Definition: We can refer to Management Accounting as an accounting system that provides information to perform management functions directed toward achieving organizational objectives.
If we emphasize the keyword, it is explanatory to denote the managerial aspect of accounting. Besides, it has a differentiated lookout directed towards decision-making and control.

It is variedly referred to as:
- Management-oriented Accounting
- Accounting for Managers
- Management Accountancy
It was first introduced in the 1950s but became popular in the 1980s. This accounting branch emerged as a consequence of the cut-throat and challenging environment.
Accounting information is a powerful tool for managers to discharge their responsibilities.
The process includes the accumulation & analysis of financial information. And further utilizing it for evaluation and control.
Basically, it sources information from financial and cost accounting and uses it for:
- Policy formulation
- Decision-making
- Planning and Control
Its scope is not restricted to just recording and classifying business transactions. But, it presents essential information logically to ease managerial decision-making.
Content: Management Accounting
- Functions/Objectives
- Importance
- Nature
- Uses
- Importance
- Tools and Techniques
- Role of Management Accounting in Decision Making
- Scope
- Limitations
- Relationship between Cost, Financial and Management Accounting
- Career Opportunities in the field of Management Accounting
- Management Accounting vs Financial Accounting
- Example
- Conclusion
Management Accounting Functions/Objectives
The primary function of this accounting system is Analysis and Presentation. The objectives, as well as functions of management accounting, are as follows:
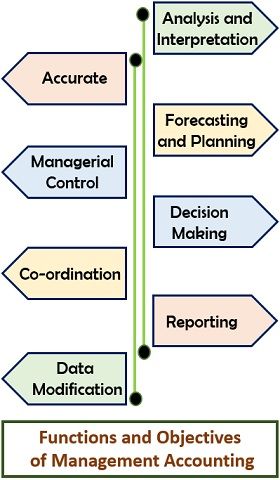
- Analysis and Interpretation: Managers analyze and interpret complex information in a simplified way.
- Accurate: The efficiency of the management depends on the authenticity of the Management Reports.
- Forecasting and Planning: These are the roadmap that the firms follow to accomplish their goals. Thus, Management Accounting assists in making estimates for future planning.
- Managerial Control: One of its essential functions is obtaining managerial control within the firm. And management tools like Budgetary Control help in attaining this objective.
- Decision-Making: Decision-making is the core function of management. For effective and efficient decision-making, information is retrieved from the managerial reports.
- Coordination: It helps in maintaining coordination across management levels and various departments.
- Reporting: Reporting is another critical function as it conveys essential managerial information.
- Data Modification: It transforms the technical data into an easy and understandable form.
Importance
This accounting system benefits the organization in the following ways:
- Profit Maximization: The increase in efficiency and management control helps firms in profit maximization.
- Boost Efficiency: The implication of management accounting and its functions results in improved efficiency of the workforce.
- Revitalized Customer Services: The value addition in managerial processes and focus on quality reduce costs. Further helps in delivering quality services to the customers.
- Risk Management: Risks are an unavoidable part of the firms. Hence, with management, accounting firms can make projections and manage the associated risks.
- Performance Evaluation: Also, it has significance in performance evaluation. Tools like Standard Costing and Budgeting help in the assessment.
- Healthy Trade Cycle: It reviews and compares past Trade cycles. Besides, it plays a vital role in managing the ongoing trade cycle.
Nature/Characteristics
Management accounting inherits the following characteristics:
- Selective Approach: Only the data relevant to management is taken into consideration.
- Science & Art: The accounting includes Techniques, Formulas and Subjective Data for judgement.
- Futuristic: Firms conduct this accounting for future concerns. For Example, Policy formulation, Planning and Budgeting.
- Object-oriented: It is an object-oriented system that aims toward achieving the firm’s ultimate objectives.
- Cause and Effect Analysis: The analysis is based on the cause-and-effect relationship between the variables.
Tools and Techniques
Several tools and techniques are available for arranging & analyzing data under Management Accounting. Following are some of the essential techniques available for disposal:
- Financial Statement Analysis
- Cost Accounting Technique
- Budgetary Control
- Standard Costing
- Marginal Costing
- Decision Accounting
- Revaluation Accounting
- Financial Planning
- Control Accounting
- Managerial Reporting
- Management Information System
- Quantitative Techniques
Role of Management Accounting in Decision Making
The information contained in the management reports forms a base for managerial decision-making. As the top management makes plans and takes strategic decisions for the future.
In addition, the ultimate aim of any undertaking is the fulfilment of its long and short-term goals with profitability. For this purpose, they have to maintain efficiency at all levels of management.
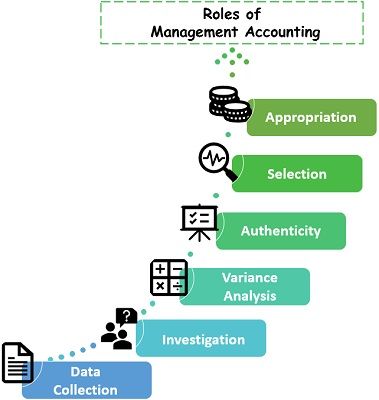
Key areas of Decision-making include:
- Data Collection
- Investigation of Financial Health
- Variance Analysis
- Authenticity of Information
- Selection from Alternatives
- Appropriation of Working Capital
Scope
Besides various features, it has a wide scope in comparison to other accounting systems. Some areas that it covers are as follows:
- Financial Management
- Budgetary Control
- Inventory Control
- Management Reports
- Taxation
- Internal Auditing
- Inhouse Services
Limitations
It suffers the drawbacks of being in the developing stage. Thus, it possesses certain limitations, which are listed below:
- Its accuracy depends on the reliability of the financial data.
- Requires due expertise in the subject areas.
- It demands a high degree of coordination. Otherwise, it will generate misleading results.
- The installation of the management accounting systems is an expensive affair.
- This field of accounting has a broader scope, thereby increasing complexity.
- Like financial statements, it is also affected by the personal bias of the personnel.
Relationship between Cost, Financial and Management Accounting
All three branches of accounting are closely interrelated with each other.
Let’s understand how?

The oldest accounting system is Financial accounting, followed by Cost accounting. At the same time, management accounting has its roots in these two.
It uses secondary data for the analysis, from cost and financial accounting reports. Managers apply tools and techniques to the extracted information. Thereafter, pass on the results generated to the top management.
Career Opportunities in the field of Management Accounting
The ones who aspire to work and explore the field of management accounting can apply for the following job roles:
- Chief Financial Officer (CFO)
- Financial or Budget Analyst
- Internal Auditor
- Controller
- Financial Vice President (VP)
- Staff Accountant
- Data Analytics
- Management Accountant
To develop the required skills, one can opt for career paths like – CPA & CMA. It stands for – Certified Public Accountant and Certified Management Accountant respectively.
Management Accounting vs Financial Accounting
So far, we can conclude that Financial Accounting serves as a base for Management Accounting. Now, let us see how these branches of accountancy differ from each other.
| Basis | Management Accounting | Financial Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Management Accounting is the branch of accountancy that aids management in effective planning and control | Financial Accounting involves recording, classifying and reporting the financial transaction that occurred during the financial year |
| Focus Area | Its prime concern is providing data useful for the management that is further used for decision-making | However, it focuses on ascertaining the financial position and profitability of the undertaking |
| Duration | It can be prepared for the calendar year as well. And delivers insights as and when needed | Firms perform financial accounting for a financial year |
| Perspective | It has a broader scope as it covers each department along with the firm | In contrast, it is limited to generating statements for the firm as a whole |
| Presentation | It does not have any specific format for presenting the results | Whereas, it has separate formats for preparing various statements |
| Past and Future Data | It uses the historical data as a base for making Future Projections | On the other hand, it is purely based on the historical data |
Example
Some examples of management accounting may include:
- Creation of the Fund Flow Statements to assess funds positions.
- Preparing Flexible Budgets to plan production at various output levels.
- Performing Responsibility Accounting to assign due responsibility to numerous departments.
- Making Sales Budgets based on the previous year’s management report.
Conclusion
To conclude, Management Accounting and its functions help in bringing efficiency to management using accounting information. Also, it is a powerful tool for firms delivering reports that are the basis for many strategic decisions.
In the end, using management reports in a manner that is fruitful to the management.
Leave a Reply