Definition: Macroeconomics is that specialized field of economics which focuses on the overall economy. It works on the aggregate value of the various individual units, to determine its more substantial impact on the whole nation. All the prominent reforms and policies are based on this concept.
For instance; the nation’s income is computed as the per capita income, which is nothing but the average of the total earning of all the citizens in that country.
Content: Macroeconomics
Scope of Macroeconomics
Macroeconomics is a vital field of study for the economists, government, financial bodies and researchers to analyze the general national issues and economic well-being of a country.
Macroeconomics widely cover two major fundamentals which are further sub-parted into multiple topics, as explained below: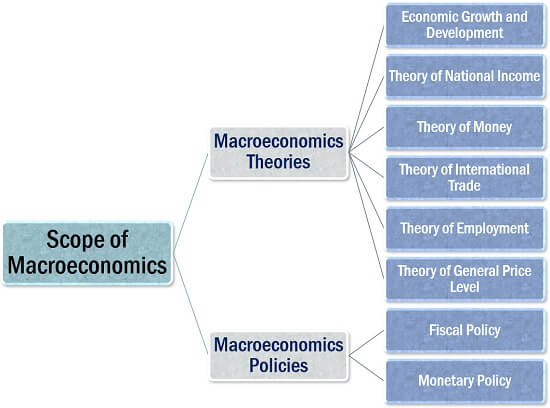
Macroeconomics Theories
Government, as we know, is the regulatory body of a nation, it considers the various aspects which are crucial and impacts the lives of the citizens.
There are six significant theories under macroeconomics:
Economic Growth and Development: The status of a country’s economy can be evaluated in terms of the per capita real income, as studied under macroeconomics.
Theory of National Income: It covers the various topics related to the evaluation of national income, including the income, expenditure and budgeting.
Theory of Money: Macroeconomics analyzes the functions of the reserve bank in the economy, the inflow and outflow of money, along with its impact on the employment level.
Theory of International Trade: It is a field of study that enlightens upon the export and import of goods or services. In brief, it determines the impact of cross-border trade and duty charged, on the economy.
Theory of Employment: This stream of macroeconomics helps to figures out the level of unemployment and prevailing employment conditions in the country. Also, to know how it affects the supply, demand, savings, consumption, expenditure behaviour.
Theory of General Price Level: The most important of all is the analysis of product pricing and how these price levels fluctuate because of inflation or deflation.
Macroeconomics Policies
The government and the reserve bank functions together while determining the macroeconomic policies, for the nation’s welfare and development.
The two segments of this section are as follows:
Fiscal Policy: As we know, fiscal policy is a means of meeting the deficit of income over the expenditure; it is a form of budgetary decision under macroeconomics.
Monetary Policy: Monetary policy is framed by the reserve bank in collaboration with the government. These policies are the measures taken to maintain economic stability and growth in the country by regulating the various interest rates.
Importance of Macroeconomics
Why do we need to dig into macroeconomics?
The answer is macroeconomics is a vital concept that considers the whole nation and works for the welfare of the economy.
Let us now find out its other significance:
Trade Cycle Analysis
It is beneficial for timing the economic fluctuations to avoid or be prepared for any financial crises or adverse situations.
Economic Policies Formulation
Framing of the monetary and fiscal policies majorly depends upon the study of prevailing macroeconomic conditions in the country.
Downsizes the Effect of Inflation and Deflation
Macroeconomics also helps the government and the financial bodies to be prepared for the situations of economic instability.
Facilitates Material Welfare
This stream of economics gives a broader perspective of social or national issues. Therefore, the ones who look forward to contributing to the welfare of society needs to study macroeconomics.
Regulates Economic System
It ensures or keeps a check over the proper functioning of the country’s economy and actual position.
Resolves Economic Issues
The analysis of macroeconomics theories and issues helps the economists and the government to figure out the causes and possible solutions of such macro-level problems.
Economic Development
Dealing with different economic conditions by making use of macroeconomics research, opens up the way towards the country’s growth.
Issues Related to Macroeconomics
An economist needs to deeply analyze the following problems prevailing in the society as well as the economy while studying macroeconomics:
Issues Related to Government Policies
The business operations often lead to social costs such as pollution, soil erosion, depletion of natural resources, endangering wildlife, etc.
To control this social cost, the government frames specific policies and regulations which act as a hurdle for business organizations.
Issues Related to Macroeconomic Trends in the Economy
The economic conditions of a country exceedingly influence the operations of any organization.
Various economic trends or factors affecting the business are Gross Domestic Product (GDP), employment conditions, investment opportunities, banking, pricing policies, etc.
Issues Related to Foreign Trade
Many organizations trade (i.e. either export or imports goods from other countries) in international markets. They are sensitive to the fluctuations in the economy of other countries, exchange rates, prices, etc.
Such changes may even influence the economic conditions of the country, ultimately affecting the business organizations.
Limitations of Macroeconomics
Why do some economists criticize macroeconomics?
The following shortcomings of this approach have to lead to its criticism: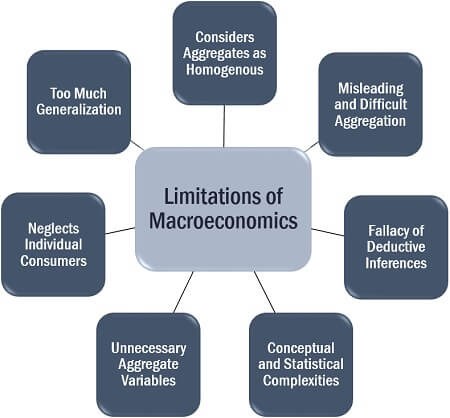
- Considers Aggregates as Homogenous: The individual data may not be similar in structure or composition. Thus, when such single figures are compiled to get an aggregate value, it may not seem to be that useful.
- Misleading: The extensive application of the macroeconomics measures seems to be irrelevant when aimed at 100% results.
- Fallacy of Deductive Inferences: Macroeconomics function on aggregate values. But, the interpretation of the individual activities may not be the same as compared to the conclusion drawn on a mass level.
- Conceptual and Statistical Complexities: When the individual data have different units, its aggregation becomes arduous and holds no significance.
- Unnecessary Aggregate Variables: When the individual elements need to be examined separately, the aggregate values cannot be used for the purpose.
- Neglects Individual Consumers: The concept of macroeconomics overlooks the importance of the individual unit or consumer since the fundamental is to make use of the aggregates.
- Too Much Generalization: The conclusion derived from the aggregation of the data, is generally taken to be true for all the individuals.
Conclusion
Macroeconomics is the basis of various economic reforms and the national decision model in a country.
However, the policies framed under this concept usually have a dual impact, i.e., on the society as a whole and individual citizens.
Therefore, it requires a highly analytical, logical and extraordinary approach while reaching to such interferences.
Nayma says
This page really helped me thanks to the writer
Prachi M says
thanks a lot
Nasir husain says
Very helpful content
Thank you so much
Favour says
Thank you ❤️
Bhavishya says
nice content thank you
Eve says
Thanks alot
Rofiah says
Thank u
Bola says
Contents are well summarized, detailed, and explanatory enough.
Very useful
Muhammad Khalid says
Thanks u
Shubham Maurya says
Thank you