Marketing and selling seem to be correlative, however, there is a huge difference between marketing and selling. Both create precise adjustments to the business. Thus, the manager is anticipated to follow the various distinctive class of strategies for the success of their business.
Selling has a product target and is often manufacturer driven. It is the only operational portion of the marketing and has an interim objective of attaining a certain level of income, gain or market share. More priority is given to “price variation” to close a sale where the aim can be framed as “I must anyhow sell the product to the consumer”. This limited focus does not predict adequately for cost-effective planning and brand creation. There is no effect to build strategies for creating comprehensive competing benefit. The closure of any sales task is increasing profits through sales acceleration. When the aim attention is on selling, the businessmen believe that sales must start directly after the promotion program is concluded and also the functions of the sales department to sell whatsoever the production unit has produced. Aggressive sales methods are rationalized to satisfy this aim. Consumer’s actual desires and gratification are taken-for-granted. Selling turns the product into money for the company temporarily.
However, Marketing has a broad approach than selling and is productive in nature. Its emphasis is on the consumer instead of the product. Although selling depends on the needs and curiosity of the producer or marketer, marketing depends on the need of the customer. It is merely a procedure of accepting and fulfilling the consumer wants. Manufacturing and selling are compassed to fulfill the consumer at a gain. Marketing involves all those actions that are related to planning, pricing, promoting and dispensing the product or service. In marketing, the procedure initiated with the recognition of customer wants and will not be concluded before customer’s feedback is taken, to evaluate his or her satisfaction. It is recognized as a long series of actions which consist of manufacturing, packaging, promotion, appraising, dispersion and then selling. Customer wants are the directing force responsible for all these actions. Profits are not neglected, but in the procedure, the marketer is competent to develop a bigger customer franchise and creates profit for the company. Mind share is more relevant than market share in marketing.
Marketing Vs Selling is summarized in the following comparison chart shown below:
Content: Marketing Vs Selling
- Difference and Comparison
- What is Marketing?
- Types of Marketing
- What is Selling?
- Types of Selling
- Summary
- Conclusion
Difference and Comparison
| Basis of Difference | Marketing | Selling |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Marketing is a new means of arriving | Selling is a humanistic word |
| Actions | It involves the integrated procedure of determining and fulfilling the customer needs | It involves only the material distribution of goods and services |
| Extent | Marketing involves the conducts of many associated actions also | Selling is restricted only to the substantial dispersion |
| Product/Customer orientation | It is customer aligned | It is product aligned |
| Goals | The goal of marketing is to fulfill the customer wants | The goal of selling is to draw the utmost profit |
| Way to Profit | It emphasizes on the escalation of gains by highest social contentment | It emphasizes on the escalation of gains by the expansion of sale |
| Essence | Marketing has continuing goals with certain rational suggestions | Selling is a day-to-day periodic activity with interim goals |
| Product assurance | What shall be provided as a "product." is resolved by the consumer | The seller decides what "product." is to be presented |
| Perspective | Marketing considers business as a " Consumer gratifying procedure." | Selling consider business as a "product manufacturing procedure." |
| Perseverance of cost | In marketing customer regulates price and price ascertain the cost | In selling cost ascertains price |
| consumer's importance | Marketing perceives the consumer as the "king." | Selling consider the consumer as the determinant channel in the business |
| Significance | Marketing gives the prominence on an integrated approach, by an unified plan of action which covers product, promotion, pricing and dispersion | Selling gives importance "on anyhow selling", there is no strategy amidst the distinctive activities of the overall marketing assignments. |
What is Marketing?
The principle of marketing is a trade or deal intended to fulfill human wants and desires by way of exchange mechanism. A demand is a wish for which customer is inclined to pay an amount. A wish or desire can be any element or service the consumer wants or look for. Desires become demands when reinforced by purchasing power. A want is any item the buyer feels to retain herself rife and active. An exchange involves an amount between two parties. But, the exchange is different from the transfer, there are chances that transferor will not get anything in return, but the aim of marketing is to generate sales to earn feasible profit for the manufacturer.
Marketing in its prior explanation and in statutory aspect is said to be the effort by which the transmission of possession in products among the seller and the purchaser is implemented, priority ownership transfer. It confines the extent of marketing to the absolute transfer of holding” Marketing involves all the actions which are related to enacting changes in the holding and control of goods and services”.
Marketing in an economic viewpoint is determined as a trade function by managing supply and demand in symmetry. It targets the formation of well-being and standard of living of the community as the purpose of marketing. It is also described as” That portion of economics which manages the formation of time, place and ownership utilities”. “That stage of business life by which human desires are fulfilled by the transfer of goods and services for some worthwhile payment”.
Types of Marketing
The word marketing can be determined from two points of view, i.e., Micro (Firm’s point of view) and Macro (Nation’s point of view).
Micro Marketing
Under micro marketing, if a company plan and enforce strategies for development of the product, pricing, promotion and dispersion, that assure circulation of want fulfilling and services at a gain. The eventual goal of micro marketing is the fulfillment of human wants and desires. i.e., it is customer-oriented. Again, the definite point or what is noticed as “micro marketing” is the procedure of regulating an individual company so as to gratify its particular consumers. Marketing also includes the administration of every facet of a business with the eventual customer in mind. It can be related to the inspection aspect of a scientist who examines a small substance by a microscope. The approach of micro marketing reveals two facets, they are:
- Marketing should guarantee desires fulfilling goods and services, i.e., marketing starts with the consumer and not with the manufacturing procedure.
- Instead of manufacturing marketing must conclude what products are to be manufactured.
The above two facets suggest that all actions of marketing concentrate ultimately on the customer; the manufacturer does not decide the product.
Macro Marketing
From the wider viewpoint of macro marketing, marketing is the complicated structure of companies and actions by which a country’s resources are dispersed amidst the individuals to fulfill their desires and wants. Therefore, here the spotlight is on the complete system, instead of the actions of the company. Thus, it assists the community as a whole, and this approach keeps the manufacturer learned of the developing desires of the “customers” and adjust it by “distribution”, and to understand the “demand” and “supply” of the products, through establishing price-cohesion in the long-term for the benefit of the community and the specific consumers and sellers.
What is Selling?
Selling is defined as an act of transferring something to another for some value. It is the act of helping and sometimes persuading people to invest in a product or service that we believe they could benefit from. Now, notice that I have used the word “Act”. When you work in professional selling, you very often fall into an acting role. One of the most wonderful benefits of working in professional selling is “The freedom of being able to be yourself”.
People buy from people they like, but they are also very quick to judge others based on their first impression. So, remember it is fine to wear a mask while selling, just make sure that it is a professional business mask and not the selling mask because your prospects will see for it very quickly. Next, I said that selling is about helping and sometimes persuading people. You will often hear; people use the term exchange of service or exchange of items when they define selling. They usually look selling is offering to exchange an item of value for a different item.
Types of Selling
The diversified nature of the purchasing condition measure that there are various types of selling. Every type of selling job will now be reviewed below in detail:
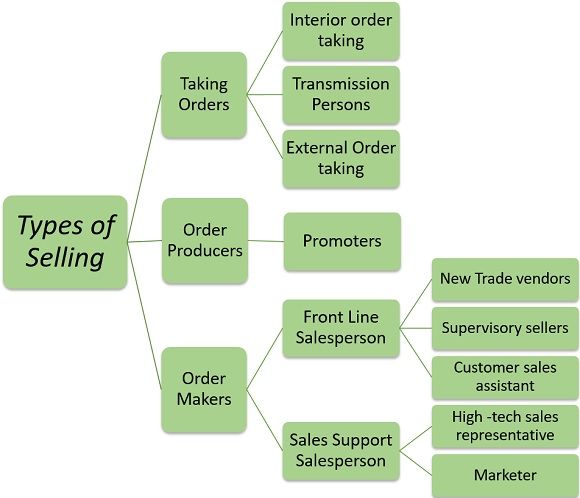
1. Taking Orders
- Interior order taking
Here, the consumer has the absolute privilege to select products without the existence of any salesperson. The sales associate’s work is entirely negotiable, i.e., accepting payment and overlook the products. Another form of interior order-taker is the telemarketing sales unit which backs field sales by taking buyer’s order over the phone.
- Transmission Persons
Generally, these salespersons are involved in the work of dispensing the products. Now-a-days many companies offer home deliveries of the products. That is a small attempt to assure the customer to increase their orders, modifications in the number of orders are customer-driven.
- External Order taking
Such salespersons visit consumers, but their main function is to reply to consumer requests instead of advising. Outside order-takers do not hand over products, and somewhat they are being interchanged by the other cost-effective telemarketing units.
2. Order Producers
- Promoters
In a few industries, especially in the pharmaceutical industry, the sales target is not to halt the sale but to convince the consumer to mention the seller’s products.
3. Order Maker
- New Trade vendors
The aim is to have a new business by recognizing and selling to a person or a company who have not earlier purchased from the salesperson organization.
- Supervisory sellers
These sellers have the work of managing, stable relations with the organizational consumers, i.e., industrialized buyers, purchasing for resale and corporate buyers. The selling work may include crew selling where prevailing salesperson backed by the product and economic specialists.
- Customer sales assistant
These persons sell tangible products and services like security apparatus, cars, insurance and special pension plans to an individual. Enough selling in this group turns to be “one-off” and salesperson are usually paid by way of commission. Thus, the incentive to complete an order is predominant, and it is a group that draws much attention to criticism in terms of “high pressure”, i.e., for pressurizing customers to make a purchase.
- High -tech sales representative
This crew of order-makers supplies sales assistance to front-line salespersons where a product is exceptionally technological and arbitration is complicated; salespeople may be backed by the product and economic specialists, who can supply the comprehensive technological facts needs by the consumers.
- Marketer
These persons contribute sales assistance in retail and wholesale selling conditions. Order can be arranged nationwide at head office, but sales to respective outlets are backed by merchandisers who express recommendations on display, enforce sales promotion, examine inventory levels and retain reach with store managers.
Summary
- Marketing is originated as a new means of arriving; whereas selling is a humanistic word.
- Marketing activities involves the integrated procedure of determining and fulfilling the customer’s needs; whereas selling involves only the material distribution of goods and services.
- Marketing involves the conduct of many associated actions; whereas the scope of selling is restricted only to the substantial dispersion.
- Marketing is customer-aligned; whereas selling is product aligned.
- The aim of the marketing is to fulfill the customer’s desires; whereas the aim of the selling is to draw the utmost profit.
- Marketing gives emphasis upon escalation of profits by highest social contentment’s; whereas selling gives emphasis on the escalation of profits by expansion of sale.
- Marketing has continuing targets with certain rational suggestions; whereas selling is a periodic activity with interim targets.
- In marketing, what shall be provided as a product is resolved by the consumer; whereas in selling the seller decides what product is to be presented.
- Marketing considers business as consumer gratifying procedure; whereas selling considers business as a product manufacturing procedure.
- In marketing customer regulates price, and price ascertains cost; whereas in selling cost ascertains price.
- Marketing perceives the consumers as the king; whereas in selling consumer is considered as a determinative channel of the business.
- Marketing gives the prominence to an integrated approach, by a unified plan of action which covers, products, promotion, pricing and dispersion; whereas selling gives importance on anyhow selling, there is no strategy amidst the distinct activities of the overall marketing assignments.
Conclusion
The terms “Marketing” and “Selling” are generally used as if they had similar significances. Still, it is recommended to be precise as to the distinction in the explanation to be drawn in. Selling usually attracts the plans and suggestions to make customer barter money for goods and services. Marketing is engaged with the belief of gratifying a customer’s necessities by virtue of the product along with the supply of value-satisfaction to the consumer.
Abu Zafor Iqbal Ahamed says
Very good article. Helpful
Prachi M says
thank you so much