Definition: Integrated Accounts are statements in which financial and cost accounting transactions are maintained jointly. In other words, when the cost and financial accounts are merged and recorded in the same set of books, it is referred to as Integrated Accounts.
It accommodates complete information about both areas. However, the transactions are recorded based on the double-entry system.
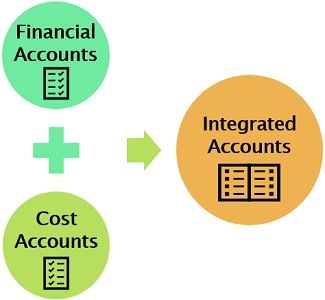
It reduces duplication, increases accuracy and facilitates control over the assets & liabilities.
When it comes to suitability, integrated accounting works best for mechanized accounting as well as similar data processing methods. It majorly focuses on the concept of centralized accounting.
This approach ascertains a variety of factors like:
- Cost of product
- Job cost
- Process cost
- Operations cost
- Marginal cost
- Variance
- Abnormal loss and gains, etc
Cost accounting records transactions functionally, whereas transactions are recorded based on their nature in financial accounts. Integrated accounts inculcate both the above qualities while preparing books.
Content: Integrated Accounts
- Advantages and Disadvantages
- Features
- Journal Entries
- Third Entry Method
- Difference between Integrated and Non-Integrated Accounting Systems
- Example
- Final Words
Advantages and Disadvantages of Integrated Accounts
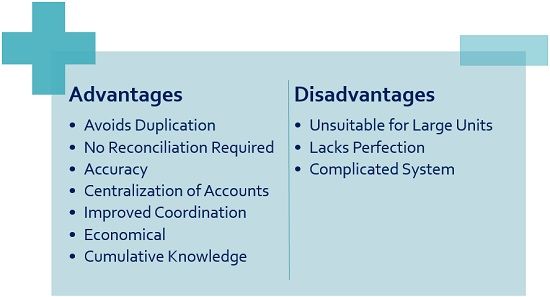
Following are the advantages of the Integrated accounts:
- Avoids duplication of work
As it combines statements, a single entry for one transaction is passed. Thus, there is no requirement to record transactions at multiple places. Consequently, it helps in avoiding duplication of work. - No reconciliation required
There is no need for Reconciliation as we get only one profit and loss figure in the set of accounts. - Accuracy
The data and information recorded are more accurate. This is because it considers two essential aspects of accounting. - Centralization of Accounts
The centralization of accounts occurs as accounts of two departments are prepared by one. - Improved coordination
It facilitates coordination among the cost and finance departments. - Economical
Instead of multiple ledgers, we need to maintain only one set of books, saving time and money. - Cumulative Knowledge
A combination of cost and financial knowledge results in better output.
Following are the disadvantages of Integrated accounts:
- Unsuitable for large units
The integrated accounting method is not suitable for large units. The reason behind it is that we require cost & financial data continuously. - Lacks perfection
The data and information are vast, so perfect integration is impossible. - Complicated system
Integrating requires expertise while merging the two broad accounting areas. Hence, it’s a complex task for accountants.
Features of Integrated Accounting System
Distinctive features of integrated accounts are as follows:
- Management
Management plays an essential role in this system. The management has to decide the required degree of integration. - Accounts Head
We can classify the accounts heads in subsidiary ledgers like:- Sales Ledger
- Purchase Ledger
- Store Ledger
- Stock Ledger
- Overhead ledger, etc
- Training
The responsible person should be provided with proper training to perform this accounting system. - Coding
Proper codes should be allotted to the accounts to provide relevant information timely. - Control Accounts
The control accounts are prepared for each subsidiary account. These control accounts follow the concept of a double-entry system. Some control accounts are listed below:- Store Ledger Control Account
- Stock Ledger Control Account
- Job Ledger Control Account
- Overhead Ledger Account
- Debtor Account
- Creditor Account, etc
- Accounts Manual
The managers prepare accounts manual under an integrated accounting system. It provides necessary information regarding accounting format, method of calculation, etc.
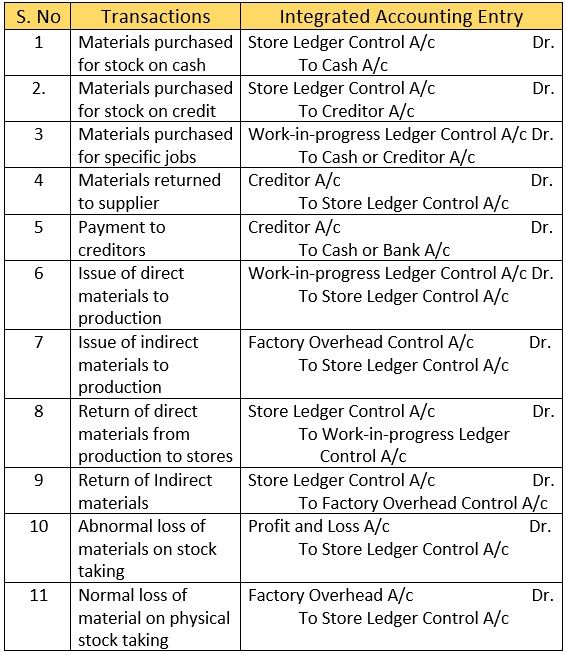
Journal Entries of Integrated Accounts
The cost ledger control account is not prepared in an integrated accounting system. As we maintain the cost & financial records in a single book. Here, we debit and credit the accounts head like Cash, Bank, Debtor and Creditors.
The table given below depicts journal entries for various transactions under integrated accounting.
Materials
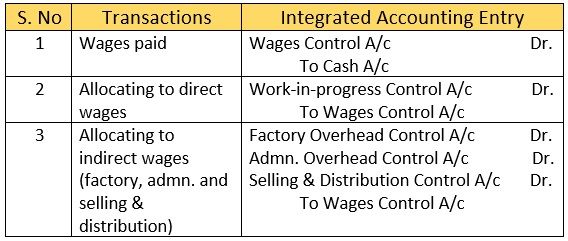
 Labour
Labour
 Direct Expenses
Direct Expenses
 Overheads
Overheads
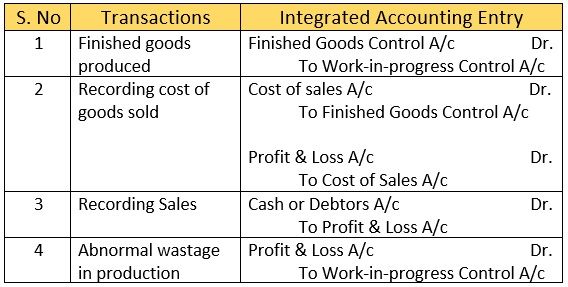
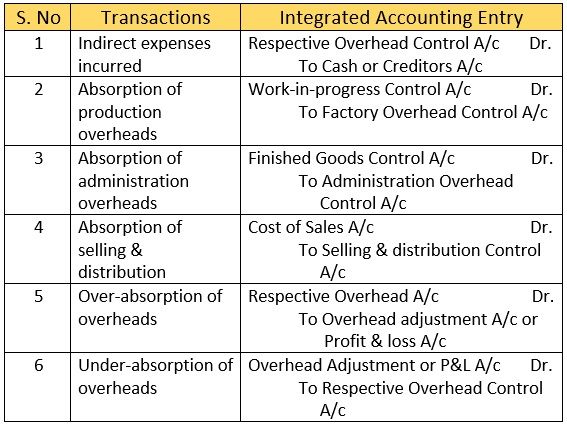 Other Transactions
Other Transactions
Third Entry Method
The third entry method is another alternative to the integrated accounting system. It follows the approach of the double-entry system but differs from it in respect of cost.
Here, we record all the cost items under an additional account called the ‘Cost Ledger Control Account’.
Important points regarding the Third Entry Method are as follows:
- Open an additional account called a cost ledger control account.
- When any expense is incurred, this account is debited along with that expense account.
- There is no requirement to pass double entry for the cost ledger control account.
- The third entry analysis sheet called the cost ledger is prepared to show the cost of production of various jobs.
- This cost ledger control account is credited and closed when the expenses are transferred to the profit and loss account, work-in-progress account, etc.
For example, the journal entry under the third entry method for raw material purchased of Rs.10,000/- will be recorded as shown below:

Difference between Integrated and Non-Integrated Accounting Systems
| Basis | Integrated Accounts | Non-Integrated Accounts |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | It is a combination of financial and cost accounts | It is a system in which financial and cost accounts are prepared separately |
| Reconciliation | Reconciliation is not required | Reconciliation is required |
| Number of books | One set of books is prepared | Separate books for cost and financial accounts are prepared |
| Duplication | Duplication of work doesn't take place | Duplication of work occurs, as one transaction is recorded in two books and reconciled at the end |
| Economical | It is economical as it saves time and money while maintaining books of accounts | It is less economical as compared to Integrated Accounts |
| Profit and Loss Figure | Only one profit and loss figure is shown because of a single set of books | Profit and loss are displayed in both books |
| Ledger | Subsidiary ledgers are prepared | Cost ledgers are prepared |
| Interdependence | Cost and Financial accounts are dependent on each other | It is an independent system of accounting |
Example of Integrated Accounts
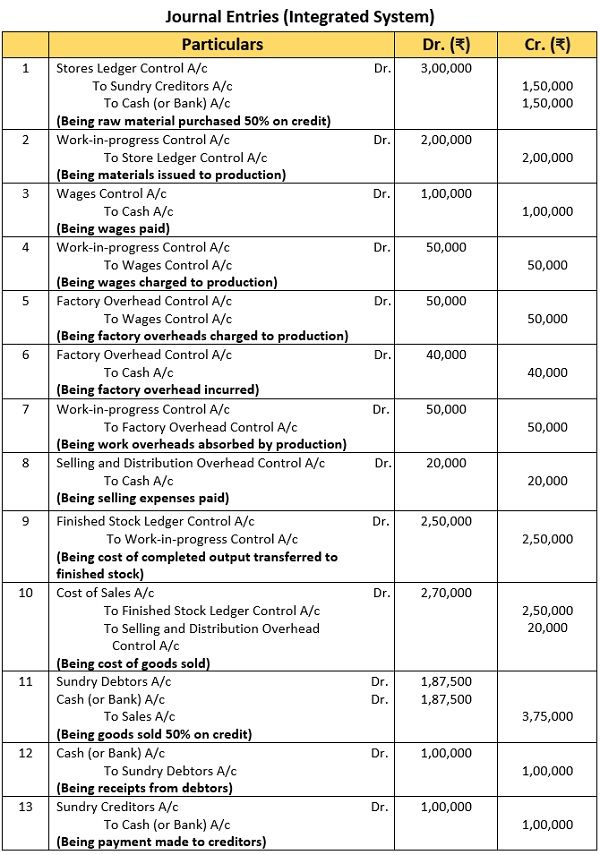
Alex Enterprises operates an integrated system of accounting. Pass required journal entries for the transactions listed below:
- Raw material purchased (50% on Credit) Rs. 3,00,000/-
- Materials issued to production Rs.2,00,000/-
- Wages paid (50% Direct) Rs.1,00,000/-
- Wages charged to production Rs.50,000/-
- Factory overheads incurred Rs.40,000/-
- Factory overheads charged to production Rs.50,000/-
- Selling and distribution overheads incurred Rs.20,000/-
- Finished goods at cost Rs.2,50,000/-
- Sales (50% credit) Rs.3,75,000/-
- Closing stock nil
- Receipts from debtors Rs.1,00,000/-
- Payments to creditors Rs.1,00,000/-
Final Words
An integrated accounting system is the maintenance of cost and financial accounts into one. Besides, it retrieves data and information from both departments. And prepares a summary of all the costs and financial transactions.
Through an integrated accounting system, one can reduce duplication of work. In addition, it saves costs as the preparation of accounts takes place in a consolidated form.
Python samuel says
Interested page 🤞✌️🥰
Extratech says
It is really interesting. Thank you for providing such well-written content on your website, kudos.