Definition: Break-even analysis is a tool used by the business organizations to find out the minimum number of units it needs to sell or the amount of sales revenue it has to generate for meeting up the total cost incurred. It is the initial judgement on whether the project is viable or not.
Break-even analysis is an essential tool for any business. All the initial decisions related to the launching of a new product or technique are dependent upon it.
Content: Break-Even Analysis
- Need
- Uses
- Benefits
- What is a Break-Even Point?
- Graphical Representation
- Ways
- Limitations
- How to Calculate Break-Even Point?
Need for Break-Even Analysis
You must be wondering why there is a need for performing break-even analysis? When is it done?
To answer the above queries, let us now understand the three major business decisions which are taken with the help of break-even analysis:
Setting Up of New Business: To start a new business, the initial step is finding out the feasibility of the project. It helps to determine whether the business idea is profitable and also provides an actual estimation of cost to frame the pricing strategy in a better way.
Replacing the Business Model: It plays a vital role when the management plans to change the business model. For instance, the organization decides to convert from an assembling unit to a manufacturing unit. It needs to clearly understand and interpret the cost involved, output and prospective revenue and profit, before implementing such decisions.
Creating New Product: If the organization is planning to launch a new product which involves huge cost and capital expenditure; it must find out the potential of the product in the market through break-even analysis.
Using Break-Even Analysis for Day to Day Business Operations
Break-even analysis is not only used for taking strategical decisions but has also proved to be applicable in day to day business activities.
Let us now go through its following uses in business functions:
- Goals: Through the break-even analysis, the company can determine the number of units to be sold or sales revenue to be generated for reaching the break-even point.
- Planning: The further plans of expansion or growth can be set easily if the management knows what exactly is to be aimed.
- Material: Material management becomes easy with break-even analysis since the company decides to advance the cost and quality of material to be used as input.
- New Product: Break-even analysis is also used by the management for monitoring the performance of a new product.
- Prices: It is an essential tool for balancing the cost of a product and setting up a competitive price. For instance, if the price is low, it becomes difficult for the company to attain a break-even position on time.
Benefits of Break-Even Analysis
Break-even analysis has been widely used by the companies to determine the profitability of the business.
Following are some of the advantages it has for business organizations: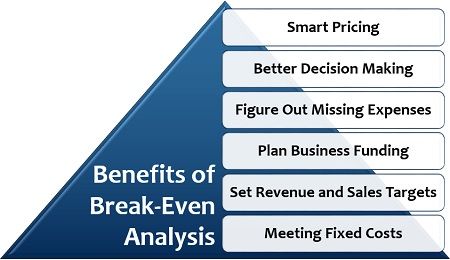
Smart Pricing: Break-even analysis is widely used by the companies for determining the appropriate price of the products or services such that the profit increases and the cost incurred are recovered.
Better Decision Making: It provides a solid base for decision making on the viability of a project leaving aside the emotional thinking.
Figure Out Missing Expenses: While implementing the break-even analysis, the organizations can easily find out and include those expenses also which are otherwise left out or ignored.
Plan Business Funding: If the business lacks sufficient capital for the project, it can approach to the external sources of funds, only after analyzing its break-even position which should be strong enough to pay off the debts.
Set Revenue and Sales Targets: Break-even analysis gives a clear picture of the number of units to be sold or the amount of revenue to be generated for covering up the cost and achieving profitability. These figures set a target for the lower levels to perform accordingly.
Meeting Fixed Costs: It even helps the company to cover up the fixed cost of the project.
What is a Break-Even Point?
Break-even point is that point of sale where the revenue generated by the company is equal to the total cost incurred by it. It is a position where the organization is at a no-profit no loss situation.
Graphical Representation of Break-Even Point
To understand the concept of break-even point in detail, let us have a look at the following graph of break-even analysis: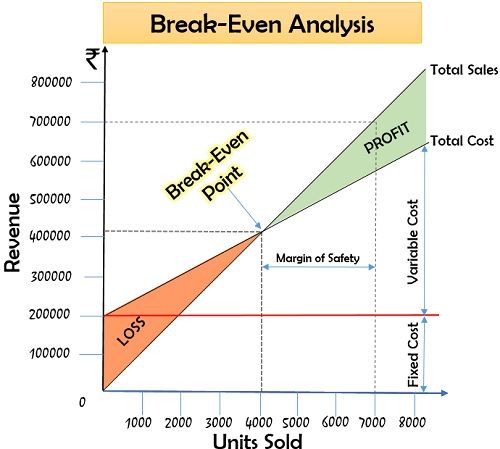
With the help of the above diagram, we can identify that the break-even point is where the company can meet its expenses from the sales revenue it generates.
Ways to Reduce Break-Even Point
Break-even point has a broader scope in business other than just recovering the total cost by revenue. A minimum break-even point is considered to be optimal for the company.
Following are some of the means to reduce the break-even point: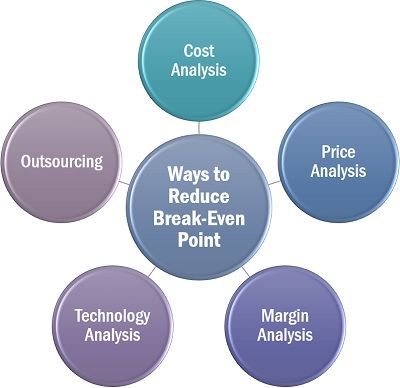
- Cost Analysis: The total cost of a product can be decreased by eliminating the unwanted fixed and variable costs, which ultimately increases the profitability and reduces the break-even point.
- Price Analysis: Keeping control over the price of the products by reducing discounts and other coupons is another means since it accelerates the break-even point.
- Margin Analysis: Another method is monitoring the profit margin. Thus, taking essential steps to boost the sales of those products which have a high margin to minimize the break-even point.
- Technology Analysis: Break-even point can also be reduced by implementing the latest technology in the business, which increases an organization’s productivity and performance at a minimal cost.
- Outsourcing: One of the most effective ways is to reduce fixed cost by outsourcing a product or service which was earlier being produced by the company itself. This will convert such fixed value into a variable cost, charged per unit.
Limitations of Break-Even Analysis
As we know that break-even analysis is a cost-revenue-output relationship, it has a limited arena to determine the viability of any project.
Let us now understand the various other drawbacks of a break-even analysis:
- It is a mere interpretation of the future by past business functions.
- Break-Even Analysis considers only cost and output for profit determination when management skills, market conditions, technological factors, etc. also affect the business.
- It is assumed that the selling price is constant, and the cost function is linear, which is not the case in reality.
- There exist no tax provisions in the break-even chart.
- Break-even analysis always relates cost to the output, which may not be the case every time.
- It may result in a poor analysis if the company lacks an efficient accounting system.
- The analysis considers that the price of output as per assumed horizontal demand curve, which is only possible under perfect competitions.
- It is not suitable for determining long-term profits due to the assumption of the linear relationship between cost, revenue and output since many other factors affect the business operations in the long run.
How to Calculate Break-Even Point?
We know that break-even analysis is a financial tool and is majorly used for calculating the break-even point of any project, product or service. It also determines the various other elements, such as margin of safety and contribution margin.
To further gain knowledge about, how to calculate break-even analysis? Please read our next content.
Leave a Reply