Definition: The term service costing or operating costing refers to the computation of the total operational cost incurred on each unit of the intangible product. These intangible products or services can be either in the form of internal services that are carried out by industries as supporting activities for the manufacturing of goods. Or in the way of external services that are offered as a significant product to the customers by the service sector companies.
Service costing is an essential concept since every service organization needs to ascertain its business overheads. It is to ensure fair pricing of the products, i.e., services; and for keeping a control over its fixed and variable costs.
Content: Service Costing
Features of Service Costing
The costing in a service industry can be better understood with the help of the following characteristics:

Intangible Products: Service costing deals with the operating cost of products which does not have any physical form but satisfies consumer needs and wants.
Collection of Cost Data: The documents used for service costing of products include cost sheet, bills payables, daily log sheet, etc.
Unique and Standard Service: The services so offered by such organizations are specialized and exclusive.
Less Working Capital: The service costing involves less working capital since the direct cost of raw material and other direct expenses is comparatively low.
Cost Per Unit: The cost per unit is mainly calculated in service costing. Here, the cost unit is determined by the type of service industry the business belongs to, and it usually differs from company to company. Like, in the case of goods transport it is ‘tonne-miles’; whereas, in boilers, it is ‘per cubic centimetre-litre’.
Internal or External Service: The service costing can be performed internally, to determine the operating cost of the supporting activities in manufacturing industries. Else, it can be carried out externally, by the companies dedicated to rendering such services.
Cost Classification by Behaviour: In the operating cost sheet format, all the business costs are classified according to their behaviour, i.e., fixed costs, semi-variable costs and variable costs.
Periodic or Order Wise Computation: The service costing records the overheads at regular intervals, i.e., monthly or yearly but for operating cost of vehicles like tractors and JCB machines, order wise computation is adopted.
Cost Unit in Service Costing
To measure the cost of business operations in a service industry is a complex activity where all the cost parameters are to be considered while deciding a suitable unit for costing.
Following are the two different kinds of cost unit ascertained under service costing:
Simple Cost Unit
The cost unit, which uses only one single parameter for measurement of the service cost, is termed as a simple cost unit.
The different types of service organizations and their simple cost units are mentioned below:
| Nature of Service Organization | Cost Unit |
|---|---|
| Water Supply | Per Kiloliter |
| Canteen | Per Meal / Per Person / Per Staff |
| Road Maintenance | Per Kilometer |
| Street Lighting | Per Lamp / Per Point |
| Boiler House | Per 1000 Ibs |
| Gas | Per Cubic Meter / Per Kilogram |
| Private Transport | Per Kilometer / Per Hour / Per Trip / Per Passenger |
Composite Cost Unit
The most commonly used cost unit in service costing is the composite cost unit. Here, the measurement of two parameters is combined to form a single cost unit.
Following are the different types of service organizations and their composite cost units:
| Nature of Service Organization | Cost Unit |
|---|---|
| Hospital | Per Bed-Day / Per Patient-Day |
| Hotel | Per Room-Day / Per Room-Night / Per Bed-Day |
| Electricity | Per Kilowatt-Hour |
| Entertainment in Cinema or Theater | Per Ticket-Show |
| Boiler House | Per Cubic Centimeter-Liter |
| Passenger Transport | Per Passenger-Kilometer / Per Passenger-Mile |
| Goods Transport | Per Tonne-Mile / Per Quintal-Kilometer |
Calculation of Cost Per Unit: The formula for computing the cost of each service unit (i.e., cost per unit) is given below:
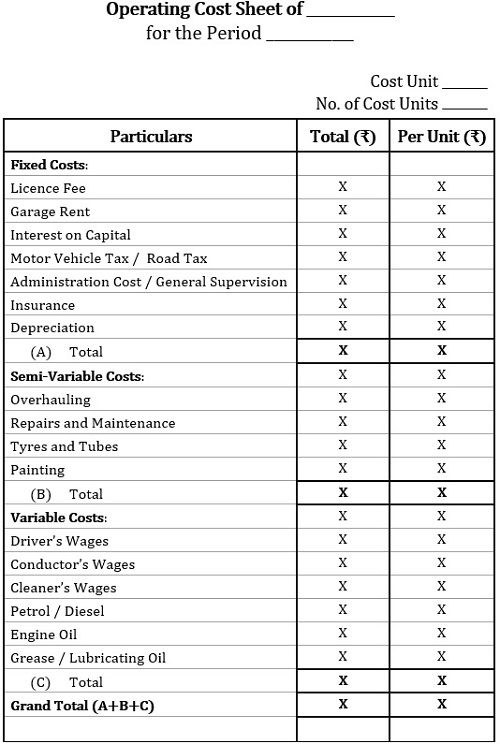
Format of Service Costing
Further, we will be discussing on transport costing as an illustration of service costing. Therefore, we are going to view the computation of transport costing in this section.
Transport is one of the significant service industry these days, and it is essential to have an insight of the proforma for determining the operating costing of such organizations:
Types of Service Costing
When we talk about services, our mind recalls the multiple intangible products we use on a day to day basis. But do you know that all these services have different cost units and elements during computation?
This is because each of these services is unique and involves a variety of different type of overheads. Thus, the service costing for each kind of service organization varies and can be classified as follows:

Transport Costing
The costing in the transport industry meets multiple objectives. These objectives can be segregated as follows by the type of transport service an organization provides:
- Private Transport: When the vehicle is hired individually for private tours, service costing is used to determine the hiring charges to be applied.
- Passenger Transport: It also ascertains the cost of conveyance, per passenger up to to a certain distance in case of public or passenger transport companies.
- Goods Transport: When we talk about goods transport services, the cost of carrying a defined quantity of goods up to a particular distance is also decided through service costing.
The common objectives of transport costing include a comparison between two different vehicles or group of vehicles and; whether to use an alternative source of transport or own vehicle, in terms of cost involved.
To get a practical overview of transport costing, please go through the example given in this article which is in the context of goods transport services.
Power Generation and Distribution Costing
The powerhouses produce energy in the form of electricity through water, gas or sunlight. The cost of power generation services majorly includes fixed costs, i.e., interest on capital, depreciation, repairs and maintenance, administration expenses; and variable costs such as steam consumed, labour wages, lubricants, coal, etc.
Boiler House Costing
The boiler house provides supporting services to power and electricity generation units, in the form of steam which is used in the air conditioning, power generation and air compression.
The overheads involved in the total cost of boiler services include fuel (coal, oil), direct and indirect labour, water and its processing, indirect material (tools, service material), maintenance and fixed costs (rent, taxes, depreciation, administration expenses, etc.)
Canteen Costing
The government organizations, factories, companies, offices, colleges, schools and even hospitals have canteens to provide affordable foodstuff like meals, refreshment, snacks, etc. to the staff, students and patients.
The canteen manager or supervisor keeps control over the costs and performs service costing to ascertain revenue of these business organizations.
The costs involved in canteen services include the cost of material, labour, services, consumable stores and miscellaneous overheads.
Hospital Costing
The services provided by the medical organizations like hospitals health centres, nursing homes, medical camps and clinics require cost analysis, which is possible through service costing.
The hospital cost includes fixed charges such as labour salaries, maintenance charges, rent, administration expenses and other overheads. Also, the variable charges like medicines, bed charges, doctors fees, etc. are involved in the total cost.
Hotel Costing
The hotels provide accommodation to the guests as services; thus, it involves a high maintenance cost along with the fixed cost. The fixed cost includes depreciation, staff salaries, interest on capital, taxes, etc. Whereas, variable cost involves electricity charges, temporary staff salary, etc.
Example
XYZ Transport Co. provides the following data for the month ending on January 31, 2019:
| Particulars | Vehicle |
|---|---|
| No. of Vehicles | 5 |
| Cost of Each Vehicle | ₹200000 |
| Garage Rent (Monthly) | ₹5000 |
| Depreciation | 12% p.a. |
| Insurance (Yearly) | ₹28800 |
| Licence Fee | ₹3000 |
| Overhauling (Monthly) | ₹7500 |
| Diesel | ₹50 per trip each way |
| General Supervision | ₹7200 p.a. |
| Drivers' Wages (Monthly) | ₹10000 |
| Engine Oil (Monthly) | ₹1500 |
Note that:
We have assumed that the licence fee was calculated every month. Also, each vehicle has the capacity of 2-tonne of goods.
If,
- each vehicle covers a distance of 100 miles each way daily to and from the city;
- each vehicle runs on an average of 20 days a month; and
- while going to the city, the capacity was full and while returning the capacity is 25% occupied;
find out the following:
- Operating cost per tonne-mile; and
- Rate per trip to be charged, if the company plans to make 40% profit on freightage.
Computation:
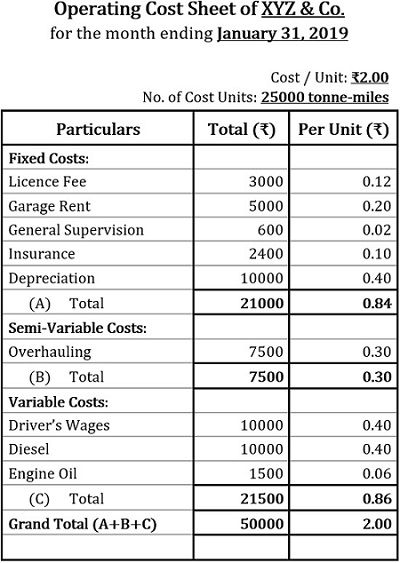
No. of Cost Units:
On the first way of the trip: 100% capacity was occupied, i.e., 2-tonnes
No. of Cost Units=Distance×Capacity Occupied×Working Days×No. of Vehicles
No. of Cost Units=100×2×20×5=20000 tonne-miles
On the second way of the trip: 25% capacity was occupied, i.e., 0.5-tonnes; Similarly,
No. of Cost Units=100×0.5×20×5=5000 tonne-miles
Hence,
Total No. of Cost Units=20000+5000=25000 tonne-miles
General Supervision:
It is given annually, therefore;
Monthly expense on general supervision=7200/12=₹600
Insurance:
It is given annually, therefore;
Monthly expense on insurance=28800/12=₹2400
Depreciation:
It is given annually, therefore;
Monthly depreciation=(Total Cost of 5 Vehicles×Rate of Depreciation)/(100×12)
Monthly depreciation=(1000000×12)/(100×12)=₹10000
Diesel:
Monthly expense on diesel=Cost per Trip×No. of Ways per Trip×No. of Working Days×No. of Vehicles
Monthly expense on diesel=50×2×20×5=₹10000
Service costing has given a new dimension to the intangible products in the accounting world. This is also important in the sense that the service industry has rapidly evolved in recent years, introducing a variety of service products for consumers.
Leave a Reply