Both monetary policy and fiscal policy go hand in hand when it comes to the economic stability and growth of a nation. The most significant difference between the two is that monetary policy is introduced as a corrective measure by the central bank to control inflation or recession and strengthen the Gross Domestic Product (GDP). Whereas, fiscal policy is implemented each year by the ministry of finance to promote the economic development of the nation.
Both of these policies play an essential role in the economy since many crucial decisions are taken by the government, on this basis. The success or failure of an economic decision depends majorly upon the change in monetary and fiscal policies.
Content: Difference Between Monetary Policy and Fiscal Policy
- Difference and Comparison
- Example
- What is Monetary Policy?
- What is Fiscal Policy?
- Types
- Tools
- Summary
Difference and Comparison
| Basis | Monetary Policy | Fiscal Policy |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Monetary policy is a financial tool implemented by the central bank to control inflation and enhance the growth of the country. | Fiscal policy is the revenue or expendiure measure used by the finance ministry to facilitate economic development. |
| Primary objective | Economic stability | Economic development |
| Principle | Controlling the money supply in the market and economy | Influencing the market demand in the economy |
| Complexity | Complex | Comparatively less complex |
| Controlled by | Central bank | Ministry of finance |
| Nature | Change depends on economic condition of the country | Changes every year |
| Policy instruments | Interest rates and credit ratios | Tax rates and government spending |
| Political influence | No | Yes |
| Tools used | Open market operations, reserve requirement, discount rate, interest rates, currency peg | Taxation, public spending, debt |
| Restrictions | Institutional restrictions | Discourage private investment |
Example
Let us suppose that there is a recession in a country. Now, let us see how the monetary policy and fiscal policy impacts this unfavourable economic condition.
Monetary Policy
In case of recession, the expansionary monetary policy is applicable. The central bank plans to increase the money supply in the market to stabilize the economy.
For this purpose, it can decrease the discount rates and the reserve requirement to lower the rate of interest on loans. Along with it, buying of government bonds can be done to facilitate money in the hands of the public and to increase their purchasing power. This will lead to an increase in the market demand and circulation of money in the market.
Fiscal Policy
To deal with a situation like the recession, the ministry of finance uses expansionary fiscal policy.
The government has two options; either it can increase its spendings on public welfare and revival of unfinished or dead projects to generate employment and reduce recession. Or it can provide relaxation on taxes to enhance the purchasing power of the public, ultimately increasing the demand for goods and services.
What is Monetary Policy?
Monetary policy is a financial tool applied by the central bank majorly to accomplish one of the two objectives; either to control unfavourable economic conditions like inflation or recession or to increase the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of the country.
Objectives of Monetary Policy
Monetary policy is primarily used by the central bank to control unfavourable economic conditions and crisis. Its various other purposes mentioned below: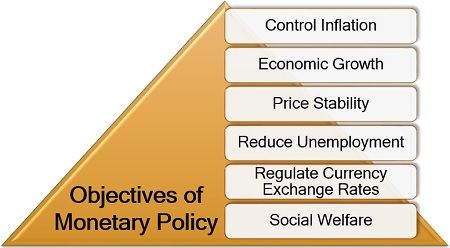
- Control Inflation: Expansionary monetary policy is applied to deal with the economic situation like high inflation.
- Economic Growth: The gross domestic product (GDP), determines the growth of a nation’s economy. Thus monetary policy focuses on increasing the GDP of a country.
- Price Stability: At the time of recession and inflation, the monetary policy tries to bring stability to the price of goods and services.
- Reduce Unemployment: It also aims at reducing unemployment in a nation by promoting business and trade activities.
- Regulate Currency Exchange Rates: The central bank uses monetary policy to manage the exchange rates by regulating the supply of domestic and foreign currencies.
- Social Welfare: Another vital purpose of this policy is to facilitate social welfare like redistribution of wealth, to control the prices of goods and services and attaining monetary stability.
What is Fiscal Policy?
Fiscal policy is the revenue or expenditure measure taken every year by the finance ministry to ensure growth and development of the economy as a whole.
Objectives of Fiscal Policy
Fiscal policy has a broader scope since it is implemented for the overall economic development of a nation. The following points illustrate the different goals of this financial tool:
- Economic Growth and Development: With the help of fiscal policy, the government aims at developing the country and its economy by collecting revenue through taxes ultimately used for enhancement of defence, infrastructure and other amenities.
- Employment Generation: The government initiates various business projects by increasing its expenditure to create employment opportunities for the citizens.
- Price Stability: The government uses such a policy to bring stability to the price of goods or services in the market and reduce the impact of inflation or recession.
- Efficient Allocation of Financial Resources: The government manages and allocates its financial resources by planning its revenue and expenditure wisely with the help of fiscal policy.
- Exchange Rate Stability: While import and export of goods or services, such a policy ensures favourable exchange rates with the help of proper taxation and subsidy.
- Equitable Distribution of Wealth and Income: The government tries to eliminate inequality in the country by practising the equal distribution of wealth and income among the rich and the poor in a country through proper implementation of fiscal policy.
- Reduce Poverty: Poverty is directly proportional to unemployment. Therefore, a change in fiscal policy leads to the generation of employment in the nation, thus reducing the level of poverty.
- Infrastructure Development: Developing countries require capital formation through building up of hospitals, roads, airports, etc. Thus, the government primarily aims at developing the infrastructure of the country by generating revenue through collection and amendment of taxes.
Types of Monetary Policy
Based on its purpose and objective, the monetary policy can be categorized as follows: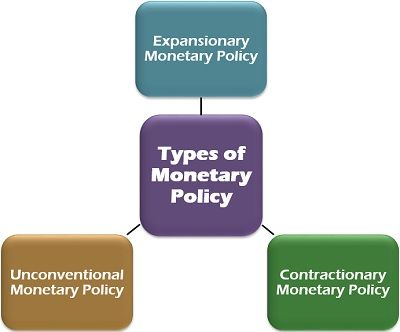
Expansionary Monetary Policy
The monetary policy which is adapted to increase the supply of money in the market to control recession is termed as expansionary monetary policy.
The corrective measure used under this policy includes lowering of the various interest rates, decreasing the reserve requirements of the banks and purchasing or buying back of the government bonds and securities to infuse money in the economy.
Contractionary Monetary Policy
Opposite to the expansionary policy, the contractionary policy deals with situations like inflation by withdrawing the surplus money from the economy.
For this purpose, the central bank raises the interest rates, increases the reserve requirements of the banks and sell out the government bonds and securities to the public.
Unconventional Monetary Policy
The alternative monetary policy comes into action when both the expansionary and contractionary policies fail to control the situation of the extreme financial crisis in a country.
One of the ways adopted is quantitative easing is where the central bank buys government securities to increase the flow of money in the economy. On the other hand, the central bank supplies the financial institutions with ample capital to give out as loans for increasing liquidity in the market.
Types of Fiscal Policy
The fiscal policy can be bifurcated into the following two types, based on its objectives: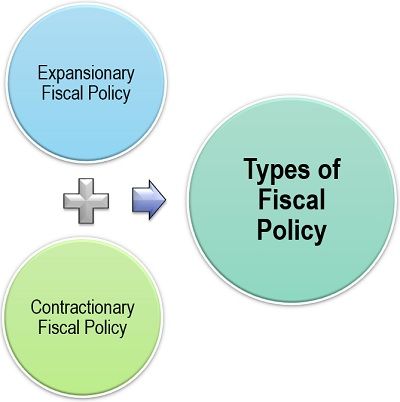
Expansionary Fiscal Policy
The government uses expansionary fiscal policy to increase the demand in the market along with the purchasing power of the consumers; either by spending more on the public benefits; or by levying low taxes on them.
Contractionary Fiscal Policy
On the other hand, contractionary fiscal policy aims at decreasing the demand of goods and services and withdrawing the surplus money from the market by either holding back government expenditure on public welfare or by imposing high taxes on the public.
However, this policy is not commonly applicable due to its extreme adverse effects.
Tools of Monetary Policy
The primary tools used for implementing the monetary policy are the adjustment of interest rates, change in reserve requirements and open market operations (OMO). These are explained in detail below: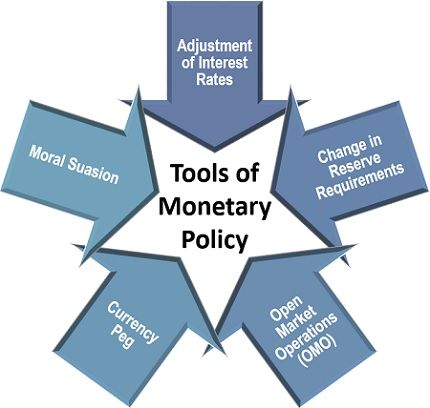
Adjustment of Interest Rates: The primary means to control the money supply in the economy used by the central bank is modifying the discount rates, at which it provides short term loans and advances to the commercial banks.
Change in Reserve Requirements: Every commercial bank is supposed to maintain a minimum sum as the reserve, and this reserve limit is decided by the central bank. Thus, the central bank fluctuates this minimum reserve requirement limit to deal with inflation and recession.
Open Market Operations (OMO): Another useful tool for infusing and withdrawing money from the economy is the buying and selling of government bond and securities in the open market by the central bank.
Currency Peg: In case of hyperinflation (rare economic situation), the central bank secures the nation’s currency. It is done by pegging it against the currency of a stronger economy to create stability of trading activities.
Moral Suasion: Communication has proved to be an efficient way of handling complex issues. Thus, the central bank uses oral or written communication on the grounds of morality to make the commercial banks act in the desired manner, to protect the economic interest of a nation.
Tools of Fiscal Policy
The tools used for implementing fiscal policy by the government can be classified majorly into taxes and expenditure. Let us understand both in detail below:
Taxes: The primary source of revenue for the government of any country is, the charge that it collects from the individuals and business entities. Thus, it acts as an efficient fiscal policy tool for controlling and regulating the economy of the country.
Government Spending: Also known as expenditure, the government plans its expenses on the various projects to develop the infrastructure and economy of the nation.
Summary
The monetary and fiscal policies are the essential financial tools used for economic growth and development of a nation. The following illustration of the above comparison chart will give you a clear picture of the differences between the two:
- When monetary policy is a central bank’s financial tool to deal with inflation and promote economic growth. Fiscal policy is a finance ministry’s measure using government revenue and expenditure to facilitate economic development.
- The monetary policy primarily aims at economic stability, whereas fiscal policy’s principal objective is to develop the economy as a whole.
- The principle on which monetary policy functions is the regulation of money supply in the economy. However, the law of fiscal policy is influencing the market demand for goods and services.
- Where the former is highly complex and strategical, the latter is comparatively less complicated.
- The monetary policy is formulated by the central bank of the country; fiscal policy is governed by the ministry of finance.
- The change under the former is implemented to deal with a particular economic condition; the change under the latter is applicable each year.
- The essential policy instruments used under the monetary policy includes interest rates and credit rations. However, the fiscal policy involves tax rates and government spending as policy instruments.
- The former is purely governed by the central bank and has no political influence, whereas the latter is implemented by the government of the country itself.
- The monetary policy tools include open market operations, reserve requirement, discount rate, interest rates, currency peg and moral suasion. However, there are only two fiscal policy tools available, i.e. taxes and government spending.
- The former restricts the financial institutions like commercial banks since it aims at economic stability. Whereas, the latter limit private investment in profitable business ventures to achieve the social objective and ensure public welfare.
The central bank and the government unanimously function to serve the objectives like economic growth and development of a nation; however, they use different tools to accomplish their goals. Both hold equal importance to the country, though the former focuses on the economic crisis, the latter focuses on sustainable development.
R.M.Kasjin says
very useful datas