Definition: A ledger is the second step of preparing the financial books of accounts just after posting the journal entries. It is prepared for posting and balancing monetary transactions in a summarized form that arises in the business during the financial year.
Separate ledger accounts are prepared to identify the dues and payments of the parties individually at the end of the year which is impossible to trace only with the journal entries, as thousands of transaction took place during the year with different parties.
Content: Ledger
- Format
- Some Relevant heads of Ledger Accounts
- Example
- Classification
- Types
- Importance
- Ledger in Accounting
- Ledger Balancing
- Difference between Journal and Ledger
- Points to Remember
- Conclusion
Format of Ledger
Ledger can be prepared in any of the following two formats-
Format 1-
—–(Name of account) —– —-Ledger Folio no.—-
Dr. Cr.
| Date | Particulars | Folio | Amount (₹) | Date | Particulars | Folio | Amount ( ₹) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DD/MM/YY | XXX | X | XX | DD/MM/YY | XXX | X | XX |
Format 2-
—–(Name of account) —– —-Ledger Folio no.—-
| Date | Particulars | Folio | Debit amount(₹) | Credit amount(₹) | Balance (₹) | Dr./Cr. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DD/MM/YY | XXX | X | XX | XX | XX | XX |
Some Relevant heads of Ledger Accounts
1. Assets: some heads of ledgers under asset are as follows-
- Cash-in-hand Account
- Building Account
- Machinery Account
- Furniture Account
- Receivable Account
- Debtors Account
- Goodwill Account
2. Liabilities: some heads of ledgers under liabilities are as follows-
- Bank Overdraft Account
- Creditors Account
- Bills Payable Account
- Loans and Advances Account
- Taxes Payable Account
3. Operating expenses: some heads of ledgers under operating expense are as follows-
- Wages and Salaries Account
- Depreciation Account
- Electricity Account
- Stationery Account
Example
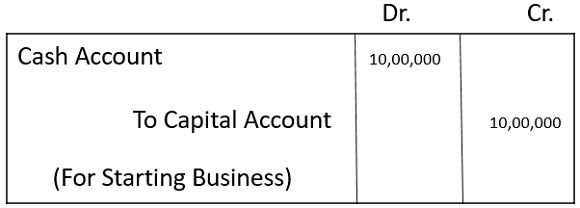
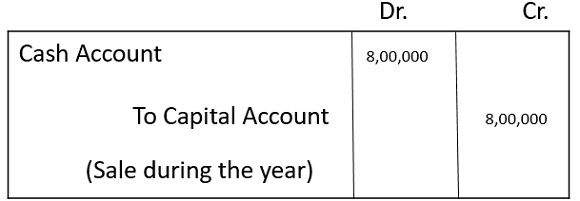
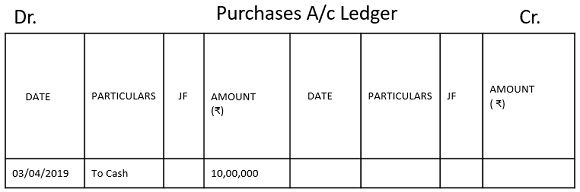
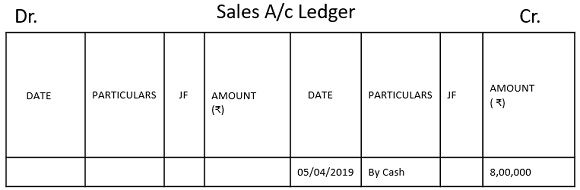
Every single transaction of journal entry gets recorded in two separate ledger accounts. Let us understand it with an example of starting a business on 1st April 2019 with 10,00,000 rupees, purchases of 4,00,000 rupees are made on 03 April 2019 is rupees and sales of 8,00,000 rupees made on 05/04/2019. Pass Journal Entries and make Ledger Accounts.
Solution:
Journal Entries
1. For starting a business :
2. For Purchases made :

3. For Sales made :
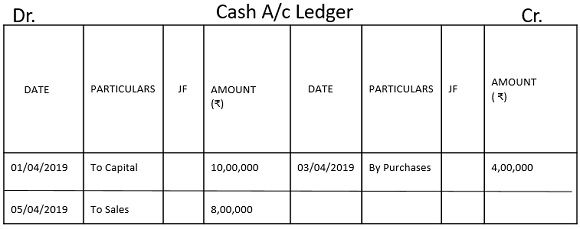
Various Ledger Accounts prepared from the above journal entries.
1. Cash Account Ledger
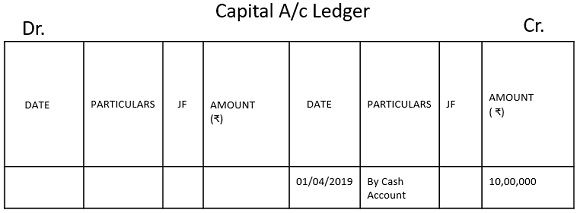
2. Capital Account Ledger
3. Purchases Account Ledger
4. Sales Account Ledger
Classification of Ledgers
The ledgers can also be classified in the following two categories-
- Permanent Ledger: These are the ledgers having opening and closing balances which get forwarded to the next year.
- Temporary Ledger: They don’t have any opening and closing balance, and the account gets closed by transferring the amount to the profit and loss account at the end of the year.
Types of Ledger
Following are the types of the ledger:
1. Bought Ledger/Creditors Ledger: This ledger is prepared for recording the credit purchase transactions, i.e., the transactions of the parties from whom the goods have been acquired in credit. It can also be termed as purchase ledger.
2. Sales Ledger/Debtors Ledger: In this ledger, date wise transaction of the debtors, i.e. to whom goods have been depleted in credit is recorded. It helps in determining the due amount of the debtors at the end of the year.
3. General Ledger: In General ledger, all the other account’s entries are recorded other than sales and purchase account. It can also be termed as summarise ledger of all the nominal and real accounts such as a/c receivable, inventory account, cash account, investment account, machinery account, etc.
Various subsidiary ledgers are prepared for providing details to the general ledger, and at last, all are sum-up in one ledger called the general ledger. Thus, this account is also termed as “master account” or “main account“.
4. Private Ledger: This type of ledger is prepared to maintain the personal records of the proprietor, and are not intended for general observation such as capital account, current account, drawing account, personal loan account, etc.
Importance of Ledger
Following are the importance of preparing ledger:
- Calculation of profit/Loss: Ledger preparation is an unescapable step for any business organisation for calculating the exact profit or loss of their business in a year. Every organization needs to create a profit and loss statement to determine the true and fair position of the financial statements which is impossible to make without preparing relevant ledger accounts.
- Exact position of an account: Ledger accounts convey the exact position of the accounts whether they have an outstanding or owing balance at the time of closing the account.
- Time saver: As all the entries are recorded in one place, it becomes easier and time- saving while preparing further accounts such as trading, profit and loss accounts.
- Imperative: It is obligatory for any business organization to prepare ledger accounts of the parties involved in every transaction for maintaining the correctness or accuracy of the transactions that occurred during the year. Creating separate ledger accounts reduces the chances of omitting any transaction as ledger account will not get balance if any transaction gets omitted.
Ledger in Accounting
In accounting, the preparing ledgers are the second most important step after passing journal entries, in which various transactions are recorded in separate account heads, such as sales, purchase, investment, inventory, etc.
For preparing further relevant accounts such as trading and profit and loss account it is essential to make a record of various accounts in a summarized form for which separate ledger accounts are created for every item. Ledger acts as a book of the final entry in the accounting system as all the entries from ledger accounts gets transferred to the appropriate account.
Ledger Balancing
At the last of the year, all the ledger accounts get closed by balancing the Debit and Credit balances of the accounts to determine the difference amount amongst Debit and Credit items. If any account’s debit balance exceeds the credit balance, then that account will be considered as an account with debit balance visa-versa if credit balance exceeds it will be regarded as a credit balance account.
At the time of closing the accounts, their balances get balanced or become nil and the accounts which do not get balanced (nominal account) will be transferred to trading, profit and loss a/c.
Difference between Journal and Ledger
| Basis for comparison | Journal | Ledger |
|---|---|---|
| On the basis of recording | Recording transactions in the journal is the first stage of accounting. | Recording in the ledger is the second stage of accounting. |
| On the basis of nature | Journal is the book of prime or original entries. | Ledgers are the books of final entry. |
| On the basis of method/ process of recording | Process of recording entries is known as journalization. | The method of recording in the ledger is known as posting. |
| On the basis of use | Journal is used on a daily basis to record transactions in a chronological manner. | Ledgers are used periodically such as weekly or monthly. |
| On the basis of preparation | Journals are prepared on the basis of source documents such as vouchers, bills. | Ledgers are prepared on the basis of a journal. |
| On the basis of balancing | Journal cannot be balanced. | Except nominal account, all other accounts will get balanced in the ledger. |
| On the basis of narration | Narration is given after each journal entry showing the details of the transaction. | No such narration is required in the ledger. |
| On the basis of information | In the journal, providing entire facts about accounting activities is not possible at a time. | Ledger makes it possible to provide full and entire facts. |
Points to Remember
- Creating Ledger accounts facilitates in preparing accurate financial records of the company.
- Posting entries in the ledger is the second stage of recording entries.
- Ledgers are termed as a book of final entry.
- Various accounts are maintained under different heads in ledgers.
Conclusion
Ledger is a compiled book of all the journal transactions including all the assets and liabilities, income and expenses of the financial statement and the balance gets transferred to trial balance for maintaining further accounts. Hence it can be concluded that preparing ledger is the essential part of the accounting process.
cleolia says
really helpful, thanks