Definition: Hedging means limiting something by certain conditions in general terms; however, in financial terminology, hedging is a process of protecting oneself against any loss in investment, i.e., it is a method of using market instrument tactically to compensate any unfavourable movements of prices, or we can say the investor hedge one investment by hedging another.
Content: Hedging
Principle of Hedging
Exquisitely two investments that are correlated perfectly are looked for when you want to hedge. For Example, the return of P and Q are correlated perfectly, you buy P and sell Q to hedge, the ultimate result will be riskless, but in reality, some residual risks exist despite hedge.
However, the mode in which hedge is initiated will be same regardless of perfect or imperfect correlation. Suppose you have X liability and you want to buy Y to hedge this liability, here the relation amidst X and Y becomes the base for the investment in Y. For Example, the existing relationship would be:
![]()
Where a will remain constant, and 𝛿 (delta) indicates X’s sensitivity to variation in Y’s value which is a hedge ratio. If you purchase 𝛿 (delta) units of Y, you reduce your risk on liability X.
Types of Hedging
The hedging is of two types; they are as follows:

Hedge Purchase
By buying equivalent quantity in a future market, the producer can cover himself counter to rise in price when he sells some commodities in cash and making such buying in the future market to safeguard oneself from price rise is known as hedge purchase.
Hedge Sale
Hedge sale is selling such commodities in future market which are purchased in cash to safeguard himself against price fall when he holds the stock.
Example of Hedging
Suppose, there is a village having numerous farmers cultivating wheat crops.
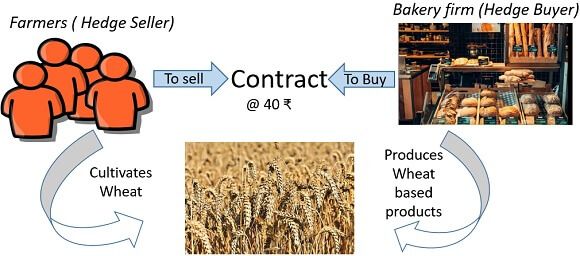
Here, the farmer is a hedge seller, and the problem is that the crop will grow after 3 months from now, and the current price of the wheat is 40 ₹/kg. But the farmers are in doubt that the price may fall from 40 ₹/kg to 30 ₹/kg after 3 months when crop cultivates; thus, he wants a buyer who can purchase his wheat stock in 40 ₹/kg.
Therefore, let us take an example of hedge buyer also, there is a bakery firm who will need wheat for producing their products, but he is also in doubt that the price may rise in next 3 months from 40 ₹/kg to 60 ₹/kg and wants a seller who can sale his wheat stock in 40 ₹/kg. In such circumstances, both farmer (Hedge Seller) and bakery firm (Hedge Buyer) can a make a contract to sell and buy wheat @ 40 ₹/kg even after the price goes up or fall.
This hedging process will secure both the buyer and seller from the risk of fall or rise of price in the future market.
Hedging Strategies
There are many strategies of hedging, few of them amongst them are as follow:
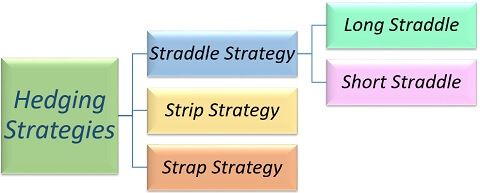
Straddle Strategy
This strategy consists of two positions:
- Long Straddle
Here, long means “Buy”; thus, when we take a position with the buy, it is known as a long straddle. In this straddle, investors have mixed market view, i.e., investors think the market may go down or may go up, and he wants to earn profit in this volatility too. He carries no one-sided view, neither bullish nor bearish; he has a mixed view; therefore, he will go for a long straddle. i.e., he will buy both CALL and a PUT on the same stock with the same exercise price for both options. Here the profit potential is unlimited because as you have CALL option and the loss potential is limited up to the amount of premium paid.
- Short Straddle
In this straddle short means “Sale” and here loss potential becomes unlimited because of becoming a seller of an option, you sell a PUT as well as CALL at the same exercise price, same stock, and same expiration date. Profit potential here is limited up to a premium amount received. However, this position looks like a lousy option for many of us, because this straddle is for the experts having full and more in-depth knowledge of the market.
For Example, Insurance companies take such positions from thousands of individuals, but claims come from very few individuals, here gaining is in thousands and loss is in just a countable number; thus, this straddle becomes profitable for them.
Strip Strategy
Strip strategy shows the bearish market view of the investor, i.e. when the market goes down than the investor gets profit, it consists of buying 2 PUT options and 1 CALL option on the same stock with same exchange price and same expiration date. However, in case the market goes up, we have an option to lapse 2 PUT options and exercise 1 CALL option, this will atleast cover the amount of premium and protect the investor from the loss.
Strap Strategy
Strap strategy shows the bullish market view and consists of 2 CALL Options and 1 PUT option on the same stock with the same exchange price and same expiration date. When the market goes up, then the investor will get double profit, and if the market goes down, we can lapse 2 CALL and exercise 1 PUT to cover the amount of premium and safeguard yourself from loss.
Conclusion
Hedging is a method of compensating loss on the value of any commodities; it can protect your trading capital in price fluctuations. In other words, hedging is protecting investors from the risk of loss which he does not want to bear.
Leave a Reply