An entrepreneur contributes to the economy by undertaking a business activity. He integrates and regulates the 5 M’s, i.e., Men, Material, Money, Machine and Method. During this while, he performs some critical functions that help the enterprise to grow and succeed. In this post, we will discuss some crucial Functions of an Entrepreneur.
These functions are proposed differently by classical and modern economists.
Classical economists suggest an entrepreneur owns the business and invests the required capital. They did not distinguish between an entrepreneur and a capitalist. Consequently, there was no clear distinction between interest and profit.
In contrast, modern economists believe that an enterprise’s ownership and control differ. In the corporate sector, shareholders are the business owners, and control remains in the hands of the broad.
Here, the risk is borne by the shareholders. And to ensure effective management, the company hire personnel at various levels.
Before moving to functions, let’s understand who is an entrepreneur.
Content: Functions of an Entrepreneur
Who is an Entrepreneur?
The word ‘Entrepreneur’ is taken from the French language, which means ‘To Undertake’.
He is an individual who commences business activity to serve certain demands in the market. He carries out the production process and transforms the market demand into supply.
Basically, he makes decisions about What, How and How Much to Produce. In addition, they are the ones who take the risk of setting up a new enterprise from scratch.
An entrepreneur is the biggest opportunity seeker and acts as a catalyst for economic development. He perceives the business activity and arranges and mobilizes required resources.
Moreover, he gathers the required resources and taps the best market opportunities to earn profits.
Enterprise is an integration of ‘Innovation‘ and ‘Entrepreneur‘. As the entrepreneur innovates products and processes in the enterprise.
Thus, an entrepreneur does the following three jobs:
- Risk Bearing
- Organizing
- Innovating
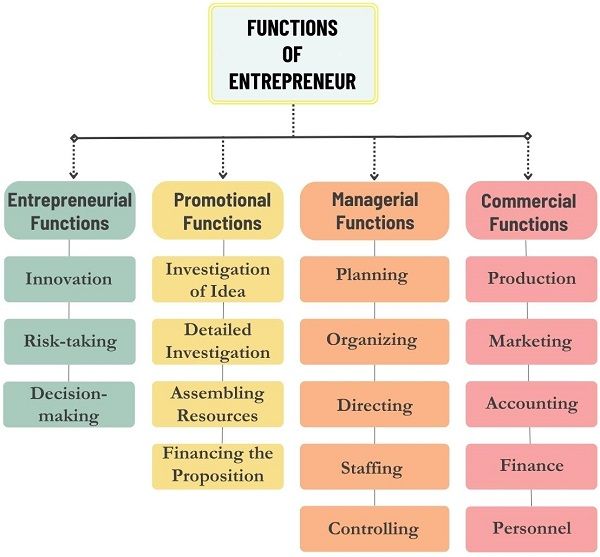
Functions of an Entrepreneur
The responsibility of an entrepreneur spans the entire organization. To become a successful business owner, he must perform his functions effectively.
These functions are discussed in brief below:
Entrepreneurial Functions
1. Innovation: An entrepreneur constantly innovates new and existing products. They continuously update their organization by upgrading technology and trends. It includes activities like:
- Introducing new production methods.
- Finding new sources of raw materials.
- Upgrading the distribution system.
- Exploring new products and markets.
Example: E-bikes and E-cars are great examples of innovation in the transportation sector.
2. Risk-taking: Risk is choosing one among various alternatives, the result of which is unpredictable. Risk bearing is the pre-requisite function of an entrepreneur. However, he tries to mitigate the risk to become successful. This is because they can only earn huge profits by bearing greater risk.
Example: Drew Houston, who owns Dropbox, took a massive risk by not selling his business to Apple. However, things turned out in his favour, and Dropbox became a billionaire company.
3. Decision-making: Another function of an entrepreneur is taking decisions for the organization. The major ones include:
- Formulating organizational aims and objectives.
- Make strategies to make the organization profitable.
- Optimum distribution of work across enterprises.
- Arranging and managing the finance resources.
- Crucial decisions about the production to distribution of products.
Example: Decisions regarding Mergers, Acquisitions, Expansion and Contraction of the business.
Promotional Functions
1. Investigation of an Idea: An entrepreneur investigates the market needs and wants and then discovers a unique business idea. He not only finds one such idea but a number of ideas.
Example: Ola and Uber are amazing examples of this entrepreneurial function.
2. Detailed Investigation: After finding a bunch of business ideas, entrepreneurs critically analyze each one of them. Also, they forecast the business idea’s future potential and growth possibilities. On completing the detailed investigation, he proceeds with the most suitable one.
Example: Before launching any product, the board conduct a detailed market survey.
3. Assembling Resources: Next function is to assemble the required resources to implement the selected idea. Entrepreneur arranges everything from facility location to installation of machinery and manpower.
Example: Recruitment and Material sourcing are prevalent examples of this function.
4. Financing the proposition: An entrepreneur ensures short- and long-term finance sufficiency. He defines the capital structure of the organization. Also, it identifies the sources from where the funds are to be raised and utilized.
Example: The decision of the entrepreneur to raise funds by diluting ownership (Shares) or borrowing funds (Debentures).
Managerial Functions
1. Planning: On the managerial front, the entrepreneur sets the organizational goals. And to accomplish these goals, they formulate short and long-term plans.
Example: Recently, Reliance separated its financial segment. Ambani did so to achieve the aim of becoming India’s largest NBFC.
2. Organizing: The next function is the organization of resources to implement the formulated plan. It includes all the resources like Manpower, Funds and Physical Facilities. It effectively coordinates all the factors of production.
Example: NIKE has a unique organizational structure. It operates in a flat organizational structure. The departments have the liberty to work independently while maintaining quality and consistency.
3. Directing: An entrepreneur is a leader who leads their enterprise towards success. He directs his team and guides them to achieve the preset organizational goals. Also, he communicates his vision, mission and long-term goals with his team. Besides, he allocates the duties and responsibilities with a clearly defined reporting relationship.
Example: Assigning roles and responsibilities considering the employee’s skills.
4. Staffing: Next managerial function is Staffing. Besides recruitment, the entrepreneurs perform the following activities:
- Manpower Planning
- Recruitment
- Selection
- Training
- Promotion
- Transfer
- Rewards and Appraisal
Example: Layoffs in the corporate world are making headlines lately. It is a part of human resource planning in enterprises.
5. Controlling: Here, entrepreneurs practice control over the organization. He ensures that the implementation of plans is as per the plan or not. In case of deviations, the entrepreneur identifies and fixes them. It involves activities like:
- Establishing Standards
- Measuring Performance
- Comparing Performance
- Finding Variations
- Taking Corrective Actions
Example: Comparing the quantity produced with the targets set in the production plan.
Commercial Functions
1. Production: Entrepreneurs carry out production to produce goods. For this, they make use of the factors of production. The type and size of the business will determine its scale.
Example: Entrepreneurs operating on a small-scale offering handcraft produce products on their own. Whereas, similar types of products are manufactured in the plants at a large scale.
2. Marketing: Here, the entrepreneur tries to build a unique image of his products. He uses various tools and strategies to differentiate the products in the market.
Example: Apple has positioned itself as a range of premium phones and accessories in the electronics market.
3. Personnel: Yet another crucial function of an entrepreneur is managing the vital resource in the organization, i.e., Human Resources. It involves activities like:
- Giving suitable work conditions.
- Ensure the employee’s job satisfaction.
- Giving justified monetary compensation.
Example: Entrepreneurs conduct Employee Development Programs for the betterment of employees.
4. Accounting: Entrepreneurs are keen to know their financial positions while conducting a business. For this purpose, they maintain accounts of all the transactions.
Example: The financial statements prepared at the year’s end reflect the current financial position.
5. Finance: It is the blood of an enterprise. Thus, raising and arranging finance becomes one of the important functions of an entrepreneur. It involves the following activities:
- Designing the capital structure.
- Arranging the long and short-term finance.
- Determining the sources of finance.
Example: Tracking the performance by calculating various ratios like PR Ratio, Operating Efficiency Ratio etc.
Parting Words
All and all, an entrepreneur is the one who forms the organization and takes full responsibility for its functioning and success. He coordinates and compiles all the agents of production.
So far, we have discussed the functions of an entrepreneur in length. It gives an idea about his importance and contribution to the enterprise and economy.
Leave a Reply