Definition: Marketing control refers to the measurement of the company’s marketing performance in terms of the sales revenue generated, market share captured, and profit earned. Here, the actual result is compared with the standard set, to find out the deviation and make rectifications accordingly.
Marketing is one of the crucial functions of any organization. Therefore, the management must exercise proper control over the marketing operations to ensure error-free results, optimum utilization of the resources and achievement of the planned objectives.
Content: Marketing Control
Types of Marketing Control
When we say control, it is not about overpowering the personnel, but it means enhancement of efficiency, by reducing the chances of errors and meeting the standards set by the management.
Let us now discuss the four major types of control, implemented in an organization:
Annual Plan Control
As the name suggests, the plans which are determined for one year for the control of operational activities through the successful implementation of management by objectives is termed as annual plan control.
Such programs are usually framed and controlled by the top management of the organization.
Following are the five vital tools used under the annual plan control mechanism:
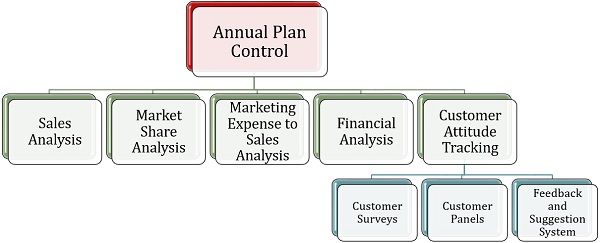
Sales Analysis
The first one is the sales analysis, where the manager determines whether the sales target of the organization have been achieved or not. For this purpose, the actual sales are compared with the desired sales and deviation is computed.
This method is also used for finding out the efficiency of sales personnel by comparing the individual sales with the target set for each salesperson.
Market Share Analysis
To evaluate the competitiveness, the management needs to find out the market share acquired by the organization.
However, it is quite challenging to determine the market share of other organizations which constitute of unorganized firms, due to lack of sufficient data.
Marketing Expense to Sales Analysis
Sometimes the firms spend much on the marketing of products, which diminishes their profit margin or increases the product price.
Therefore, a marketing expense to sales ratio is calculated to know the percentage of sales value paid off as a marketing expense.
Let us now go through the other ratios computed to determine the share of each marketing expense in sales value:
- SalesForce Cost to Sales Ratio estimates the percentage of sales value used to pay the salespeople.
- Sales Administration to Sales Ratio determines the share of sales amount utilized for meeting the selling and administration expenses.
- Sales Promotion to Sales Ratio is the value of sales invested in the sales promotion activities.
- Advertising to Sales Ratio is the percentage of sales value, which is contributed to the advertising expenses of the products.
- Distribution Expenses to Sales Ratio is the value of sales, which is utilized for paying off distribution expenses.
Financial Analysis
The management needs to handle its finances well. It should examine the reasons and factors which influence the rate of return and financial leverage and return on assets in the organization through financial analysis tools.
It also helps to enhance the financial leverage position of the company.
Customer Attitude Tracking
Consumer satisfaction has been considered as an essential parameter to analyze the organization’s performance. It is a qualitative analysis tool which can be of the following three types:
- Customer Surveys: The companies get the questionnaires filled or make calls to the past customers for finding out the level of consumer satisfaction. It provides a direction to the sales team and the management.
- Customer Panels: The organizations form consumer panels where the customers are hired to review the products, advertisements and other marketing activities. It helps the management to know about the consumer’s perception and attitude.
- Feedback and Suggestion Systems: Market performance of the products can be analyzed with the help of genuine feedback from the customers, and the same can be improved through their suggestions and input.
Profitability Control
Maximizing the profit margin has become a difficult task in today’s highly competitive market. This has enforced pressure on the marketing team of the organizations too.
They now need to frame strategies for profit assessment and control in the different product line, trade channels and territories.
Following is the process of profitability control in an organization:
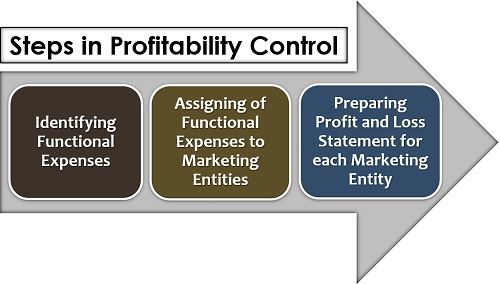
The first step is to understand the functional expenses, i.e., selling, distribution, administrative and advertising expenses incurred while carrying out the marketing function of a territory or marketing channel.
The second step is to segregate the non-marketing expenses from the marketing overheads and then to associate these pure marketing expenses to the marketing entities (like apportioning the building rent into marketing function).
Lastly, to compile everything systematically and to ascertain the profit or loss incurred on carrying out the particular marketing activity, an individual profit and loss account is prepared for each operation.
Efficiency Control
The management and the marketers are regularly involved in finding out ways to improve the task performance in the organization. These improvements bring in efficiency and perfection in marketing operations.
The three essential mechanisms used under efficiency control are as follows:
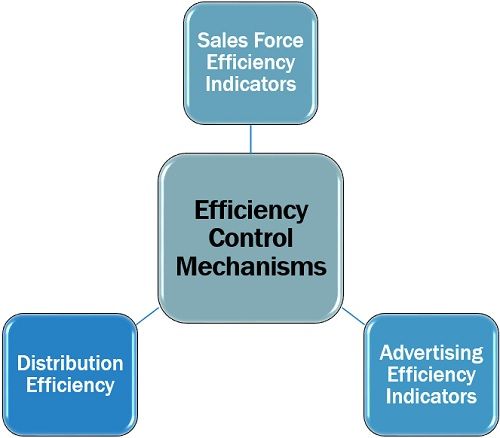
SalesForce Efficiency Indicators
The competence of the sales team can be determined by evaluating the various factors. It includes acquisition of new customers, customer turnover, average cost incurred on each sales call, return on time invested on the prospective customers, market share lost to the competitors, average sales made by each person per day, etc.
Advertising Efficiency Indicators
To know the effectiveness of the advertising activities, the marketers analyze the various advertising functions on different grounds. For this purpose, it finds out the brand awareness, cost incurred on each enquiry, media cost to reach per thousand customers, advertising campaign reach, etc.
Distribution Efficiency
The performance of the distribution channels in comparison to the cost incurred on channel partners and distribution of products can be analyzed through the distribution efficiency control.
It includes the measurement of the channel member’s market reach, cost incurred on operating a particular channel and the contribution of each channel member in selling the brand’s products.
Strategic Control
The external environment creates a significant impact on the organization’s marketing strategies. To understand and align the plans with the prevailing external environment, the organization can adopt any of the following control functions:

Customer Relationship Barometer
To determine the customer’s loyalty towards the brand and its products, the organization uses the relationship barometer.
Here, the company studies the customer’s perception based on the criteria like organization’s core values, system, policies, structure, customer orientation strategy, technology, personnel attitude, knowledge, skills and behaviour.
Marketing Audit
Like accounting audits, marketers carry out marketing audit to get a clear picture of the company’s performance while executing the various marketing operations.
It is a systematic record which periodically examines the problem areas and provides for the means of rectification, to overcome the weakness by utilizing the organizational strength and grab the current opportunities.
Marketing Control Process
Marketing control is a systematic and integrated process. A marketer follows the following steps while exercising control over the marketing operation in an organization:
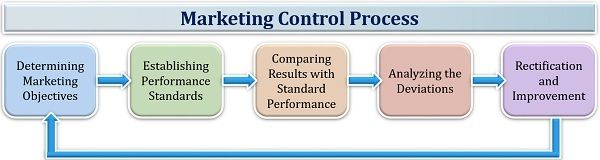
- Determining Marketing Objectives: The initial step in marketing control is the setting up of the marketing goals, which are in alignment with the organizational objectives.
- Establishing Performance Standards: To streamline the marketing process, benchmarking is essential. Therefore, performance standards are set for carrying out marketing operations.
- Comparing Results with Standard Performance: The actual marketing performance is compared and matched with the set standards and variation is measured.
- Analyzing the Deviations: This difference is then examined to find out the areas which require correction, and if the deviation exceeds the decided range, it should be informed to the top management.
- Rectification and Improvement: After studying the problem area responsible for low performance, necessary steps should be taken to fill in the gap between the actual and expected returns.
Thus, marketing can be seen as a complete function, which needs to be performed successfully through proper control over the related activities, to ascertain the achievement of the set goals and objectives.
Garang B says
I like the way this article is written, it is rich with required information
Stephen Nyamwange says
please give me a reference to this journal
Glory David Simbeye says
Thanks dearest for the good work
fine Berly says
very happy for this … very helpfull
Amarachi okuani says
the write up is very elaborate one