Definition: In Marginal Costing, we study the impact of variable cost at distinctive levels of production capacity for that we need to divide the total cost into fixed and variable cost because the fixed cost does not make any impact on marginal cost. However, fluctuations in variable cost in different production capacities are known as the marginal cost for the company.
Importance of marginal cost is to determine the profit of spending access money over variable cost; thus, it helps in decision making for the company.
Content: Marginal Costing
Marginal Costing Formula
Format of Income statement under Marginal Costing
| Particulars | Amount (₹) | Amount (₹) |
|---|---|---|
| A. Sales | XXX | |
| B. (-) Variable cost *Direct Material *Direct Labour *Direct Expenses *Other variable costs | xx xx xx xx ----- | |
| Variable Cost of Produced Goods | XXX | |
| (+) Opening Stock | xx | |
| (-) Closing Stock | (xx) ----- | |
| Variable Cost of Sold Goods | XXX | |
| (+) Variable Administrative Overheads | xx | |
| (+) Variable Selling and distribution overhead | xx ----- | |
| Variable Cost of Sales | XXX ------- |
|
| C. Contribution ( A-B) | XXX | |
| D. (-) Fixed Overheads *Fixed production overhead *Fixed administrative overheads *Fixed selling and distribution overheads | (xx) (xx) (xx) ----- | XXX ------ |
| E. Profit Under Marginal Costing (C-D) | XXX |
Examples of Marginal Costing
To understand the marginal costing, we need to learn what is marginal cost as costing is a method of ascertaining cost.
Let us take a few examples to understand it properly.
Example I
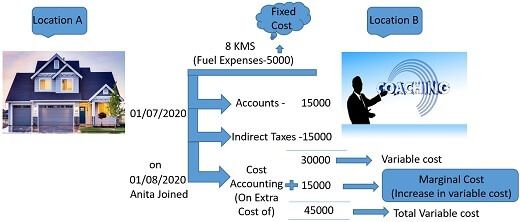
Anita is a Chartered Accountancy student and she uses to go to a coaching centre 8 km away from her home at the location (A) for taking coaching classes.
Batch for the classes started on 01/07/2020 and Anita is taking classes for accounts and indirect taxes, for which coaching centre charged rupees 15,000 per subject, i.e., total 30,000 rupees has been charged by the coaching institute for providing coaching of two subjects.
Both the subjects are taught in the same location, i.e., location (B).
But, after one month, i.e., on 01/08/2020 Anita also joined a class for one more subject, i.e., cost accounting in the same coaching centre @15000 rupees and total cost becomes 45,000 rupees for all three subjects.
It clarifies that the coaching fee is a variable cost as an increase or decrease of the subject will vary the cost.
Here, the marginal cost is the additional cost after adding another subject after one month, i.e., (45,000 – 30000 = 15000), here rupees 15,000 is a marginal cost for Anita.
It signifies that the change in variable cost by increasing or decreasing one unit is a marginal cost.
And overall fees taken by the institute is a variable cost for Anita; hence, it is noticed clearly that variable cost and marginal cost has a relation since marginal cost gets derived from the variable cost.
The other aspect of the transaction if fixed cost, let us take a look on it, Anita spends 5,000 rupees/month as a fuel expense.
Although the fixed cost will remain the same for all subjects as a coaching centre is same, and no extra cost will incur to reach the coaching centre for all the subjects.
However, marginal costing does not get affected by the fixed cost.
Therefore, to find out the marginal cost total cost should be divided amidst fixed and variable cost.
Example 2
Let us take another example from the business point of view.
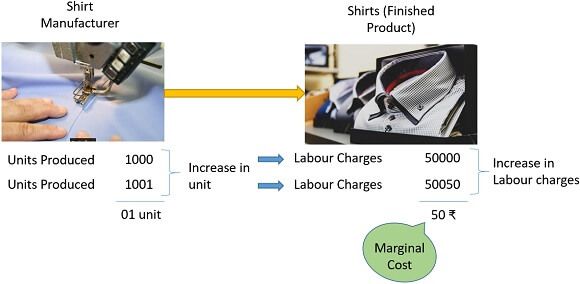
The manufacturer makes 1,000 shirts costing rupees 50,000 (Labour charges).
If he increases the units from 1,000 shirts to 1,001 shirts, the cost will also increase by 50 rupees (50,000/1000) as labour charge for 1 extra shirt produced will increase.
Here, the extra cost incurred on manufacturing one extra unit is a Marginal cost for the manufacturer, whereas overall labour cost (50,000+50,050) is a variable cost.
Thus, it is very clear that marginal cost will occur where there is a variable cost, and there is no relation between marginal cost and fixed cost.
Advantages of Marginal Costing
Marginal costing has an ability to manage the administrative tasks and decision-making process of the management.
It is advantageous for the management in various aspects such as:
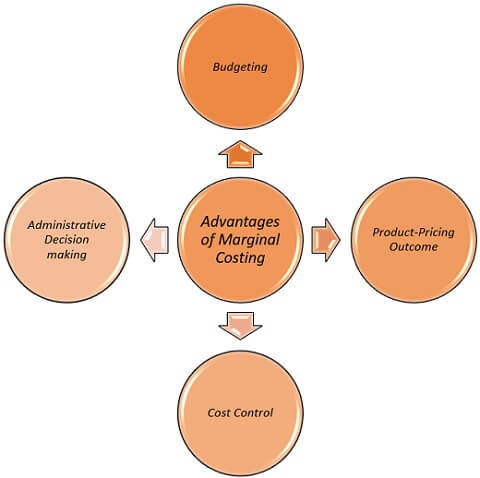
- Budgeting
Marginal costing plays a vital role in making the companies budget for attaining future goals or targets.
It helps in gathering cost data for profit planning from the accounting statements.
It analyses the cost-volume relation by segregating fixed and variable costs and appraises the profits emerged because of increase/ decrease in the volume.
- Product-Pricing Outcome
In numerous cases marginal costing serves as the basis for making product-planning decisions for the short-run.
It is more beneficial than absorption costing for the management, and other than normal circumstances, when it is desirable to take orders, is determined by the data gathered from the marginal income statement.
However, product pricing is a long-run decision and hence cannot be based on only fixed or only variable cost; thus, it is to be made on the basis of the total cost incurred in the production.
- Cost Control
The relation amidst period cost and net income can be analysed with the marginal costing. To control the cost of the company variable and period costs are separated, which helps the management to learn the use of standards and preparing budget.
Based on the division of cost into a fixed and variable cost, marginal costing provides aid in preparing reports for all the departments of the company.
- Administrative Decision making
For acquiring and analysing the cost, a framework is provided by the marginal costing explaining whether the cost is variable or fixed, which becomes the basis for the proposed changes in the production levels regarding contraction.
The accumulated figure of the marginal income statement is a valuable figure for the administration for calculating net income increments followed by sales increments.
Disadvantages of Marginal Costing
The following are the disadvantages :
- Excluding fixed cost from the inventory may affect the profit as inventory and work-in-progress are undervalued beneath marginal costing because of which there are chances that statement may not show the fair view of the inventory.
- In the case of high-level variations in production, the data of the marginal cost statement becomes impractical, and marginal costing cannot explain the reason behind such changes in sales or production.
- The complete cost of a product cannot be ascertained by marginal costing as it shows only the variable cost of the product. For taking long-run policy decisions fixed and variable, both costs should be known.
Conclusion
Marginal Costing is a method of finding the product’s cost after reducing the fixed cost from the total cost, i.e., it is a technique used by the management for making decisions for the company showing the changes in the behaviour of cost with the change in unit.
Leave a Reply