Definition: Stock split is a corporate strategy to divide each share of the company into a particular number of shares by reducing the share price proportionately without changing the market capitalization or company’s net worth. It is usually done when the share prices become too high, restricting the small investors from investing in these stocks.
A stock split is a strategical decision taken by the board of directors. It can either be a division or merger of shares depending upon its objective.
Content: Stock Split
Types of Stock Split
Based on the division or merger of the stock, it can be bifurcated into the following two types:
Forward Stock Split
A forward stock split is the same concept as discussed above (in the definition) and is commonly known as a stock split. In simple words, it is nothing but dividing a high price share into multiple low price shares to reduce their price.
It is a strategy which is mostly adopted for blue chip stocks with different objectives.
Reverse Stock Split
Unlike forward stock split, in reverse stock split, the shares of the company are reduced in number by merging some shares into a single unit. Thus, appreciating their price automatically.
The reverse stock split is not very common but can be adopted under unfavourable market conditions when the price of the shares goes on falling. This strategy protects the company against being delisted from the stock exchange if the share prices fall beyond a certain level required for being listed.
Example
Let us now have a look at the real-life examples of both the types of stock split to understand its practical impact and the purpose of applying it in the business organizations:
Forward Stock Split
Netflix splits its NFLX stocks in the ratio of 7:1 in the year 2015 after reaching the value of $702.6 per share, raising the number of shares to 5 billion. The primary purpose behind this stock split was to make the shares appealing to the small investors, who so far were unable to pool in their money in this profitable company.
Reverse Stock Split
The AIG adopted the reverse stock split strategy after experiencing a massive fall in its share prices, touching the minimum share price requirement of $1 to stay listed on the NYSE. It accumulated 20 shares to form a single share, i.e. in the ratio of 1:20, after which it managed to survive. However, the value of its stocks has fallen excessively.
Objectives of Stock Split
Why is stock splitting done? Why do bluechip companies adopt this strategy?
The answer to the above questions and the purpose of the stock split is discussed in details below:
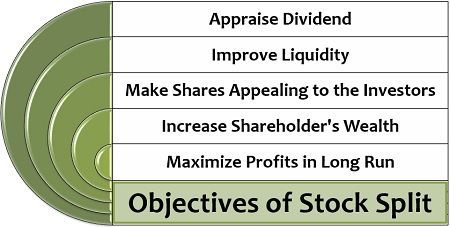
- Appraise Dividend: The company usually pays off a higher dividend after the stock split, thus increasing the gain of the shareholders.
- Improve Liquidity: By splitting each share into multiple shares, the trading of the company’s stock is boosted, which ultimately enhances the liquidity.
- Make Shares Appealing to the Investors: It decreases the price of each share, making the stocks affordable to the new investors.
- Increase Shareholder’s Wealth: The low priced shares are considered healthy for trading purpose. They appreciate the market value of the stocks proportionately and derives wealth to the shareholders.
- Maximize Profits in Long Run: The stock split indicates that the company has the potential for high profits. Thus, the investors can yield high returns in future by investing in such stocks.
Advantages of Stock Split
A stock split makes it convenient for the companies to reach out to small investors and encourage them to invest in high-value stocks.
The multiple benefits to the bluechip companies of going for stock splits are as follows:

- Decreases Share Price: The price of each share is brought down through stock splitting, to make it affordable for the small investors.
- Hikes Share Value: The value of the shares increases with the appraisal of the dividends, generating better returns for the shareholders.
- Increases Affordability: Shares of low price attracts the individual or small investors which is not possible otherwise for the high priced shares.
- Indicates Company’s Growth: Stock split is usually adopted by the companies which have tremendous growth and thus have high valued stocks.
- More Number of Shares to Current Shareholders: The existing shareholders can own an extra number of shares of a particular company without even investing any extra penny.
- No Excess Tax Liability: The company need not pay any extra tax on the increased number of shares since the market capitalization does not change.
- Investors May Get Bonus Shares: The existing shareholders are sometimes benefitted with some extra number of shares as a bonus by the company.
Disadvantages of Stock Split
Stock splits have certain drawbacks, which cannot be overlooked while taking this strategical decision. Let us now read about each of these limitations individually:
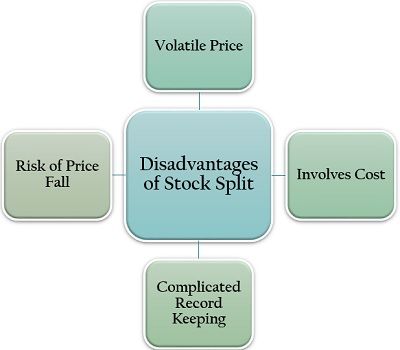
Stock split encourages the comfortable and convenient trading of the company’s shares and increasing the number of investors, thus making the stock price volatile in the market. Due to this, the investment in these stocks become quite risky and uncertain.
The company need to pay different costs while splitting its stock. It includes charges for meeting the legal obligations while listing stock on the exchange, banking and record-keeping formalities and cost of notifying the shareholders about the changes.
The effect of stock splitting can be seen as a downfall in the stock price over the stock market. This record-keeping adjustment comes up as a challenge for the analysts, company experts and accountants making the process of record-keeping quite complicated.
Stock splits are often adopted by the companies when markets are favourable. However, in an unfavourable market condition, the price of the split shares may go down by even more than 50% of its new price, creating a loss to the investors.
Leave a Reply