Definition: Group Decision-making is a form of participative decision-making, where a group of individuals work together to solve a problem complex in nature. The group members try to discover and test creative alternatives to solve complicated problems.
It is a participatory process in which the group members share their Ideas, Knowledge, Expertise and Experience. The group decisions depend upon:
- Maturity Rule
- Truths
- Status-Quo, etc.
In organizations, significant decisions are taken by more than one person. The involvement of people in the process gives them a sense of ownership. However, they also bear the risk associated with it.

Group is the number of individuals who come together and work to attain a common objective.What is Decision-making?
It is a process of selecting the best solution to solve a critical problem.
Group Decision Making aims to:
- Gain commitment towards the decisions.
- Invest more knowledge and expertise during the process.
- Bring synergy among the group members.
Content: Group Decision-making
Advantages of Group Decision-making
The advantages of group decision
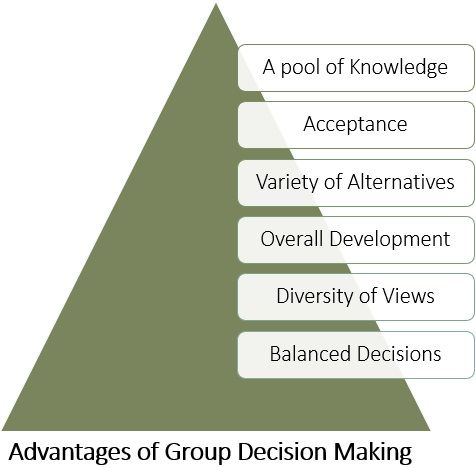
- A pool of Knowledge
Decision-making in a group involves many people during the process. This brings more knowledge and expertise at the time of decision-making. - Acceptance
As the decision is taken collectively, the members easily accept the decisions. - Variety of Alternatives
A group can generate more alternatives than individuals. - Overall Development
Group decision-making is an interactive process in which all members share their skills and knowledge. Thus, it results in the overall development of the group members. - Diversity of Views
Different individuals possess different views towards a situation. Thus, there is a collection of different ideas for specific problems during decision-making. - Balanced Decisions
Group members ascertain multiple consequences and risks associated with the idea. Hence, results in balanced decision-making.
Disadvantages of Group Decision-making
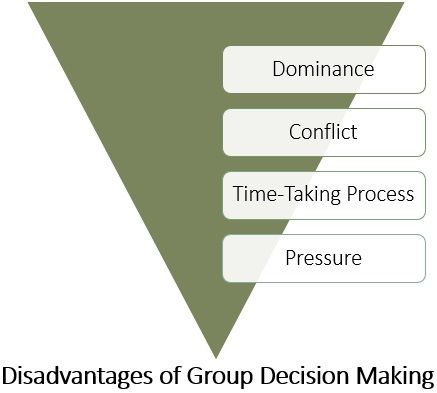
- Dominance
The group members have to agree with one or more dominating members to make a decision. - Conflict
Disagreement among the group members may lead to conflict in the group. - Time-Taking Process
It may take plenty of time if the group members cannot reach any suitable decision. - Pressure
The group members may feel pressure to accept the decisions taken by others.
Techniques of Group Decision-making
Group decision-making techniques are the processes that help group leaders in idea generation regarding a business problem. The creativity and expertise of the group members facilitate hedging risks associated with the decision.
The techniques which one can use for group decision-making are discussed in detail below:
Brainstorming

Brainstorming is a group decision-making technique developed by Alex Osborn. This technique aims to generate a pool of ideas in a judgement-free environment.
In this technique, the group manager clearly states the problem. The group members are asked to generate as many ideas as possible spontaneously.
No criticism, comments, or judgements are allowed during the process. All the ideas are recorded and evaluated by the manager later on.
Pros:
- A list of a large number of creative ideas is created.
- The process is carried out in a bias-free environment.
- It results in a low cost per idea.
- The size of the group is small, which leads to increased participation of group members.
- As there is no restriction or judgement, quality ideas are received.
- The idea is acceptable to all.
Cons:
- In the end, no plan or solution is generated. Only a list of ideas is left with the manager.
- Due to lack of closure, group members are left dissatisfied.
Delphi Technique
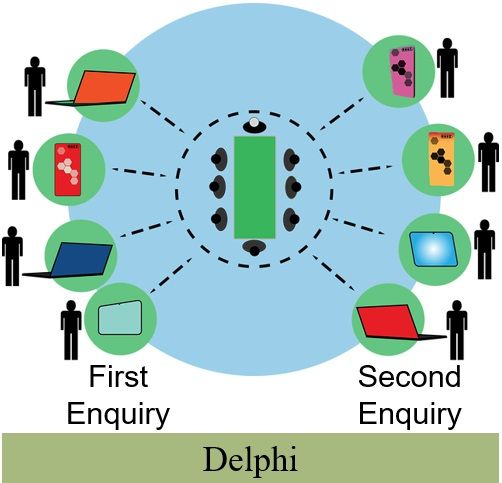
Delphi Technique is a group decision-making and planning process. Norman C.Dalkey and his associates at the Rand Corporation developed this technique.
In this, we obtain judgements and solutions through group members without physical interaction. Communication takes place through e-mails or other methods via questionnaires.
The steps taken to perform Delphi Technique are as follows:
- Delphi Question and the first enquiry
The group coordinator sends the Delphi Question and Questionnaires to the group members. Post this, they ask group members to share their ideas or solutions for the given problem. - The first response
The members write their views, ideas and possible solutions. Thereafter, they send their answers to the group coordinator. - Analysis of first response, feedback and second enquiry
The group coordinator collects and summarises their responses. He prepares another questionnaire asking for more refined solutions, clarification, agreements & disagreements of previous ones. - The second response
The group members again record their responses and send them to the coordinator. - Continuation of the process
This process continues until they reach a suitable solution.
Nominal Group Technique (NGT)
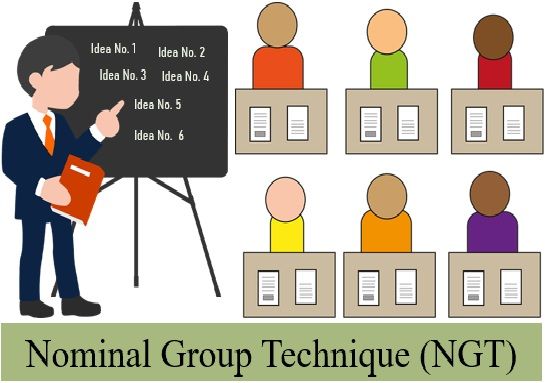
This decision-making technique doesn’t involve interaction among the group members. The group members are present but don’t interact with each other that is why it is called nominal.
The group members need to write their ideas without any discussion. Their opinions are noted on a chart one by one and clarified without any criticism.
The steps involved in NGT are as follows:
- The group members list their ideas silently.
- Group members write their ideas on a chart until all the ideas are listed.
- After that, the members collectively discuss the ideas without criticism.
- In the end, collect a written vote from all the members.
Fish Bowling

Here the group members sit in a circle and one of the group members sits at the centre. Generally, the member seated in the centre is the decision-maker. Besides, he suggests solutions for the problem given by the group members.
All the members will ask questions and critically evaluate the solution suggested by the person in the centre. But, the group members cannot interact with each other. After all the views are expressed, select the ones with conses.
Electronic Meeting

It is a blend of the NGT technique and technology. In this method, the group hosts the meetings through an electronic medium.
The problem is shared with the group online, and the members submit their responses through votes. However, the vote signifies agreement or disagreement with the idea or suggestions.
Pros:
- The group members can be honest without any pressure.
- It is a less time taking process.
Cons:
- The members with good typing speed can excel compared to those with low or average typing speed.
- Excellent ideas are not recognized.
Devils Advocacy

This technique identifies the flaws during the group decision-making process. The benefit of this technique is that it highlights every possible loophole in the solution.
It is a technique where two group members are appointed as ‘devils‘. These devils have to identify flaws in the ideas suggested by the group members. The other members have to satisfy these devils with solutions.
Didactic Interaction
This technique is useful when the answer is to be drawn in Yes or No. Here we divide the entire group into two parts. One part suggests points favouring the decision and the other part presents points against the decision.
The steps involved in Didactic Interaction are as follows:
- The process begins with defining the problem/issue for which we need to take a Yes or No decision.
- Then divide the group into two parts, one favouring Yes and the other favouring No.
- The groups support their side of the decision while discussing.
- Then they inter-change their sides and continue the discussion. That is to say, the members in favour of No will support the Yes ones and vice versa.
- Mutual acceptance of both parties obtains the result of the discussion.
Also, read the difference between Group and Team.
Example of Group Decision Making
The marketing department has to decide the marketing medium for the product. The marketing manager opted for the Brainstorming technique.
He organized a group meeting and shared the objective with the members. He then asked the members to brainstorm and suggest ideas for marketing the product.
The group generated enough creative alternatives by the end of the process. The managers evaluated the ideas and selected the most suitable ones for the product.
Final Words
Group decision-making is an important tool for managers to make decisions more wisely. The business can make use of different techniques available for the process.
The group should opt for the most suitable techniques for the decision. The wrong technique selection may lead to reduced trust in the group and may erode creativity and synergy.
Delphi Development says
What a really awesome post this is. Truly, one of the best posts I’ve ever witnessed to see in my whole life. Wow, just keep it up.