Definition: A Public Limited Company (PLC) is a separate legal business entity which offers its shares to be traded on the stock exchange for the general public. According to the regulations of the corporate law, a PLC has to compulsorily present its financial stats and position publicly to maintain transparency.
Example: Barclays Public Limited Company incorporated in the year 1896 is one of the global financial service company providing investment and banking solution to the customers (individuals and business entities).
The company is primarily listed on the London Stock Exchange and secondly on the New York Stock Exchange. The investors can easily buy and sell the shares of Barclays PLC on these stock exchanges.
Content: Public Limited Company (PLC)
Characteristics of Public Limited Company (PLC)
A public limited company is very different from private limited companies; however, both are there in the business for profit earning. Following are the various features of a PLC:
- Ownership: The ownership of a PLC lies with two or more shareholders who own the shares of the company.
- Index of Members: A public limited company needs to keep an index of its members with their names.
- Paid Up Capital: The company needs to have a minimum paid-up capital as decided by the corporate law of that country. According to the Companies Act, 2013, a PLC in India needs to keep rupees five lacs as a minimum paid-up capital.
- Perpetual Succession: The company’s existence is independent of the death, bankruptcy or insolvency of any of the member.
- Formation: A PLC can be formed with the appointment of at least two directors and one qualified company secretary.
- Directors: A public company needs to have three or more directors for its existence.
- Name: The company has to end its registered name with the word ‘limited’ for making it a PLC.
- Limited Liability: The liability of the shareholders of a public limited company in case of loss or debts is only limited to the amount of investment they have made in the company. Their assets cannot be charged liable for any such damages.
- Prospectus: It is mandatory for a public limited company to issue a prospectus which is the statement of present and plans of the company.
- Abided by Law: A public limited company has to abide by the corporate laws of the country. Indian PLCs have to follow the regulations of the Companies Act, 2013.
- Minimum Subscription: A PLC needs to acquire at least 90% amount of the shares issued by the company within a particular period.
Incorporation of a Public Limited Company (PLC) in India
A public limited company has a distinct identity and is owned by the public and managed by the board of directors.
Therefore, the registration procedure of a PLC is quite lengthy and involves a lot more formalities. Let us now go through the various requirements for this form of business organization:
Eligibility
The basic requirements or eligibility criteria for setting up a public limited company are as follows:
- One Resident Director: Out of the three or more directors of a public limited company, one has to be a resident of India compulsorily.
- Minimum Seven People: To establish a PLC, minimum of seven people are required who can become directors, shareholders or both.
- Unique Name: Every PLC needs to have an exclusive name to get the trademark registered. This name should not be identical to any other company.
- No Minimum Capital: A PLC can be started with the amount of capital required, and there is no minimum capital specified. However, the minimum share capital (both authorized and subscribed) needed is rupees five lacs.
Documents Required
A PLC next requires certain documents as evidence of the directors’ identities and the registered office of the business. These are explained in detail below:
Identity Proof: The disclosure of the identity of the company’s directors include the following:
- One personal identity proof like voter id, driving license, adhaar card or passport
- PAN card for Indian nationals and passport for foreign nationals is compulsory
- Nationality proof for foreign nationals
- Two passport size photographs
- Resolution of the board of company / LLP for authorization of directors or partners
Address Proof: The address proof of the directors involve electricity bill, mobile bill, telephone bill or bank statement (any one of these and not older than two months).
Proof of Registered Office: The place where the business is to be commenced or controlled is its registered office. Such documents include:
- NOC from Landlord
- Rent receipts along with the rental agreement, conveyance, lease deed, etc. (any one of these)
- Photocopy of gas bill, telephone bill or electricity bill (either one of these) which is not older than two months.
Other Documents: Other than the documents mentioned, the following are some more relevant documents need to be submitted under particular conditions or otherwise:
- Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) physically signed by the directors and the shareholders.
- In the case of foreign directors, all the documents should meet the following obligations:
- Notarized; if residing in Commonwealth countries
- Notarized & Apostiled; if living in a country which is a signatory to Hague convention
- Notarized & Consularised; if not covered in the above categories.
Registration Procedure of Public Limited Company (PLC)
As we already know about the various requirements and essential documents for the registration of the company, let us move forward towards the procedure of incorporation under the following eight steps: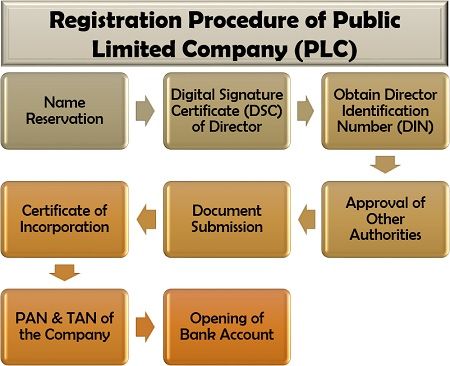
Name Reservation: The company needs to get the company name approved under the Companies Act, 2013, which is valid up to twenty days from the date of approval.
A company can propose and apply for two names and can go for one resubmission (RSUB) under Reserving Unique Names (RUN) web service.
Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) of Director: Filing of the online application form for a public limited company requires signatures supported by the DSC of the directors and the shareholders.
DSC can be taken by submitting a DSC application attached with identity proof, address proof, photographs of the respective signatory.
Obtain Director Identification Number (DIN): The directors need to file a DIN application attached with the address proof id proof attested by any CS, CMA or CA.
The Registrar of Companies (ROC) is responsible for issuing a unique identification number known as Directors Identification Number (DIN) to become the official director in India.
Approval of Other Authorities: The applicant should next take and furnish the approval from the respective department, appropriate authority, regulatory body or ministry of Central or State Government depending on the type of business and the work, to the ROC.
Document Submission: An application for incorporation or registration of the PLC supported by declaration, affidavits, Memorandum and Article of Associations is to be submitted to the ROC.
Certificate of Incorporation: A registration certificate, also known as a certificate of incorporation is issued by the ROC after inspecting the application and documents submitted. The business can be now commenced under the norms of a public limited company.
PAN & TAN of the Company: Simultaneously with the certificate of incorporation, the applicant needs to apply for the Permanent Account Number (PAN) and Tax Deduction and Collection Account Number (TAN). It is issued with and mentioned in the certificate of incorporation.
Opening of Bank Account: Lastly, the PLC so formed, has to compulsorily open a current account with any bank, by submitting the registration certificate and the other required documents.
Advantages of Public Limited Company (PLC)
Public limited companies have contributed a lot to economic growth and development in a country. The different benefits of a PLC are explained one by one in detail below: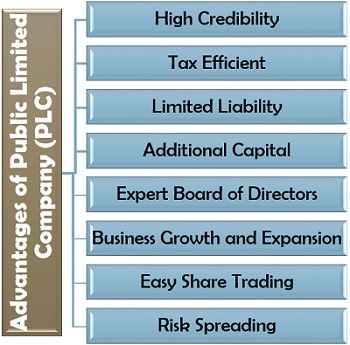
- High Credibility: The investors find the public limited company to be more reliable and trustworthy, increasing its credibility.
- Tax Efficient: A PLC gets various tax benefits like tax-deductible costs and other allowances. On paying off the corporation tax, the company is saved from paying high-income tax.
- Limited Liability: The shareholders are not liable to pay the company’s debts or losses beyond their investment value in case of insolvency or bankruptcy.
- Additional Capital: Initial Public Offering (IPO) is a source of raising funds for the public limited company to meet the capital requirement of the business.
- Expert Board of Directors: The company is efficiently managed by the board of directors comprising of expert and talented people.
- Business Growth and Expansion: The acquisition of additional by issuing of shares, provide financial strength to the business and develops the scope of growth.
- Easy Share Trading: The shares of a public limited company can be bought or sold in seconds on the stock exchange market. Thus, making it convenient for the investors and shareholders to acquire a part of the company.
- Risk Spreading: Since, there are many shareholders owning small portions in the company, the risk of loss and insolvency is also widespread among them.
Disadvantages of Public Limited Company (PLC)
Though PLC is an excellent option for the entrepreneurs who lack capital for starting a business, it has certain drawbacks making it unsuitable for business aspirants. Following are the limitations of the public limited companies: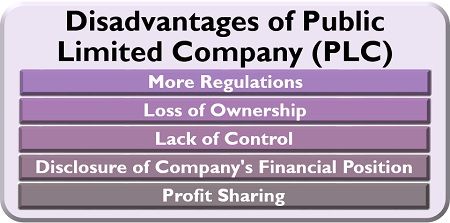
- More Regulations: A company is abided by the laws and regulations formed by the corporate houses to function as a public limited company which is a hefty task.
- Loss of Ownership: Ultimately, a company has to go public to work as a PLC, which leads to giving up of owner’s possession over the company.
- Lack of Control: The loss of ownership leads to the loss of control over the decision making of the company.
- Disclosure of Company’s Financial Position: A PLC has to disclose the complete financial health of the company in front of the public to assure a high level of transparency.
- Profit-Sharing: The profit sharing is done on a vast scale among all the shareholders, which entitle each one of them a tiny proportion of that profit.
Conclusion
A public limited company is usually established to generate capital from external sources, i.e. the general public for commencing a business, business expansion, technological advancement. global expansion, etc.
But a PLC is more suitable only to the large organizations which have a comprehensive perspective and higher growth possibilities, rather than a small shop located next door.
John Vlasic says
This article is so clear and informative. I got a lot of information from this post. Keep writing this way on your site.