Definition: Managerial economics is a stream of management studies which emphasises solving business problems and decision-making by applying the theories and principles of microeconomics and macroeconomics. It is a specialised stream dealing with the organisation’s internal issues by using various economic theories.
Economics is an inevitable part of any business. All the business assumptions, forecasting and investments are based on this one single concept.
Content: Managerial Economics
Nature of Managerial Economics
To know more about managerial economics, we must know about its various characteristics. Let us read about the nature of this concept in the following points: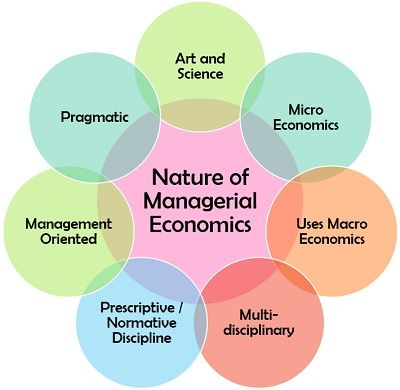
Art and Science: Managerial economics requires a lot of logical thinking and creative skills for decision making or problem-solving. It is also considered to be a stream of science by some economist claiming that it involves the application of different economic principles, techniques and methods, to solve business problems.
Micro Economics: In managerial economics, managers generally deal with the problems related to a particular organisation instead of the whole economy. Therefore it is considered to be a part of microeconomics.
Uses Macro Economics: A business functions in an external environment, i.e. it serves the market, which is a part of the economy as a whole.
Therefore, it is essential for managers to analyse the different factors of macroeconomics such as market conditions, economic reforms, government policies, etc. and their impact on the organisation.
Multi-disciplinary: It uses many tools and principles belonging to various disciplines such as accounting, finance, statistics, mathematics, production, operation research, human resource, marketing, etc.
Prescriptive / Normative Discipline: It aims at goal achievement and deals with practical situations or problems by implementing corrective measures.
Management Oriented: It acts as a tool in the hands of managers to deal with business-related problems and uncertainties appropriately. It also provides for goal establishment, policy formulation and effective decision making.
Pragmatic: It is a practical and logical approach towards the day to day business problems.
Types of Managerial Economics
All managers take the concept of managerial economics differently. Some may be more focused on customer’s satisfaction while others may prioritize efficient production.
The various approach to managerial economics can be seen in detail below:
Liberal Managerialism
A market is a democratic place where people are liberal to make their choices and decisions. The organisation and the managers have to function according to the customer’s demand and market trend; else it may lead to business failures.
Normative Managerialism
The normative view of managerial economics states that administrative decisions are based on real-life experiences and practices. They have a practical approach to demand analysis, forecasting, cost management, product design and promotion, recruitment, etc.
Radical Managerialism
Managers must have a revolutionary attitude towards business problems, i.e. they must make decisions to change the present situation or condition. They focus more on the customer’s requirement and satisfaction rather than only profit maximisation.
Principles of Managerial Economics
The great macroeconomist N. Gregory Mankiw has given ten principles to explain the significance of managerial economics in business operations.
These principles are classified as follows: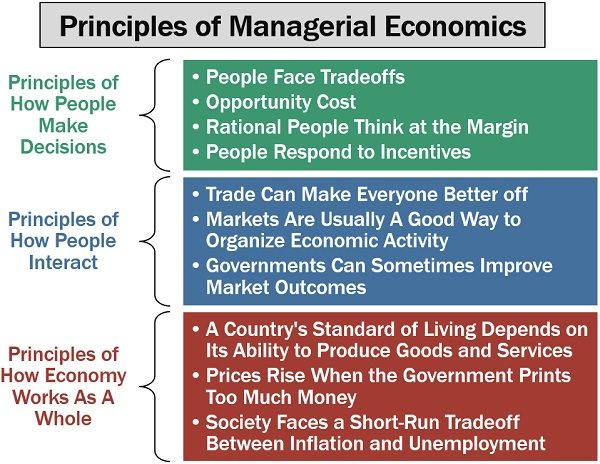
Principles of How People Make Decisions
To understand how the decision making takes place in real life, let us go through the following principles:
People Face Tradeoffs
To make decisions, people have to make choices where they have to select among the various options available.
Every decision involves an opportunity cost which the cost of those options which we let go while selecting the most appropriate one.
Rational People Think at the Margin
People usually think about the margin or the profit they will earn before investing their money or resources at a particular project or person.
People Respond to Incentives
Decisions making highly depends upon the incentives associated with a product, service or activity. Negative incentives discourage people, whereas positive incentives motivate them.
Principles of How People Interact
Communication and market affect business operations. To justify the statement, let us see the following related principles:
Trade Can Make Everyone Better off
This principle says that trade is a medium of exchange among people. Everyone gets a chance to offer those products or services which they are good at making. And purchase those products or services too, which others are good at manufacturing.
Markets Are Usually A Good Way to Organize Economic Activity
Markets mostly act as a medium of interaction among the consumers and the producers. The consumers express their needs and requirement (demands) whereas the producers decide whether to produce goods or services required or not.
Governments Can Sometimes Improve Market Outcomes
Government intervenes business operations at the time of unfavourable market conditions or for the welfare of society. One such example is when the government decides minimum wages for labour welfare.
Principles of How Economy Works As A Whole
The following principle explains the role of the economy in the functioning of an organization:
A Country’s Standard of Living Depends on Its Ability to Produce Goods and Services
For the growth of the economy of a country, the organisations must be efficient enough to produce goods and services. It ultimately meets the consumer’s demand and improves GDP to raise the country’s standard of living.
Prices Rise When the Government Prints Too Much Money
If there are surplus money available with people, their spending capacity increases, ultimately leading to a rise in demand. When the producers are unable to meet the consumer’s demand, inflation takes place.
Society Faces a Short-Run Tradeoff Between Inflation and Unemployment
To reduce unemployment, the government brings in various economic policies into action. These policies aim at boosting the economy in the short run. Such practices lead to inflation.
Scope of Managerial Economics
Managerial economics is widely applied in organizations to deal with different business issues. Both the micro and macroeconomics equally impact the business and its functioning.
Following points illustrate its scope: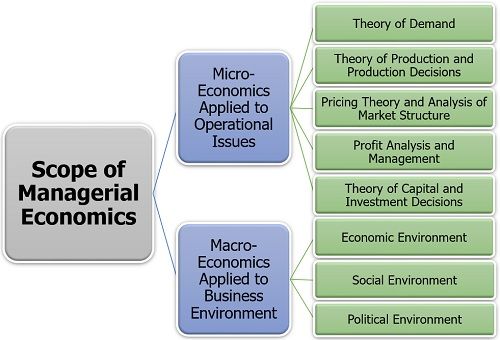
Micro-Economics Applied to Operational Issues
To resolve the organisation’s internal issues arising in business operations, the various theories or principles of microeconomics applied are as follows:
- Theory of Demand: The demand theory emphasises on the consumer’s behaviour towards a product or service. It takes into consideration the needs, wants, preferences and requirement of the consumers to enhance the production process.
- Theory of Production and Production Decisions: This theory is majorly concerned with the volume of production, process, capital and labour required, cost involved, etc. It aims at maximising the output to meet the customer’s demand.
- Pricing Theory and Analysis of Market Structure: It focuses on the price determination of a product keeping in mind the competitors, market conditions, cost of production, maximising sales volume, etc.
- Profit Analysis and Management: The organisations work for a profit. Therefore they always aim at profit maximisation. It depends upon the market demand, cost of input, competition level, etc.
- Theory of Capital and Investment Decisions: Capital is the most critical factor of business. This theory prevails the proper allocation of the organisation’s capital and making investments in profitable projects or venture to improve organisational efficiency.
Macro-Economics Applied to Business Environment
Any organisation is much affected by the environment it operates in. The business environment can be classified as follows:
- Economic Environment: The economic conditions of a country, GDP, economic policies, etc. indirectly impacts the business and its operations.
- Social Environment: The society in which the organisation functions also affects it like employment conditions, trade unions, consumer cooperatives, etc.
- Political Environment: The political structure of a country, whether authoritarian or democratic; political stability; and attitude towards the private sector, influence organizational growth and development.
Managerial economics provides an essential tool for determining the business goals and targets, the actual position of the organization, and what the management should do fill the gap between the two.
FRED AYENSU says
Very good
Charles Chekanayi says
Your notes are excellent. Thank you so much for equipping me with such powerful business techniques.
Brian Joctan says
Thank you for your notes. Your notes is very good and understandable easy to determine the meaning
Njapau Godfrey says
So educative.thanks a lot please.
Anirban Samadder says
Written in very simple language. Understood the whole past properly.
Femi says
You have submitted a thoughtful and resourceful materials for scholarstic and organizational consumptions. Kudos!
itimou says
i enjoy reading your notes. excellent write-up.
Divian says
Very useful
Eric mabele says
Good simplified notes
Ram Kumar Patel says
Thanks for sharing knowledge .your writing skill and definition so descriptive it help to easily understood.
Manfred says
This is very Help, to me as an introduction to Managerial economics
Jaymie kyla S. Ambrocio says
Noted.
Kumaran Mahalingam says
Easily understandable ! concept are clearly explained with simple examples. Thank you.
laiza mojica says
Noted.
Sharan B says
very helpful and great knowledge gaining learning
Jeevitha.B says
Thanks a lot for this wonderful book, I can clearly understand the concepts that are indulged in managerial economics and how it differs from the common economical concepts.
Abdul salam says
very helpful materials and informative sessions