Definition: Selection is the procedure of choosing persons who have appropriate qualifications to occupy jobs in the company. The primary function is to select the persons who can favourably perform the job, from the pool of competent applicants. Usually, any selection resolution can lead to four possible outcomes. Two outcomes exert the right decisions, and two would specify errors.
As displayed in the figure below, a decision is right when the candidate was forecasted to be successful and subsequently confirmed to be successful on the job and when the candidate was anticipated to be unsuccessful and if employed, would not have been capable of doing the job. In the first case, we have favourably approved, and in the second case, we have firmly rejected. Yet the problems arise when we reject applicants who would have worked favourably on the job or approve them who afterwards not performed well if employed.
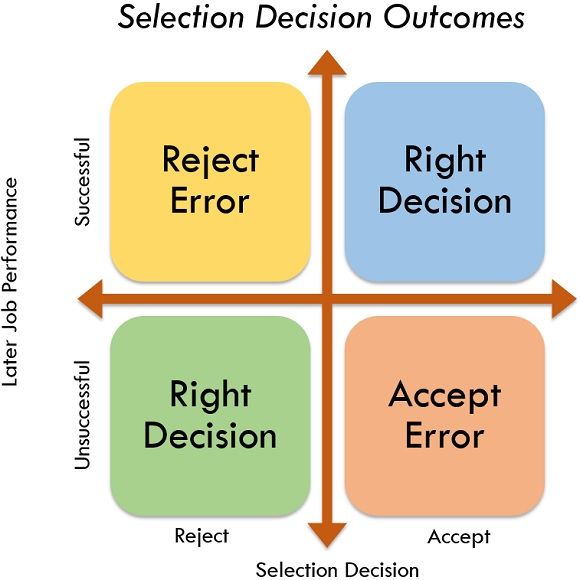
These complications are very severe as prior reject errors only signify that costs of selection were raised. Although, now-a-days, the selection method that leads to dissolving errors can open the company in the direction of charges of discrimination.
Content: Selection
Selection Process
Selection is often a string of barriers; everyone should be certified well before the candidate proceeds to the next. The figure below summarizes the significant steps in the process of selection in a company. The time and significance depend on every level and will differ from one company to another and undeniably from job to job within the same company. The arrangement of steps can also vary from job to job and company to company.
For instance, few companies may emphasize testing, whereas others may prioritize interviews and reference checks. In a like manner, a single concise selection interview might be sufficient for candidates for low-level posts, whereas the various number of peoples might interrogate candidates for administrative jobs.
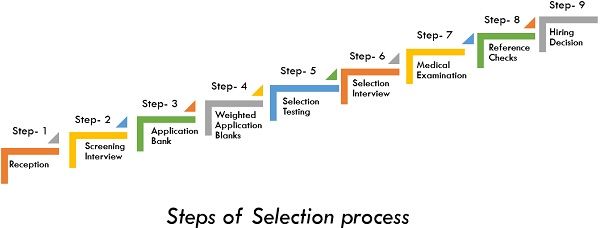
Step 1 – Reception
A company is acknowledged by the personnel it employs. To fascinate persons with ability, proficiency and experience, a company has to build a pleasing impression on the candidates right from the first step. i.e., Reception. The one who meets the candidate must be courteous and capable of offering help in a friendly and gentle way. Employment prospects should be conferred, honestly and precisely. If no jobs are vacant at that point, the candidate can be asked to contact the Human Resource Department later, when an appropriate period of time has expired.
Step 2 – Screening Interview
Big companies often plan an introductory interview to reduce selection costs by admitting only eligible applicants to go through further levels of selection. A subordinate executive from Human Resource Department can draw out responses from candidates on relevant items explaining the appropriateness of a candidate for a job like age, education, experience, salary expectations, inclination, location preferences, etc. This “courtesy interview” as it is usually called, helps the department screen out visible nonconformist. If the department finds a suitable applicant, a recommended application form is provided to the candidates to fill and submit.
Step 3 – Application Bank
Application bank or form is one of the most popular approaches used to gather information on distinct elements of the candidate’s intellectual, social, analytical, work-related background and references. It is a concise history-sheet of a personnel’s experience often contains the following information:
- Individual’s data, such as an address, sex, identification marks, if any, etc.
- Marital status; i.e., single or married.
- Physical information like weight, height, and health condition.
- Educational info such as levels of formal education, marks, etc.
- Employment data such as past experience, promotions, nature of duties, a justification for quitting previous jobs, earnings drew, etc.
- Extracurricular activities information such as participation in sports and prizes won, etc.
- References, i.e., persons who certify the appropriateness of the candidate to the advertised position.
Step 4 – Weighted Application Blanks (WABs)
For selecting the most appropriate and desirable candidate for the vacant post, the company assigns some weights factors for applications considering all the elements essential for the relevant job and candidates getting high scores on the given criteria decided by the company.
Step 5 – Selection Testing
Another significant decision in the selection process contains candidate testing and the types of tests to use. An analysis is a normalize objective measure of an individual’s behaviour, actions or attitude. It is standardized as the way the test is performed, the situation in which the test is executed and the way the person scores are evaluated are evenly applied.
It seeks to measure person differences in a scientific way, offering very little room for personal bias and interpretation. For many years, employment tests have not only acquired significance, although a certain amount of trust in employment decisions. As they try to determine how well a candidate meets job requirement impartially. Large companies do not wait to spend their time and money on selection testing in a big way.
Step 6 – Selection Interview
An interview is the oral test of applicants for a job. It a significant step in the selection procedure. In this step, the interviewer makes efforts to collect and combine information about the capabilities of the applicant and the necessity of the job. An interview provides recruiter freedom to:
- Size up the applicant’s cordiality.
- Ask questions that were not asked in the tests.
- Acquire as much relevant information as possible.
- Determine personal aspects of the applicant, such as facial expressions, presentation and stress, etc.
- Build judgement on the candidate’s devotion and ability to perceive.
- Provide internal information, programs and policies, etc. of the company to the candidate and endorse goodwill for the company.
Step 7 – Medical Examination
Numerous jobs demand physical traits like clear vision, keen hearing, extremely high stamina, resistance under challenging situations, understandable tone of voice, etc. Medical Examination discloses whether or not an applicant retains these traits and can provide the following information:
- Either the candidate is medically advisable for the explicit job or not?
- Either the candidate has health issues or physical attitudes probably to intervene with work efficiency or future attendance?
- Either the candidate endures bad health which must be improved before he can work competently?
- Either the candidate’s body measurements are alike with the job requirements or not?
Step 8 – Reference Checks
Checking references and inspecting history is most popular in the selection process. It is cost-effective, less time-exhausting, and demands least efforts. Views of prior employers and administrative heads are often used to obtain a clear picture of an applicant’s ability in a specific job. For checking references, companies can look for letters of references or at times telephonic references or by way of e-mails or periodically personal visits.
Step 9 – Hiring Decision
Once an applicant has succeeded in the previous steps successfully step by step, now the integral decision is of ultimately selecting the applicants. The final decision has to be made from various numbers of applicants who cleared the tests, interviews and reference checks and then, the job offer is given by way of appointment letter to those applicants who have cleared all the previous hurdles.
Importance of Selection Process
Following are the importance of the selection process in any organization:
- Selecting skilled personnel reduces the training costs of the organization.
- Organizations who understand their personnel’s value invest a large sum in selecting the relevant candidate for the vacant job.
- Selecting personnel who are satisfied with their work enhances the efficiency of both the personnel and the organization.
Conclusion
Selection is the procedure of selecting from a number of applicants, the most suitable candidate for the relevant job. It is a process by which all applicants are split into two categories, i.e., selected and rejected.
Leave a Reply