Definition: An intrapreneurship is a phenomenon of empowering the employees within the organization, by valuing their ideas and converting them into a profit-making model for the business. The organization would bear the associated risk and loss if the intrapreneur’s project failed.
It is the combination of employee responsibilities with his/her entrepreneurship skills that creates an intrapreneur. An intrapreneur is the employee who avails an opportunity, develops an idea and takes it to the next level for the betterment of the organization.
Content: Intrapreneurship
- Characteristics
- Importance
- Process
- Advantages
- Hurdles
- Example
- What happens when companies suppress Intrapreneurship?
Characteristics of Intrapreneurship
Intrapreneurs are often falsely conceptualized as entrepreneurs. Yes, they are entrepreneurs, but in the skin of employees.
Let us now read below the features of intrapreneurship to go through this concept in detail: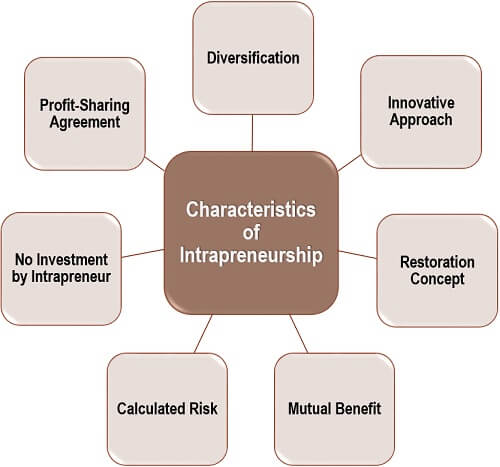
- Diversification: Intrapreneurship promotes teams with people of different gender, age groups, culture and fields.
- Innovative Approach: It is a creative initiative for the progress of both the employee and the company.
- Restoration Concept: An intrapreneur adds value to an existing company by improving the products, services, methods or perceptions.
- Mutual Benefit: Through intrapreneurship, an employee achieves empowerment and self-actualisation; and the company also grows remarkably.
- Calculated Risk: The risk involved in an intrapreneur’s project is well analyzed and planned before it is onboard.
- No Investment by Intrapreneur: The intrapreneur is the brain behind the idea but need not put even a penny into the project. The company funds it at every stage of business.
- Profit-Sharing Agreement: In many organizations, a profit-sharing agreement is signed mutually between the company and the employee.
Importance of Intrapreneurship
The present-day market is highly volatile. Constant improvement and creative inputs have become quite essential for companies to stay in the competition.
Intrapreneurs have the solution to many such problems. Let us now see how can intrapreneurship help: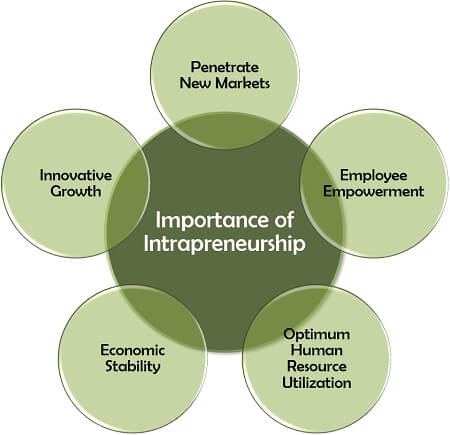
- Penetrate New Markets: An intrapreneur’s idea sometimes lead to availing of the business opportunities prevailing in the new or existing market.
- Employee Empowerment: The company can strengthen its bond with the workforce by granting them authority along with responsibility.
- Optimum Human Resource Utilization: Intrapreneurship provides an opportunity to the employees for outperforming their key responsibility area.
- Economic Stability: It is also undertaken to address market instability and economic downturns through rapid innovation.
- Innovative Growth: Idea generation is the basis of development. Thus, to nurture an entity well, intrapreneurs play a significant role in the business.
Intrapreneurship Process
To understand the basic functioning of the intrapreneurship in any organization, we have summarized the whole process into the following steps: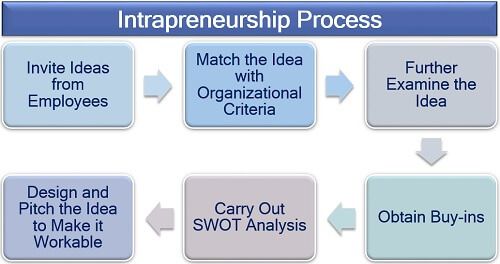
Step 1: The first step is to encourage the workers to put forward their views and opinions. Also, the employees should be made familiar with the person or authority in front of whom he/she can present the idea.
Step 2: The next is analyzing the compatibility of the idea with the organizational need, mission, objectives, values, vision, consumer demand, etc.
Step 3: Now is the time to inspect the idea from different perspectives to seek any scope of betterment.
Step 4: This step is quite crucial as it aims at getting the approval on idea implementation from all the related parties like team, associates, investors and even customers (in case of industrial buyers).
Step 5: The final feasibility test of any new project can be done by identifying the SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats) for both, the idea and the person himself or herself.
Step 6: After the idea is well tested for compatibility, applicability and feasibility, it is modified and crafted such that it becomes workable for the organization.
Advantages of Intrapreneurship
In intrapreneurship, companies grow because of and with their valuable human resource. Some of its benefits are discussed below: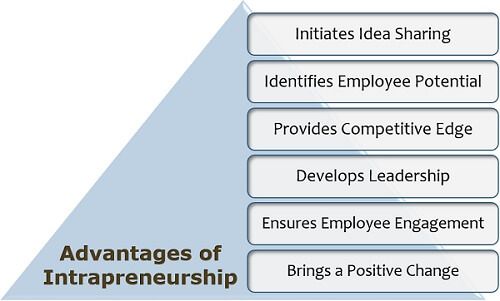
- Initiates Idea Sharing: An intrapreneur may provide a different perspective than that of the management. This idea can act as a robust input for the company.
- Identifies Employee Potential: An employee has a lot of capabilities which can be explored by bringing out the intrapreneur within him/her.
- Provides Competitive Edge: Intrapreneurs are considered to be a highly efficient workforce who have excellent problem solving and competitive skills.
- Develops Leadership: Intrapreneurs emerge as leaders when they are given a proper chance and thus, can set examples for other employees too.
- Ensures Employee Engagement: It is a pragmatic way of keeping the employees immersed in their work, thinking innovative solutions to every problem and evolving as intrapreneurs.
- Brings a Positive Change: Innovative ideas and analytical thinking is mostly assertive for the company’s development and progress.
Hurdles in Intrapreneurship
When an organization head towards adopting intrapreneurship as a part of its corporate culture, the following barriers may arise on the way of making such improvements:
- Multiple CEOs: If a company has more than one CEO with different mindsets, then the employee may not get equal support from each one of them, for intrapreneurship practice.
- Cultural Issues: Many of the other employees who do not take intrapreneurship seriously or keep themselves away from such practice may raise problems.
- Talent Acquisition Problems: Identifying an intrapreneur within an employee is a challenging task for the human resource department.
- Adverse Market Response: The consumers sometimes feel that the innovated product fail to meet their requirements.
- Lack or Shift of Suitable Resource: An intrapreneur leaving the organization or the company unable to appoint one, may lead to its failure.
Example
Happy meal, as we all know, is a kids centric meal box from McDonald’s is an intrapreneurship idea.
Dick Brams, one of the regional managers of the brand at St. Louis, developed an idea of serving the kids with a complete meal. He came with an innovation of making a box of food and beverage items in small quantities, in the year 1977.
When he presented the whole thing in front of the management, his idea was instantly taken into consideration. The company thus introduced the ‘Happy Meal Box’ in the year 1979, which was a great success.
What happens when companies suppress Intrapreneurship?
Let us understand the extent of the disaster that may take place on not taking intrapreneurs seriously. The failure of Eastman Kodak is the most prominent example of this.
When Steven Sasson was working as an electrical engineer (or say an intrapreneur) at Kodak, he developed the world’s first digital camera in the year 1975.
He demonstrated the product in front of different departments of Kodak, from managers to bosses. However, the idea was firmly rejected by all, saying that it could ruin the company’s monopoly.
This was the most prominent early bird chance missed by Kodak. The company faced bankruptcy in the year 2012, after the emergence of some popular digital camera brands like Nikon and Canon.
All this was a result of not being innovative and discouraging intrapreneurship.
ola says
great content
karki jayabahadur says
well illustration about interprenureship
caroline achola says
great info, easy to understand