Definition: Cost accounting is the accounting method for ensuring cost-effectiveness by accumulating, organising, recording, calculating, analysing and assessing the overall expenses incurred on a product, process or project, etc. It is mostly used in industrial units or factories where the goods are manufactured.
Unlike financial accounting, cost accounting is a broader perspective to review and control the performance of the industries by the management. To know more about the different types of expenses incurred in operating a business, one must be aware of the cost classification.
Content: Cost Accounting
Related Terminology
There are specific terminologies which though have a different meaning but are usually used as a substitution for cost accounting. The three of these are as follows:
Cost
Cost refers to any expense or sacrifice made to develop a product or service.
As far as manufacturing units or industries are concerned, the three significant elements of cost are material, labour and overheads. These are further bifurcated into two categories each, i.e. direct and indirect.
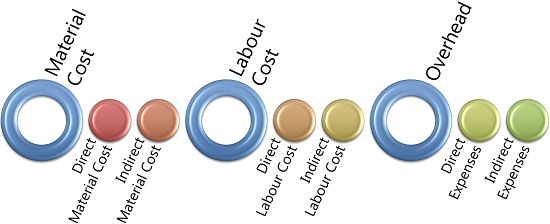 The cost can also be identified by its variability as the fixed cost, variable cost and semi-variable cost.
The cost can also be identified by its variability as the fixed cost, variable cost and semi-variable cost.
Costing
Costing is the technique and method used for calculating the cost of a product or service.
Cost Accountancy
Cost accountancy is a systematic process of applying the costing, as well as cost accounting methods in business activities. It ensures cost control and reduction.
Scope of Cost Accounting
Cost accounting is being widely applied by the production units to modify the process and maximise the profit.
Following are the various applicabilities of the cost accounting techniques:
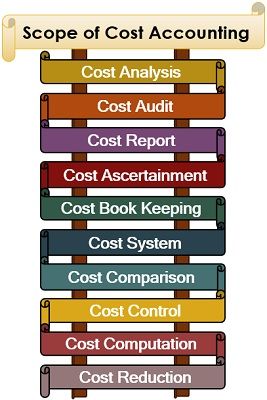
- Cost Analysis: Cost accounting determines the deviation of the actual cost as compared to the planned expense, along with the reason for such variation.
- Cost Audit: To verify the cost sheets and ensure the efficient application of cost accounting principles in the industries, cost audits are done.
- Cost Report: Cost reports are prepared from the data acquired through cost accounting to be analysed by the management for strategic decision making.
- Cost Ascertainment: To determine the price of a product or service, it is essential to know the total cost involved in generating that product or service.
- Cost Book Keeping: Similar to financial accounting; journal entries, ledger, balance sheet and profit and loss account is prepared in cost accounting too. Here, the different cost incurred is debited, and income from the product or service is credited.
- Cost System: It provides for time to time monitoring and evaluation of the cost incurred in the production of goods and services to generate cost reports for the management.
- Cost Comparison: It examines the other alternative product line or activities and the cost involved in it, to seek a better opportunity for generating high revenue.
- Cost Contol: Sometimes, the actual cost of a product or service becomes higher than its standard cost. To eliminate the difference and control the actual cost, cost accounting is required.
- Cost Computation: When the company is engaged in the production of bulk units of a particular product or commodity, the actual per-unit cost is derived through cost accounting.
- Cost Reduction: It acts as a tool in the hands of management to find out if there is any scope of reducing the standard cost involved in the production of goods and services. Its purpose is to obtain additional gain.
Objectives of Cost Accounting
Cost accounting aims at eliminating the loopholes in the production process and ensures manufacturing of goods at the lowest possible cost.
Other than this, there are multiple objectives of the cost accounting practices. Let us now discuss its importance in detail:

- Control and Reduce Cost: Cost accounting continuously focuses on managing the cost of production per unit to improve profitability without compromising with the quality of the product.
- Determine Selling Price: It provides the total cost incurred in the product or service, which is the base for fixing an appropriate selling price.
- Assist Management in Decision Making: The reports and cost sheets generated based on cost accounting back the managerial decisions of the organization.
- Ascertain Closing Inventory: It determines the closing inventory value at the end of the financial year.
- Ensure Profit from Each Activity: Cost accounting reviews the cost and takes corrective actions at each level to ensure profitability from all business activities.
- Budgeting: It generates the estimated cost of products or services to assist in budget planning, implementation and control.
- Setting Performance Standards: It provides a standard cost of goods or services to sets a level for the future course of action.
- Business Expansion: It estimates the cost of production at different stages, based on this analysis, the management can plan for expansion of the business.
- Minimizing Wastage: Cost control and reduction so attained helps in reducing the wastage during the manufacturing process.
- Improves Efficiency: Cost accounting assures cost management, profit appreciation and less wastage which ultimately enhances the overall production and manufacturing process of products.
Limitations of Cost Accounting
Cost accounting is a complex stream of accounting. It requires a lot of analysis and calculations to give accurate results.
To know more about the limitations or objections about cost accounting, read below:
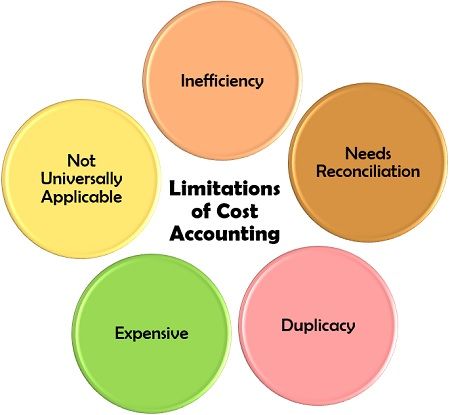
Cost accounting is not sufficient alone to control or reduce the cost of products or services. It is necessary to use the data so generated to take corrective actions which require a lot of experience and expertise.
Moreover, it differs from the financial accounting we practice in day to day life. To get an accurate result, a reconciliation statement has to be prepared.
In the books of accounts, many entries have to be made twice; once in the final accounts and then in the cost accounts, which is a tedious process. Due to the lengthy process of duplicate entries, there is a need for additional efforts from the personnel. Thus it increases the labour charges for the organisation.
It is majorly applicable to the industries, factories and manufacturing units where some production function takes place. It is less useful for service industries.
Conclusion
Cost accounting can be seen as a self-assessment tool in the hands of management. It acts as a source of information like closing inventory, capital expenditure, direct and indirect cost, etc. for the preparation of financial accounts of an organisation.
The concept of service costing is widely applied for determining the expenses incurred in business activities carried out in the service organizations. It helps in applying cost accounting in the service industries.
sangram jathar says
nice
vaibhavi says
its really useful as exam material.
Thank you so much priya for your great effort.
satyapriya.1@gmail.com says
Good and very very informative material. It’s just worthy of applauding.
Amit nagar says
It is very helpful and understanding level of language is so easy , it, s better as compared to others app . Therefore, thank you so much and I hopeful it is easy understood for all of us and very nice also. And it is very really useful for our exam purpose also .
Ashok Kumar padhi says
well explained. point to point elaboration.
informative and well communicated.
reyhan says
thanks alot of information