Definition: Internal Audit indicates an independent assessment of activities inside an organization to inspect financial, accounting and other, day-to-day business practices. It gets along with a steady and crucial review of the management’s operating and financial activities reporting to the board of directors. It provides assurance on governance and internal control checks over the management activities.
Content: Internal Audit
- Process
- Essentials
- Objectives
- Importance
- Difference between Internal Audit and External Audit
- Conclusion
Process of Internal Audit
Internal audit is implemented to check the effectiveness of the organizations quality management system. The process consists of four stages. They are as follows:
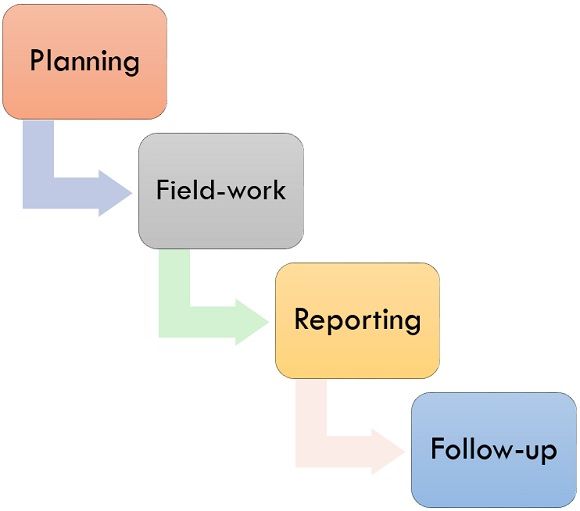
- Planning: In the course of the planning process, the audit team will describe the objectives and scope, evaluates instructions related to audit such as law, policies, procedures, etc. The audit plans are performed by analyzing the results from past audits and arranging a timetable.
- Field-work: It is a substantial act of internal auditing. During this stage, the audit team will start the audit process by reviewing supporting documents, interviewing department personnel, recognizing exceptions and identifying suggestions for improvement. In the end, the audit department furnishes written feedback and disciplinary action plan for their findings.
- Reporting: It is the third stage of the internal audit process. The auditor will formulate the internal audit report that sum-up and convey the audit results; then issues a draft report discussed with the unit management. After that, accurate, fair, short, and appropriate final report is issued by an auditor.
- Follow-up: It is the final and an important stage of internal audit which is generally ignored. In this stage, management must require time to time monitoring to achieve suggestions and findings determined during the internal audit process. Without proper and timely follow-up process management cannot expect any positive changes.
Essentials of Internal Audit
Following are some of the essentials of the internal audit:
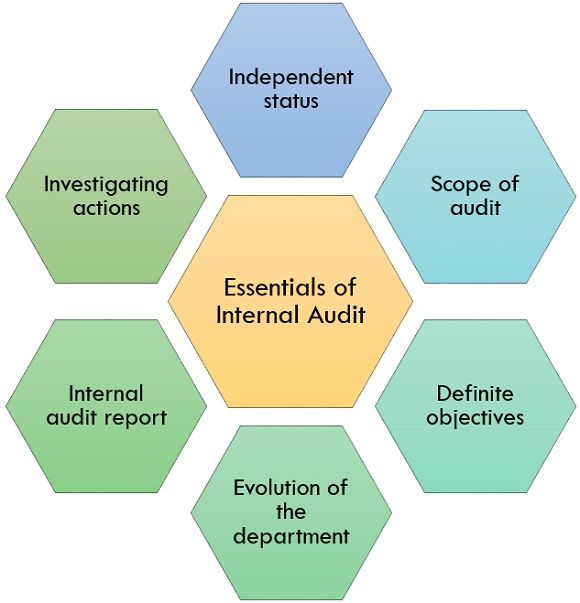
- Independent status: Internal auditor and the internal audit team of the organizations should have an independent and adequately high status in the management. They should have the independence to make their decisions without the interference of the other departments and should only be liable to answer the board of directors of the organization.
- Scope of audit: Internal audit’s scope should be stated in an absolute attainable manner. The audit department must have the power to scrutinize every financial activity of an organization.
- Definite objectives: Internal audit team must have a precise and straightforward understanding of the definite objectives of the organization on every assignment given to them.
- Evolution of the department: The organization should be strict while selecting the internal audit department staff, the qualification and size of the team should be adequate with the size of the organization.
- Internal audit report: A copy of an internal audit report prepared by the internal auditor should be made available to the statutory auditor of an organization. It helps the statutory auditor in understanding the internal areas of the organization.
- Investigating actions: Internal audit department must go through proper investigation actions, and the report submitted by them should also be checked thoroughly by the management.
Objectives of Internal Audit
The long-term objective of the internal audit is to help the management in achieving the most productive policy of management operations. It consists of:
1. Safeguarding the interest of the Management
The accomplishment of the above objective relies upon the following actions of the internal auditor:
- Verifying the degree of authenticity of the statistical and accounting data developed within the organization.
- Verifying the amount to which business assets are accurately accounted for and ensured from all kinds of losses.
- Verifying the intensity of the compliances with entrenched policies, procedures, and plans.
2. Progression of the interests of the Management
The objectives comprise the proposal of changes for the enhancement of different phases of the operations. This objective is accomplished by:
- Analyzing and evaluating the plans and policies of the management.
- Analyzing and evaluating internal evidence and procedures.
- Analyzing and evaluating the performance governing the plans, procedures and policies.
Importance of Internal Audit
Following are the importance of internal audit:
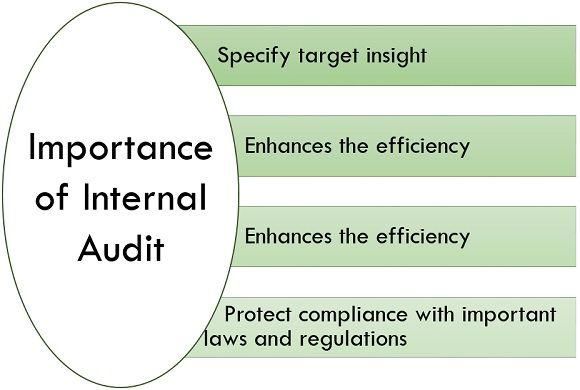
- Specify Target Insight: It becomes challenging to find the errors or mistakes in your work. By giving a separate and impartial view, the internal audit function adjoins value to your organization.
- Enhances the Efficiency: Internal auditor grants recommendations to enhance the efficiency and strength of your organization’s procedures and policies to reduce the business and financial risks.
- Classify Risks and Secure Assets: An internal audit program facilitates management and shareholders by analyzing and prioritizing risks through a précised assessment.
- Protect Compliance with Relevant Laws and Regulations: Acquiring the trust of your client and avoiding the harmful fines and damages, makes internal audit a valuable and beneficial activity for your organization.
Difference between Internal Audit and External Audit
| Basis for differences | Internal Audit | External Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Introduction | Internal audit specifies a continuous audit function operated inside an organization by a separate department called internal audit department | External audit is a done for the statutory purposes by the outside personnel or auditor who is not working as an employee of a company |
| Aim | Its aim is to analyze the conventional activities and provide opinion for the enhancement | The aim of the external audit is to evaluate and validate the financial report of the organization |
| Regulated by | Internal audit is regulated by the employees of the organization | External audit is conducted by the third party, i.e., outside person |
| Engagement | In an internal audit, the auditor is selected by the management of the organization | In external audit, auditor is selected by the members of the organization |
| Time period | Internal audit is a continuous process; thus employees regularly work upon it | External audit is conducted once in a year |
| Report users | The opinion of the management is provided on a report in internal audit | The opinion of the shareholders is provided on a report in external audit |
| Control | Internal audit controls the operational efficiency of the organization | External audit controls the certainty and soundness of the financial statement of the organization |
Conclusion
Internal audit is an assessment function incorporated by the management for providing independent assurance on governance, internal control and risk- management.
Leave a Reply