Definition: Money spent on acquiring a commodity which has the potential of making future income or wealth is known as investment. In simple terms, investment is engaging money today to maximise it in the future. An investor can be anyone, an individual, a business entity or even the government.
Two Key Aspects of Investment
The return on any investment is merely based on two aspects:

- Time: The period for which the investment is made must be at least one year. More extended the term period of investment is, higher will be the return yield. Investments like government bonds depend on this factor.
- Risk: Every investment bears some risk. Higher the potential of the investor to take a chance, better will be the return he gets. Stock market investments are majorly influenced by this factor.
Content: Investment
Key Words
Investor: An investor can be any individual, firm or organisation who has the potential of engaging one’s capital for a long-term period (usually more than a year) to earn profit or wealth in future.
Speculator: Speculators usually invest the borrowed sum in the high-risk bearing opportunities for a short-term period (not exceeding six months) to earn high returns. They rely on calculations based on market trend, psychology and technical analysis.
Trader: Traders are the ones who deal in the derivatives market or the stock market, buying and selling their holdings within a day or a week or a month. They aim to earn a profit in the form of margins derived from price fluctuation.
Gambler: Gambler is the person who put in money or valuables without any basis or calculations in a game of luck or chance. He/she invests in betting, playing cards, tosses, etc., knowing that the outcome is uncertain.
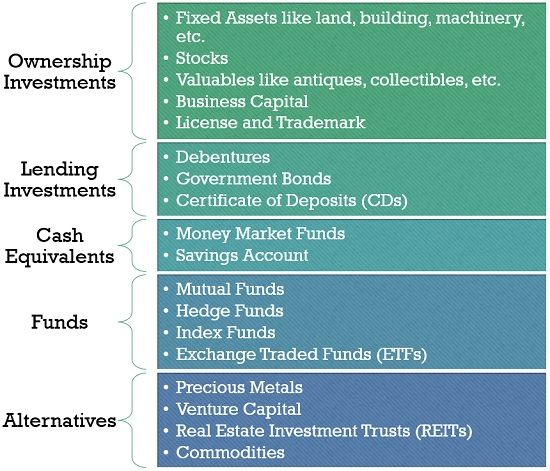
Types of Investments
Ownership Investments
The investment made to acquire the possession of any tangible or intangible asset is known as ownership investment. Some of the types of ownership investments are:
- Fixed Assets: It includes the acquisition of fixed assets (machinery, land, building, etc.) to generate some value in the future.
- Stocks: Holding shares of a public company provides the right to stake the future profits of the company.
- Valuables like antiques and collectables: Investment on some antique objects or collectables with the idea of selling them in future can be profitable.
- Business Capital: It is investing in one’s own business to earn a profit by selling goods or services.
- License and Trademark: A license or trademark gives recognition to the company by giving it a brand name which brings in more business to the company.
Lending Investments
Lending investments can be understood as buying of repayable debts to earn interest in future.
- Debentures: Debentures are non-secured debt instrument purchased by investor depending on the creditworthiness and goodwill of the issuer. The interest rate is pre-decided and may be fixed or floating.
- Government Bonds: Government bonds are debentures issued by the government like, treasury bills are another risk-free investment option where the rate of interest is nominal and fixed.
- Certificate of Deposits (CDs): A certificate of deposit is a promissory note which a bank issues in exchange for keeping your money in a saving account for a specific period.
Cash Equivalents
These investments can be treated as cash equivalents. Some of them are:
- Money Market Funds: Money Market Funds are investments which can be conveniently encashed, whenever required. They bear a low risk and give low returns in the short run.
- Savings Account: A savings account opened with a bank is an easily assessed investment, but it gives meagre returns.
Funds
Funds are another option where the sum accumulated is quite high, and investment is well planned and systematic. Some of the well-known funds are:
- Mutual Funds: Mutual Fund is the accrued fund pooled in by many investors and is invested by money manager in shares, bonds and other financial instruments. It generates a reasonably high income in the long run.
- Hedge Funds: These funds majorly aim at minimising the investment risk but are used as an investment option itself. Though similar to mutual funds, they involve high-risk strategies and invests in any potential opportunity.
- Index Funds: An index fund is the mutual fund portfolio comprising of various shares or stocks. A shareholding in an index fund means owning a percentage of the whole collection. It provides better returns due to investment in a diversified portfolio.
- Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs): These are similar to the index fund. But, unlike index fund, these are not mutual fund investment. Instead, ETFs can be seen as active trading investments in the share market, where buying and selling can be done throughout the day while share markets are open.
Alternatives
The other kind of investments which are way different from the traditional investments can be termed under alternatives. These are:
- Precious Metals: Buying of gold, silver and other precious metal in their actual form or as ornament and jewellery to sell it at a higher price in future.
- Venture Capital: A venture capitalist leverages a start-up or a small business by becoming a partner in the company and derives a return in the form of profit. This can also be a form of ownership investments.
- Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs): Real estate investing entitles the investor for partial ownership and thus relish property gain or rent earned from the property.
- Commodities: Investment in commodities are future contracts to buy and sell specific resources at the pre-decided price. It includes sugar, coffee, wheat, cocoa, cotton, natural gas, crude oil, cattle, etc.
In the present scenario, when people are technically upgraded and well-educated, everyone focusses on building a sound future out of the limited resources they own today. This can only be possible through investments.
Leave a Reply