Definition: Differential costing is a technique that examines changes in the total cost and revenue by analyzing proposed alternatives. These changes comprise an increase/decrease in the cost of crucial elements affecting decision-making.
Financial managers conduct a comparative analysis to ascertain the difference in the cost due to the change in operations. It involves estimating cost differences either by replacing the existing operation or introducing new procedures.
The changes in cost can take place due to several reasons. These reasons may include substantial changes in:
- Price
- Technology
- Product Mix
- Sales Volume
- Method of Production
- Sales Promotion, etc
Among several alternatives, management opts for the most profitable one.
The primary purpose of conducting a differential analysis is decision-making. So, we consider only relevant costs affecting the decision variables. It may include both fixed as well as variable costs.
Content: Differential Costing
- Differential Cost
- Characteristics
- Uses/Applications
- Process
- Format
- Difference between Marginal and Differential Costing
- Similarities
- Solved Example
- Conclusion
What is the Differential Cost?
Differential cost is the variation in costs (increase/decrease) between two available opportunities. It is calculated based on the relevant costs in the alternatives.
The costs that do not change in the alternatives are not part of the analysis. Such costs are known as Irrelevant Costs.
An increase in the differential cost is known as Incremental Cost. However, the Decremental Cost is a decrease in the differential cost.
There are two distinctive characteristics of the differential costs as follows:-
- Future Costs: Management calculates the differential cost for the future. The decisions taken based on these costs will affect the firm’s profitability in the long run.
- Variance among Substitutes: It considers the costs that change with adopting a substitute. Management excludes all those costs, which are irrelevant.
Differential Cost Formula
Characteristics of Differential Costing
Following are the characteristics or features of Differential Costing:
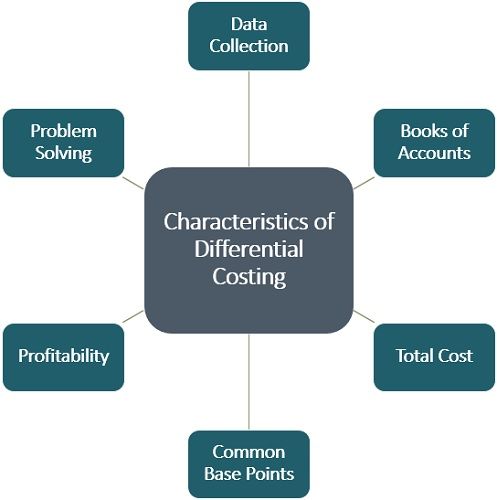
- Data Collection
The data collected for calculating differential costs are for the future. However, one can consider historical & standard costs impacting decision-making. - Books of Accounts
The differential cost statement is not a part of the financial statements. It is prepared separately for estimating the most cost-effective substitute available. - Total Cost
Here, we estimate the difference in total cost, not the cost per unit. Besides, it ignores the effect of the residual costs. - Common Base Points
The standard base points between the alternatives are analyzed. The financial managers consider these points during differential analysis. - Profitability
The essence of differential costing is selecting the most profitable substitute for operation. Thus, the management opts for the replacement carrying less cost. - Problem Solving
The organizations face problems while analyzing alternative courses available. Differential costing technique helps managers in the decision-making for the same.
Uses/Applications of Differential Costing
Differential costing is a decision-making technique in management accounting, as stated above. It is helpful for organizations in the following decision areas:
- Production Decision
The differential cost is compared with incremental revenues. The comparison is done at various output levels to assess profitability.
One must increase output until the differential cost is less than incremental revenue. It becomes less profitable when incremental revenue becomes less/equal to differential cost. - Order Management
This technique helps units in their order management. In other words, differential costing enables decision-making regarding order acceptance or rejection.
It involves decisions like accepting or rejecting orders below the current selling price. - Make or Buy Decision
One of the vital decisions for a manufacturing unit is the Make or Buy decision. They have to decide whether to acquire resources from internal or external sources.
By performing differential analysis, we can evaluate profitability from both sources. - Plant Capacity Decisions
Differential costing facilitates decision-making regarding plant capacity. These decisions include adding a new product line or increasing the productivity level. - Further Process Decision
This technique helps solve problems about sales of semi-finished products. - Pricing Decisions
Pricing is a crucial decision taken by every undertaking. Differential costing helps make these decisions by evaluating cost and revenue. - Operations vs Shut-down Decisions
There are times when companies become non-profitable due to several reasons. They can perform differential costing to ascertain the unit’s continuity/shutdown. - Change in product mix
Companies keep on changing their product mix as per user requirements. They can calculate the differential cost and find the most profitable product mix.
Process of Differential Cost Analysis
One can follow the steps mentioned below to perform differential cost analysis:
- Calculate differential cost by comparing the total cost of available alternatives.
- Computation of difference in revenue in the manner stated above.
- Find out the net gain/loss resulting from the differential cost and revenue variance.
Format of Differential Costing
A Statement of Differential Cost and Revenue is prepared to perform differential costing.
Difference between Marginal and Differential Costing
Both Differential and Marginal Costing are the techniques of decision-making. They possess some similarities but differ from each other in the following ways:
| Basis | Marginal Costing | Differential Costing |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | The marginal costing is the total of all variable costs. It is the additional cost due to the production of an extra unit | It is a technique to assess an increase or decrease in the total cost. And decision-making for selection of the alternative course of action |
| Fixed Cost | Excludes fixed cost | Includes relevant fixed cost |
| Scope | It has a narrow scope | It has a broader scope |
| Contribution | It follows the contribution approach for cost calculation | Cost calculation is not based on the contribution approach. |
| Accounting System | It is an integral part of the accounting statements | It is an ad-hoc statement |
| Purpose | General purpose statements | Special purpose statements |
| Criteria of Decision-making | Evaluation of contribution and its ratios | Analysis of increase/decrease in cost and revenue |
| Additional Units | It incorporates any number of additional units | It comprises only fixed additional units |
Similarities between Marginal and Differential Costing
Both the cost analysis techniques are similar in following ways:
- Similar Results: The results generated by both marginal and differential costing techniques are uniform.
- Cost Analysis Techniques: Both techniques are targeted towards conducting cost analysis for the units.
- Valuable Information: The information collected, processed and analyzed in both techniques are valuable for the units.
- Decision-Making: Both analyses are helpful in taking crucial decisions regarding the business.
Solved Example of Differential Costing
Soniya Ltd. is a manufacturer of Mugs and Buckets. They receive a special order for producing Mugs of 1000 units at a rate of ₹ 5/- per unit.
The company sell similar Mugs at ₹ 10/- each to existing customers. Soniya Ltd. can produce extra units with the current capacity.
The income statement for the preceding month is as follows:
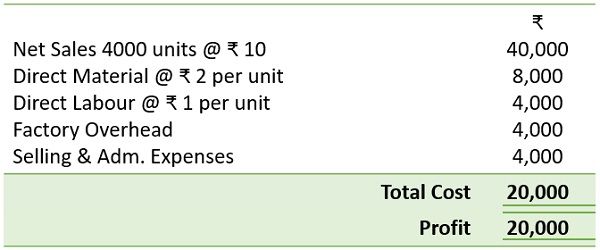
Direct material and labour will be constant for the special order. But, there is a need for special tools costing ₹ 600/- to meet additional orders’ production.
Prepare differential cost analysis to ascertain acceptance or rejection of the order.
Solution:
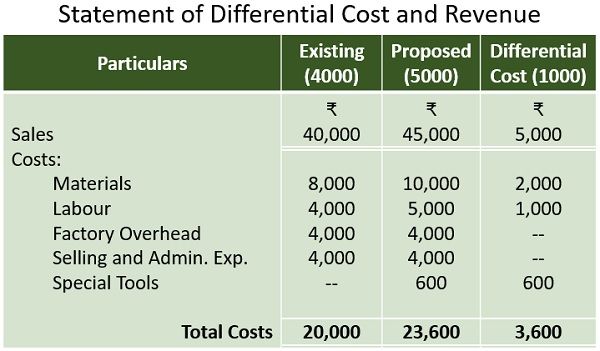
Differential Revenue Rs.5000/-
Less: Differential Cost Rs.3600/-
Thus, the Net Gain is Rs.1400/-
Decision: The company will earn a net gain of Rs.1400/- by accepting the special order. Hence, it is advisable to accept this order.
Final Words
All in all, managers often get into situations, where they have to choose from alternatives. Differential Costing is helpful in a comparative evaluation of the substitutes available.
It is a technique of decision-making based on the differences in total costs. One has to find net gain/loss by differential cost and revenue. However, the decision to accept or reject the alternative depends on the net gain/loss.

Leave a Reply