The central bank and commercial banks both form the base of a country’s economy. However, they are incredibly different from one another. When the central bank is the supreme organization of the banking system of any country, the commercial banks function under the rules, regulations, policies and guidelines of the central bank.
The significant difference between the two is that the central bank is the apex body running the whole banking system. Whereas, a commercial bank is just a constituent unit of the banking system which operates to facilitate exchange and make profits.
Content: Difference Between Central Bank and Commercial Bank
Difference and Comparison
| Basis | Central Bank | Commercial Bank |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | The apex body which regulates the supply of money in the economy and administers the banking system operations in a country | A financial institution which initiate deposits, provide loans and invest the public's money to earn profits |
| Ownership | Public | Public or private |
| Banking System | Apex Institute | Constituent Unit |
| Bank Chief | Governor | Chairman |
| Number of Banks | Single | Many |
| Customers | Other banks and government | General public |
| Motive or Objective | Controlling credit system | Profit earning |
| Foreign Currency Function | Guardian of foreign currency | Dealer of foreign currency |
| Loans | Lender of the last resort for commercial banks | Lending commercial loans, personal loans, housing loans, trade finance, vehicle loans and mortgage loans |
| Other Functions | Issuing government bonds, formulates banking regulations and fund clearance among member banks | Safe deposits service, foreign exchange provision and letter of credit |
| Note Printing Authority | Yes | No |
| Monetary Authority | Yes | No |
| Monetary Supply Function | Yes | No |
| Monopoly | Yes | No |
| Example with Reference to India | Reserve Bank of India (RBI) | State Bank of India (SBI), Central Bank of India (CBI), Canara Bank, etc. |
| Governing Body in India | Reserve Bank of India Act 1934 | Banking Regulation Act 1949 |
What is a Central Bank?
The central bank is an apex body which aims at controlling and managing the banking system operations along with regulating the money supply for the economic stability of a country.
Features of Central Bank
To clearly understand what a central bank is, let us go through its characteristics, given below:
- Monopoly: The central bank is only one in every country, enjoying the monopolistic rights and authorities.
- Apex Body: It is the supreme body of the country’s banking system regulating the other banks and supporting the whole banking structure of the nation.
- Government-Owned: The central bank is strictly owned by the government and thus belong to the public sector.
- Legal Entity: It is a legal entity established under the provisions of a particular act of the government, holding a special significance and rights.
- Banker of Other Banks and Government: The central bank provides the banking services such as deposits and withdrawals to the various commercial banks and government.
- Monetary Authority: It keeps complete control over the flow of money within a country through the formulation of various monetary policies, rules and regulations.
- Note Printing Authority: The central bank is the only bank of the country which has the authority of printing new notes except coins and Re. 1 note.
- Nation’s Gold and Foreign Exchange Reserve: This bank is also considered to be the custodian of the country’s foreign exchange as well as gold reserve keeping these assets under its supervision.
- The backbone of Banking System: Being an apex body, the central bank acts as the backbone of a country’s banking system, performing all the crucial financial functions. Such as framing the banking rules and regulations, circulation of currency in the market and advising the government on economic issues.
- Clearing House: The central bank can be seen as a clearinghouse since it initiates the settlement of bills, cheques and other financial instruments among the two or more banks to ensure smooth functioning of the banking system in a country.
What is a Commercial Bank?
A commercial bank is a financial institution which aims at making profits by initiating deposits from the public, providing loans to them and investing their money in profitable options.
Features of Commercial Bank
Commercial banks are the banks to which you, I and other general public visit from time to time to seek various financial services. Let us now go through the following features of the commercial banks for in-depth knowledge:
- Financial Institution: Commercial banks undertake financial transactions including the deposits, loans, advances, credit creation and investment.
- Public or Private Ownership: These banks can be classified into public and private banks, i.e. the ownership of such banks is not just restricted to the government.
- Dealer of Foreign Currency: Such banks accelerate foreign trade by facilitating the buying and selling of the foreign exchange currency.
- Profit Motive: Commercial banks function with the motive of earning a profit and generating income by providing financial services to the public.
Types of Commercial Banks
Commercial banks can be broadly categorized into four types on the basis of their ownership and establishment. These are explained one by one in detail below:
- Public Sector Banks: The banks which are owned by the public sector, i.e. the central bank holds 50% shares, the state government has 15%. Whereas, the commercial banks which sponsor such banks to own 35% of the holdings.
- Private Sector Banks: Private banks are the ones where private investors own maximum shares.
- Foreign Banks: All banks which are established outside the country are termed as foreign banks.
- Regional Rural Banks: The banks which are established in the rural areas for providing financial assistance in carrying out agriculture activities and other small scale industrial operations are known as rural banks.
Functions of Central Bank
The central bank holds many responsibilities and authorities which defines its services. These are as follows:
The controller of Money Supply and Credit: The primary function of the central bank is to control the supply of money and the flow of credit in the market. It is facilitated through quantitative instruments (bank rates, cash reserve ratio, statutory liquidity ratio and open market operations) and qualitative instruments, i.e. fluctuating the rate of interest for loans.
Printing Currency: The central bank has the authority of printing the notes of all denominations except for Re.1 notes and the coins.
Custodian of Cash Reserve: All the banks have accounts with the central bank where they can maintain some cash reserve for future needs.
Custodian of Foreign Exchange Reserve: This bank is responsible for managing, controlling and exchange of the foreign currency and gold in a country, by maintaining the foreign exchange reserve to keep the exchange rates stable.
Clearing House: The central bank acts as a mediator between the two or more commercial banks to settle their accounts at the time loss and manage the transactions between the commercial banks.
Lender of the Last Resort: One of the essential functions of the central bank is to provide loans to commercial banks at the time of emergency, loss and insolvency.
Banking Services to Banks and Government: This bank provides all the general banking services like accepting deposits and sanctioning loans to the other banks and the government.
Issuing Government Bonds: The central bank issues various government bonds to generate funds, encourage public deposits and investments in the country.
Formulates Banking Rules and Regulations: This bank performs various regulatory functions like licensing banks, framing banking norms and policies, preparing a judicial mechanism for debt recovery by banks, monitoring the banking operations, etc. The central bank even practices moral suasion for making the commercial banks to abide by the policies so framed.
Financial Agent and Advisor to the Government: The central bank acts as a financial advisor to the government by providing an expert opinion at the time economic crisis, fiscal deficit, and advancing loans to other countries. At the same time, it also acts as an agent by representing the country and the government in international conferences and meetings, along with issuing the government bonds and securities on behalf of the government.
Functions of Commercial Banks
The commercial banks have multiple tasks to perform. These are bifurcated into the following two heads, each including numerous activities: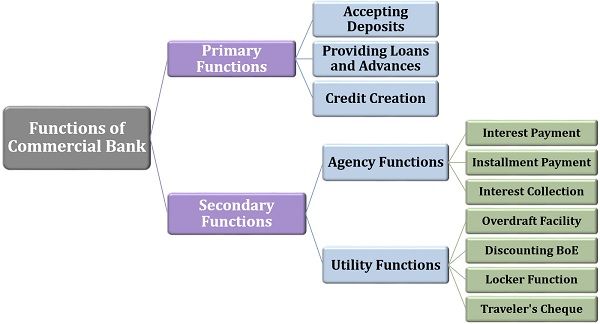
Primary Functions
The commercial banks carry out different functions, the essential ones others as follows:
- Accepting Deposits: The banks receive deposits from its customers by initiating them to open current accounts, savings accounts, fixed accounts, etc.
- Providing Loans and Advances: They also offer long-term loans, demand loans, short-term loans and many others to fulfil the customer’s financial needs.
- Credit Creation: Investing the collected sum in the profitable ventures, equities, advancing loans to the business entities, etc. leads to a generation of profits for the banks.
Secondary Functions
Other than the above mentioned basic operations of commercial banks, there are many secondary functions performed by these banks are classified into the following two categories:
- Agency Functions: Commercial banks work as agents to the public or the customers, by providing various payment and collection facilities on a weekly, monthly or yearly basis by charging some commission. It performs the following activities in this context:
- The commercial banks act as an agent by paying various interests on behalf of their customers.
- They also pay the instalments on the loans borrowed by customers, such as home loans, vehicle loans and personal loans on a monthly, quarterly or yearly basis.
- They also facilitate the payment of taxes, mutual fund instalments and insurance premium for the customers.
- The banks on behalf of their customers; collect cheques, interests, rents, dividends, etc.
- Utility Functions: Other than the agency functions, the banks also provide other facilities to the public. Some of these are mentioned below:
- The commercial banks provide the facility of bank overdraft to draw money even in the zero balance situation of the holder’s account.
- These banks provide money to customers by discounting their bills of exchange and promissory notes.
- The banks provide lockers to the customers to keep their jewellery and valuables in safe custody with the banks.
- The commercial banks also issue traveller’s cheques to carry during the journey by the customers to avoid the loss or theft of cash.
Summary
To know more about the differences in detail, read the given explanation of the above comparison chart below:
- The central bank is the apex institution administering and controlling the whole monetary and banking system of the country. On the other hand, a commercial bank is a financial institution which earns a profit by initiating deposits, advancing loans and investing the public’s money in various opportunities.
- The central bank is usually a public sector organization owned by the state in many countries. Whereas, commercial banks are held by both the public and private sectors.
- The former is an apex institution or the supreme body of the banking system. However, a commercial bank is a financial institution which functions under the regulations of the central bank.
- Central bank’s chief is the Governor of the central bank. Whereas, commercial bank’s head is the Chairman of the respective commercial bank.
- When the former is the only bank of its kind in the country, the latter has many institutions of different types.
- While central bank serves the other banks along with the government, commercial banks serve the general public, including individuals and business organizations.
- The primary objective of the central bank is credit control and economic stability. On the contrary, the commercial banks’ primary motive is to earn a profit.
- When the central bank is the guardian of the foreign currency regulating the foreign exchange operations, commercial banks are dealers of foreign currency facilitating such transactions for its customers.
- The former provides a loan to the commercial banks in case of emergency, whereas the latter offers loans to its customers regularly to generate profits.
- The various other functions of central bank involve issuing of government bonds, formulate banking regulations and clearance of funds among member banks. However, the features of commercial banks include safe deposits service, foreign exchange provision, and issuing a letter of credit.
- The central bank has the authority of printing new currency except for coins and Re. 1 notes, whereas commercial banks do not have this authority.
- The former holds various monetary authorities such as framing the fiscal policies and regulating the banking operations in a country. On the contrary, the latter has no such rights.
- The central bank exercises control over the supply of money and credit terms and conditions in the financial market. However, the commercial banks have to follow the instructions of the central bank regarding money supply and credit terms.
- The former is the only bank of its kind, enjoying the monopoly in the banking sector. But the latter are multiple in number and function under the central bank.
- The central bank of India is the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). Whereas, the various others like State Bank of India (SBI), Central Bank of India (CBI) and Canara Bank are all commercial banks.
- In India, the Reserve Bank of India is governed under the Reserve Bank of India Act 1934. However, the commercial banks are governed by the Banking Regulation Act 1949.
No business can function properly without the services of the banks. Right from taking loans to meet the financial requirement of the organization to depositing the income and profits for further needs, banks play a crucial role.
Where the commercial banks provide various such services to the public, in general, i.e. the individuals and the business entities, the central bank assists all the commercial banks and the government, to function correctly.
To conclude, we can say that both the central bank and the commercial banks are essential to the country, the economy, the business entities and the public; making everyone’s lives easier.
PSSofiya says
Good for exams