Techniques of Controlling are the tools used for establishing control over business activities, monitoring and taking necessary corrective measures. There are several Traditional and Morden techniques available for efficient business control.
The selection of the techniques must be a strategic approach. While selecting the most suitable technique, the organization must study its:
- Nature of Business
- Target Customers or Users
- Problems faced by the Organizations

Every organization differs from one another and functions differently. Thus, no such control system is available that applies to all the organizations.
Among Morden and Traditional techniques, some evaluate only a part of the process, whereas some involve an in-depth analysis. Therefore, a single method is not enough for achieving control over the organization.
Consequently, they combine one or more techniques to create an effective control system.
Content: Techniques of Controlling
- What do you mean by Controlling?
- Techniques of Controlling
- Selection of the Controlling Technique
- Final Words
What do you mean by Controlling?
Controlling lasts among five management functions that review all the preceding functions. It monitors the performance and distinct aspects of functional units of the business.
In this function, managers make a comparison of actual and planned performance and investigate the deviations. In case of any variations, the management takes suitable corrective measures.
It confirms the efficient allocation of the firm’s resources and working as per the previously set plans, goals, and objectives.
Techniques of Controlling
There are various techniques available for controlling in the field of management. We can group them under two broad categories as follows:
- Traditional Techniques
- Modern Techniques
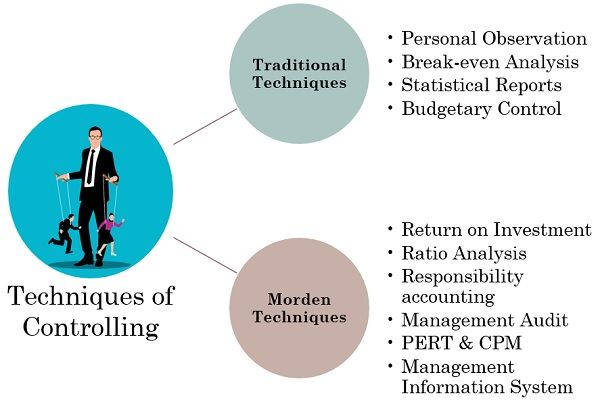
Traditional Techniques
As the name suggests, managers have developed and used these techniques for a long period of time. These techniques are still fruitful and used by the firms till date.
Following are the most commonly used traditional techniques for controlling:
- Personal Observation
- Break-even Analysis
- Statistical Reports
- Budgetary Control
Personal Observation
It is the oldest traditional method available to perform the controlling function. Here, the manager personally observes the employees/workers at the workplace.
In simple words, we can understand it as On-the-Spot or Direct Observation.
Direct observation pressurizes the employees and motivates them to work with maximum efficiency. However, this technique involves a huge amount of time during supervision.
The benefit of using it is to get first-hand and authentic information for the analysis. Also, the managers can correct the operations on the spot in case of non-performance.
Besides the above merits, the employees can share issues or problems simultaneously. In addition, it boosts the morale of the employees.
Break-even Analysis
This control technique depicts the relationship between Cost and Volume at different output levels. It is also known as the Cost, Volume and Profit analysis.
It predicts the profits and losses in response to the changes in output levels. The point where the cost price equals the selling price is the Break-even point.
Break-even Point Formula:
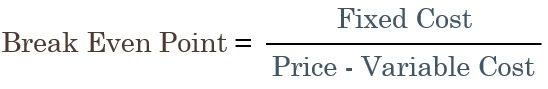
Total cost involves two costs, i.e. Fixed Costs and Variable Costs. Profits and Losses are affected by the proportional changes in both.
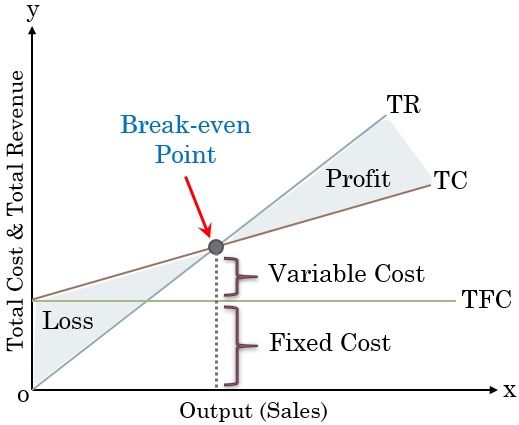
In the Break-Even Analysis technique, the evaluation is based on the elements given below:
- Break-even Point
- Angle of Incidence
- Contribution Margin
- Margin of Safety
Statistical Reports
The manager gathers information to evaluate performance in functional areas. Moreover, they use the collected information for comparison purposes. It involves the analysis of the numeric data in the form of:
- Averages
- Percentages
- Co-relation
- Ratios, etc
The organization presents the above information via Charts, Graphs, Tables, etc. These reports help visualize the data and identify the areas that demand attention. Hence, it is the most used and helpful technique for data analysis.
Budgetary Control
Budgetary Control is an important traditional control technique used in planning and controlling functions. It covers the planning of the essential operations followed by its comparisons with the actual performance.
The budgeting process includes comparing and evaluating the actual and budgeted performances. The steps in budgeting broadly cover the following:
- Creating standards by bifurcating the overall business goals into departmental targets.
- Comparison of predefined Budget/Standards with the actual performance.
- Calculate the logical deviations from the plan and take corrective measures.
Budgetary control facilitates control over day-to-day activities. Also, it assesses the need for resources and manpower to achieve business objectives.
It might be possible that the formulated budget can be inaccurate and expensive. Following are the common types of budgets prepared by organizations:
- Cash Budget
- Sale Budget
- Production Budget
- Capital Budget
- Material Budget
Morden Techniques
Morden control techniques are additions to the management literature. These are of recent origin and provide innovative methods for organizational evaluation and control.
- Return on Investment
- Financial Statement and Ratio Analysis
- Responsibility Accounting
- Management Audit
- PERT & CPM
- Management Information System
Return on Investment
Return on Investment (ROI) is the profit earned by invested capital. It is analyzed to attain financial control in the business. It is also known as the Du-Pont System of financial analysis.
To measure the generated return, we calculate the rate of ROI. This rate helps assess the financial position of the business.
ROI Formula:

As per the technique, we can increase ROI in two ways:
- By raising sales volume relatively greater than the total investment.
- Reducing total investment without reducing sale volume.
So, we can understand it as the usage of invested capital in generating returns. Moreover, organizations must aim to earn a reasonable ROI.
It helps in:
- Comparing the wealth between the two periods and companies
- Attract investors and improve the goodwill of the company
- Finding areas that adversely impact the ROI
- Interdepartmental comparisons
Financial Statement and Ratio Analysis
It helps in controlling the finances of the organization by calculating different Ratios. For this purpose, data is accumulated from the firms’ financial statements.
The most extensively used Ratios are as follows:
- Profitability Ratios
- Liquidity Ratios
- Solvency Ratios
- Turnover Ratios
Responsibility Accounting
It is an accounting system that depends upon the responsibility assigned to the employee. So businesses conduct an evaluation of the employee’s ability to fulfil the assigned responsibility as per set standards.
This control technique is suitable for large organizations containing many departments.
Generally, responsibility centres are of four types:
- Revenue Centre
- Cost Centre
- Profit Centre
- Investment Centre
Management Audit
Management or Internal Audit is the examination of the utilization of the company’s resources. The Top-level initiates it to ensure the efficient performance of the management.
Internal Auditing starts as soon as the financial audit ends. During the audit, the overall management process is critically evaluated.
However, conducting a management audit is not compulsory for organizations.
PERT & CPM
PERT is Program Evaluation and Review Technique, whereas CPM stands for Critical Path Method. These control techniques are used explicitly for project management and evaluation.
The activity or project’s success is largely affected by the time taken and steps involved. Therefore, managers strive to cut the total time and cost involved in completing the activity.
It focuses on the efficient execution of the project. But the execution must be within the stipulated time and predetermined costs.
Management Information System
Management Information system (MIS) basically provides information for effective decision-making. Managers can retrieve any data as and when needed. It is one of the cost-effective controlling techniques available for managers.
Moreover, it provides information at the right time and helps manage a huge bundle of data. The information obtained from MIS is accurate and facilitates decision-making.
MIS has two major components:
- Data Collection
- Data Management
Selection of the Controlling Techniques
Managers must consider the following factors while selecting a suitable technique of controlling:
- Area of operation
- Management policy at a higher level of management
- Purpose or focus area of control
- Availability and suitability of techniques
- Costs involved
- Industrial trends
- Staff required in the process
- Time invested in the complete process
- Reliability of the results obtained
Final Words
To sum up, an organization can use various traditional and modern techniques to exercise managerial control. These are the systematic approach for monitoring and controlling different business operations.
Managers must examine the operations and take the required measures to attain effective control.
Leave a Reply