Financial Advisers or Brokers: The investment brokers also collect the funds from various investors to invest it in the securities, bonds, equities, etc. The financial advisers even provide guidance and expert opinions to the investors.
Investment Bankers: These banks specialize in services like initial public offerings (IPO), other equity offerings, proving for mergers and acquisitions, institutional client’s broker services, underwriting debts, etc. As a result of constant mediation, between the investor or public and the companies issuing securities.
Escrow Companies: It is a third party acting as an intermediary and responsible for getting all the conditions fulfilled at the time of loan provided by one party to the other for the real estate mortgage.
Pension Funds: The government entities initiate a pension fund. A certain amount is deducted from the salary of the employees each month. This collected sum is then invested in different schemes to gain profits. The investor’s fund is returned with interest after their retirement.
Building Societies: These financial intermediaries are similar to the credit unions, owned and facilitating mortgage loans and demand deposits to its members.
Collective Investment Schemes: Under this scheme, the various investors with common investment objective come together to pool their funds and collectively invest this amount into a profitable investment option. Later they distribute the interest among themselves as per the agreement.
Advantages of Financial Intermediaries
The financial intermediaries are as crucial to the economy as the blood is to the body. Some of its significant benefits are discussed below: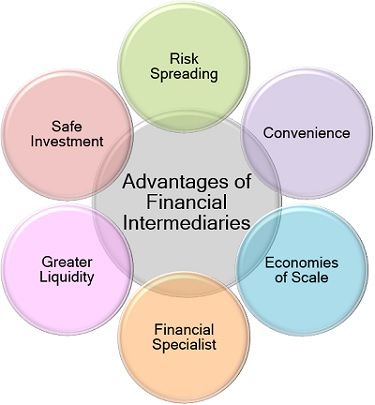
- Low Risk: The involvement of intermediaries reduces the risk of fraudulent, default and even capital loss for the lender.
- Convenience: Exchange becomes suitable for the investor as well as the borrower. Since both, the parties do not need to invest time and money in searching for each other. Instead, they have to approach the intermediary for the purpose.
- Economies of Scale: The cost involved in the lending and borrowing of funds like analyzing credit position, operational expenses and cost of paperwork decreases to a large extent. The financial intermediaries perform such activities on a massive scale.
- Financial Specialization: These organizations or companies specialize in fund management and investing activities providing better returns to the investors and easy loans to the borrowers.
- Greater Liquidity: The financial intermediaries like banks allow investors or depositors to withdraw their amount at any point of time, as per their requirement.
- Safe Investment: For the investor’s point of view, financial intermediaries are considered to be more trustworthy and reliable than lending money directly to an individual to yield interest.
Drawbacks of Financial Intermediaries
Everything has two phases, one is positive, and the other is negative. As we already know that financial intermediaries operate for profits, they are not charitable institutions; the following are some of its disadvantages:
- Low Returns on Investment: The ultimate aim of the financial intermediaries is to earn a profit and therefore, they usually provide a low rate of interest on the investment made by the depositors.
- Opposing Goals: The goals of the investors and the financial intermediaries may not complement each other, and therefore the objective of one may not be achieved.
- Fees and Commissions: These intermediaries impose charges, expenses and commission on the financial assistance they provide to their customers.
- False Opportunities: Sometimes, the financial intermediaries come up with the investment opportunities which guarantee high potential returns with the hidden risk involved in it. Even some these, may not yield the promised returns and turn out to be a failure for the investor.
- High Interest on Loans: These financial intermediaries charge a high rate of interest on the loan provided to the borrowers to earn a profit.
Conclusion
Financial intermediaries are essential for the growth of a country. They act as the backbone of the economy and facilitates the circulation of money in the market from the individual’s households and accounts.
Sithum Palihawadane says
very good explanations.
Easy to understand
Financial Brokers says
Thank you for sharing this blog. I love it.
Mortgage Broker in RoseVille says
This is such an amazing blog. I really love reading it.