Definition: Recruitment is the process of examining a vacant position in the organisation and attracting the potential candidates to apply for the same, within an appropriate time and at a desirable cost. It is the introductory stage where a job applicant gets to know about the vacancy, and the organisation identifies the candidate’s profile.
Without recruitment, companies won’t be able to function appropriately and will lack proficient human resources.
Content: Recruitment
Purpose or Objectives of Recruitment
As we know that human resource is a vital part of any organisation and to ensure the regular supply of personnel in an organisation, recruitment is a significant step.
Following are some of the objectives which justify the need for recruitment for any business: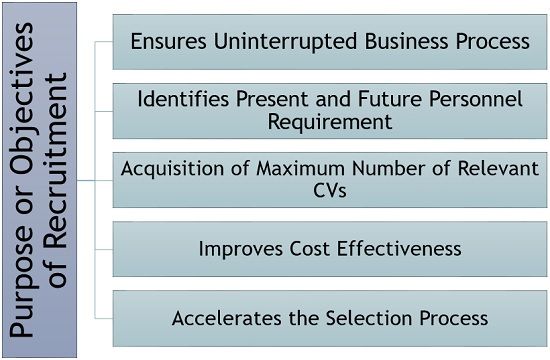
- Ensures Uninterrupted Business Process: Recruitment aims at providing the required number of skilled employees to the organisation to keep the business process going even after labour turnover.
- Identifies Present and Future Personnel Requirement: It is the initial step for detecting and analysing the workforce requirement in the organisation, at present as well as in future say within a year.
- Acquisition of Maximum Number of Relevant CVs: It advertises the vacant position such that a maximum number of prospective candidates apply for the same.
- Improves Cost-Effectiveness: It is a systematic and well-planned process. Thus it has proved to be more cost-effective.
- Accelerates the Selection Process: It backs the selection process with a pool of candidates’ Curriculum Vitae (CV).
Types of Recruitment Needs
Recruitment is a means of filling the vacant position in the organisation.
The need for recruiting new talent in the organisation can arise in the following three types of the condition: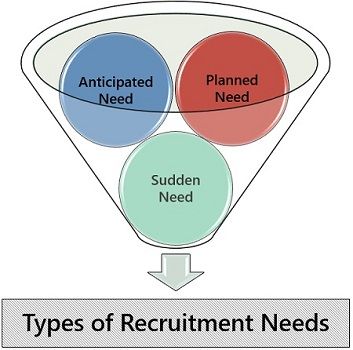
- Planned Need: When an organisation develops a requirement of hiring new employees due to a known reason and is prepared for the same in advance is a planned need.
E.g. retirement of an employee - Anticipated Need: Anticipated needs are majorly controlled by internal and external environmental factors. Such requirements can be predicted by the management with the help of past experiences, news updates, etc.
E.g. technological advancement, expansion, merger, acquisition - Sudden Need: Sometimes, the need for recruiting personnel arises due to an unexpected reason.
E.g. employee walkouts, accident, demise, sickness
Factors Influencing the Recruitment
The organisation needs to be updated with the changes in market conditions as well as with the changes taking place in the organisation to monitor the impact of such changes on the business.
Thus, recruitment is also affected by these factors, which can be classified into the following two categories: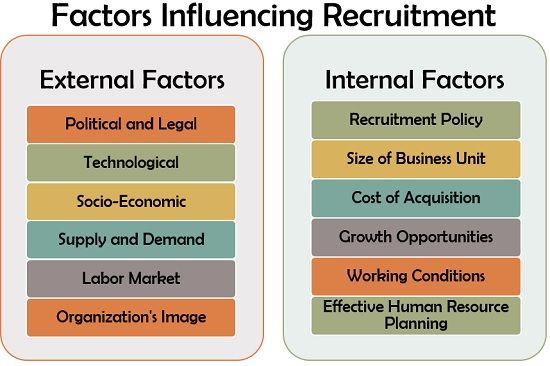
External Factors
An organisation experiences some external changes in the business environment, which affects all business process and are beyond the control of the organisation. Therefore, management has to develop strategies to adapt to such changes. The primary external factors affecting the recruitment process in the organisation are as follows:
Political and Legal: The government of India ensures the employability of scheduled castes and scheduled tribes through the reservation system. The trade unions also come into action to restrict the organisation’s recruitment process if the candidate does not fulfil its criteria.
Technological: With the emergence of new technology, the organisation experience the need for recruiting employees who are more skilled and tech-friendly.
Socio-Economic: The organisation functions in a society and is greatly influenced by business ethics, no child labour and other social views of society. The changes in economic conditions, share markets, minimum wages, recession, boom, etc., sometimes lead to employee layoffs or requirement of new employees.
Supply and Demand: At times, the organisation requires employees having a particular set of skills, recruitment of such employees is affected by the demand and supply of such personnel in the labour market.
Labour Market: The availability of labour in the area where the organisation is located influences the recruitment criteria. In case, there is surplus labour in the labour market; the organisation will relish the easy availability of human resources at a cheaper rate.
Organisation’s Image: The image of an organisation may attract or distract the prospective candidates — every personnel like to work for the organisation which holds a good reputation in the market and among the job aspirants.
Internal Factors
The changes taking place within the organisation are the controllable factors but creates a massive impact on all the business process. Recruitment is also influenced by such considerations. Some of them are as follows:
Recruitment Policy: Every organisation have a different recruitment policy. Some companies prefer internal recruitment of employees to appoint personnel who know the company in a better way, while others go for external recruitment to acquire new talent.
Size of Business Unit: A small business unit requires less number of employees. Therefore it involves short and simplified recruitment process. On the other hand, large business units need a large number of employees. Thus, they prefer bulk recruitments. The recruitment process is comparatively lengthy and complicated, involving a panel of employees to conduct interviews in such units.
Cost of Acquisition: Every organisation has a budget within which it needs to function. So goes for recruitment too. The cost incurred in hiring new employees is quite high nowadays. Therefore recruiters have to optimise this cost through different means.
Growth and Expansion: At the time business expansion, the organisation needs to hire more employees.
Working Conditions: The organisations which provide the right working conditions and take proper health and safety measures of the employees tend to get more attention from the prospective candidates.
Effective Human Resource Planning: Effective HRP provides an appropriate elaboration on the number of employees required as well as the skills and qualification they must possess.
Process of Recruitment
A recruitment process is an organised approach towards searching new talent and introducing them to the organisation.
In the absence of a systematic recruitment process, the cost of employee acquisition will rise. To carefully understand the steps involved in the recruitment process, read below: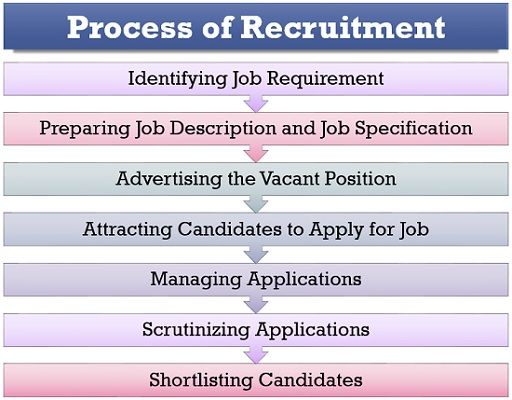
- Identifying Job Requirement: The recruiter first recognises the job opening regarding the department in which the vacancy is, number of vacancies and urgency of hiring.
- Preparing Job Description and Job Specification: The next step is making a job description disclosing the job-related details like designation, location, duties to be performed and required experience. The recruiter also chalks out the job specification having information regarding the skills, qualification, the area of expertise, etc.
- Advertising the Vacant Position: A job vacancy is advertised through newspapers, brochures, job portals, consultancies, etc. It ensures that the maximum number of relevant candidates can apply for the job.
- Attracting Candidates to Apply for Job: The recruiter needs to provide proper assistance and guidance to the candidates willing to apply for the job.
- Managing Applications: The recruiter has to arrange the applications in an orderly manner to simplify the task of scrutinising them.
- Scrutinising Applications: Next step is the initial investigation of the applications to go through the candidate’s profile thoroughly.
- Shortlisting Candidates: By scrutinising the applications, candidates with the matching profile are picked out for the process of selection.
Conclusion
Recruitment is a necessity for all organisations. It initiates the process of selection by providing the organisation with the candidates having the required set of skills, qualification and experience; and are willing to occupy the vacant position. A company seeks for different sources of recruitment to fulfil its workforce requirement.
Leave a Reply