Definition: Business cycle also termed as trade cycle displays the ebbs and flows of the economic activities occurring regularly, i.e., it shows the fluctuation movements or rhythmical changes in the level of aggregate economic activity.
In other words, business cycle is the fluctuation cycle of economic activities that are more or less regular in time sequence. The level of economic activity goes through periodic volatility from time to time. These frequent fluctuations manifest themselves in changing employment investment, national income, etc.
Content: Business Cycle
Phases in Business Cycle
Phases in the business cycle start from a depression enduring a phase of recovery and expansion followed by a phase of prosperity, and once it reaches to peak, the recession phase starts immediately after that, and then the depression phase arises, and after that, the business cycle starts again with ups and downs. Following are the phases of the business cycle:
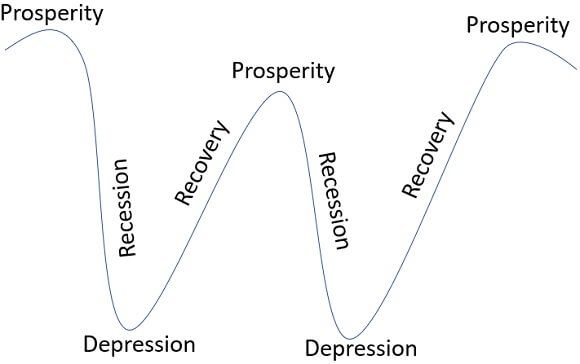
1. Prosperity Phase
With the rise in economic activity, the economy remains in a phase of expansion in these stages; it remains in the expansion phase till the maximum level of production reaches its peak, i.e., the highest level of the business cycle reaches.
2. Recession Phase
The phase of a recession gets started once the peak is reached, and the slowdown of economic activity gets started in this stage and the economic expansion comes to a standstill. Generally, the recession continues for a short period of time.
3. Depression Phase
A declining phase of economic activity, i.e., decrease in economic activity is known as a depression phase in which resources in the economy are underutilized, and this decline continuously till the economy reaches the trench and this period becomes the shutdown and unemployment period.
4. Recovery Phase
This stage is the final phase of the business cycle in which the economy starts moving from depression to expansion and economic activities starts rising and gradually economy starts recovering and starts moving towards the prosperity phase.
Causes of Business Cycle
A major cause of the business cycle is a price mechanism, i.e., Demand and Supply, which gets affected by two factors one is Internal factors, and another is external factors which are described below precisely:
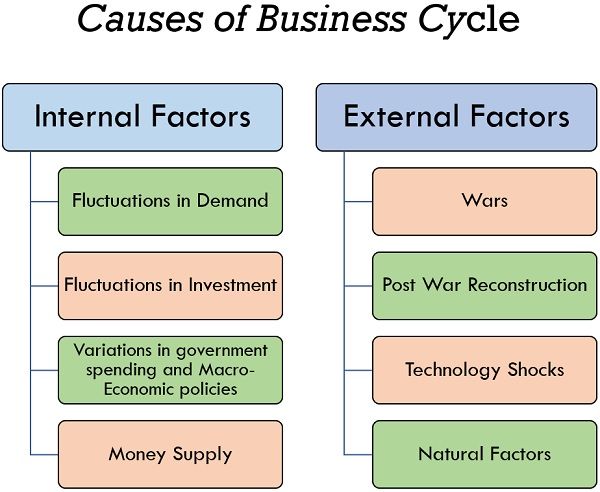
1. Internal Factors
Internal factors are those factors that create an individual impact on every organization; such factors are as follows:
- Fluctuations in Demand
If there will be an increase or decrease in demand, it will make an impact or fluctuations in the business cycle. This is because when demand increases, we move towards the expansion phase, when demand becomes stagnant, the organization reaches its peak phase. When demand decreases contraction phase gets started, and when demand gets nil and production get closed and a negative growth rate arises, then the organization comes under the phase of depression. The reasons behind all phases start because of demand, if demand rises, output also raises, and investment also increases labour or employment also increases. Thus, when demand increases expansion took place, but when demand or supply becomes excessive because of which contraction phase arises and after that organization’s business cycle starts falling due to mismatch of demand and supply.
- Fluctuations in Investment
Fluctuation in investment is a prime cause of the business cycle which gets fluctuated because of changes in the expectations of a profit of entrepreneurs. When the rate of interest is low in the economy, the investment may rise as well as new inventions encourage investors to invest in new projects which are more profit inducing. Leading to an economic expansion aggregate demand shifts to the right when investment increases, whereas a decrease in investment may shift the curve to the left.
- Variations in government spending and Macro-Economic policies
Tax cuts or increased government spending, i.e., Expansionary policies boost the aggregate demand with the help of political motives reducing inflationary effects. Similarly, softening interest rates, declining unemployment rates creates a boom in an economy. Whereas an increase in tax rates, reduction in government spending will create a downward pressure because of which aggregate demand will increase, and the economy becomes slow showing negative growth rates, and ultimately ends up in a recession.
- Money Supply
Unplanned changes in money supply can cause fluctuations in the economy as the business cycle is entirely a monetary aspect. Economic activities and aggregate demand get expanded with an increase in money supply, although an excessive rise in credit and money also get off inflation in the economy. Businesses and consumers can easily borrow capital at low rates from the market, which vitalizes more demand.
2. External Factors
Country-wise widely decisions taken on macro levels or scenario such as war because of which we have to come to recovery due to all these factors we call it external factors which are described below precisely:
- Wars
At the time of war production of weapons and arms increased and most of the resources are utilized for their production which reduces the production of consumer goods which causes a fall in income and profits and creates a contraction in economic activity and create a downturn in the business cycle.
- Post War Reconstruction
To cope-up, the country from the war destructions houses, roads, bridges are built by the government which helps economic activity is picking up, and it will push up effective demand that will increase the income, output and employment.
- Technology Shocks
Huge investments were made for new technology enactment as developing technology facilitates new and better goods production. For instance, Because of mobile phones arrival telecom industry experiences a boom, and there was an expansion of production and profits.
- Natural Factors
Instability arises in agricultural outputs because of fluctuations in weather cycles which causes instability in the agrarian economies. Sometimes because of floods and droughts, the agricultural output gets badly affected, and farmer’s income reduces due to which their demand for industrial goods also reduces. Along with this reduction in the production of food products also raises their prices and therefore, income available for purchasing industrial goods also reduces, which may cause an industrial recession.
Conclusion
Business Cycle is a regular variation in economic activities levels around the potentiality of the organization. They are mainly divided into two phases, i.e., recession and expansion.
Leave a Reply