Definition: Employee ownership is a model in which the employees own all or maximum stake in the business. It isn’t restricted to the higher level but also offered to every management level. Moreover, it provides tax benefits to businesses.
This model benefits both the business as well as employees.
Employee participation in decision-making, better incentives and ownership experience leads them to focus on the quality of work and dedicated efforts towards the customer.
The businesses which practice employee ownership is known as ‘Employee Owned Organizations’. The widely used model of employee ownership is Employee Stock Ownership Plan (ESOP) which will be discussed in detail further in this article.
Content: Employee Ownership
Forms of Employee Ownership
The organization can select the form of employee ownership according to the benefits derived from it and the degree of control needed. There are four forms of employee ownership available at disposal:

Social Ownership
It is the most common form of ownership that businesses practice. Here, the stocks of the company are available for all. Therefore, any individual from society including employees can hold stock in the company.
But, the company’s management rights remain with the management team. Thus, the shareholder elects the board of directors through voting.
Worker Co-operatives
It is a form of employee ownership in which every individual working in the business is an owner or the exclusive owner. In other words, the company is owned and managed by its employees.
The workers own the company’s shares and appoint the board of directors among themselves. The crucial decision-making in the organization is taken by the workers jointly.
It is an autonomous business model where the employees get actual holding in the business. Besides, it involves a relatively low set-up cost.
The company’s gains and losses directly affect the workers. Thus the workers show dedication and strive to work with more efficiency.
Employee Stock Ownership Plans(ESOPS)
It is an indirect form of ownership in which employees get partial or complete ownership due to the employee-ownership trust. The company creates this trust on behalf of its employees.
This form of ownership is a part of the employee benefit plan. And, the owner enjoys full control over the business and the set-up costs are high.
- The employer can sell some or all of their business to the employees.
- The employee doesn’t have to pay anything for the purchase of stock.
- The companies borrow money from financial institutions for the same.
- The institution pays the fair market value for its stocks.
The borrowing taken by the company provides tax benefits to the businesses. The employee owns the stock until he retires or leaves the organization. It is also the best retirement scheme that companies can offer to their employees.
Some types of ESOPS are as follows:
- Direct Purchase Plans
- Stock Options
- Restricted Stock
- Phantom Stock
Direct Ownership
When the employees can buy stocks of the company in which they are working is known as Direct ownership. Here, the employee has to purchase the stock by themselves.
Factors Driving Employee Ownership
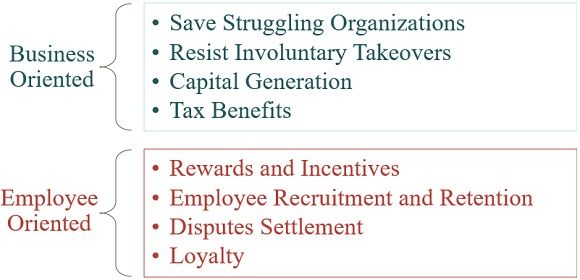
Business Oriented
- Save Struggling Organizations
Organizations at their declining stage can bounce back through ownership models. - Resist Involuntary Takeovers
By giving a stake to employees, the business can resist the forced takeover. It also increases overall productivity across the organization. - Capital Generation
The company can generate funds by providing stakes to the employees. - Tax Benefits
Companies can enjoy tax benefits by applying Employee Stock Ownership Plans. The employees can also enjoy tax-free bonuses.
Employee Oriented
- Rewards and Incentives
Employees receive incentives, bonuses and share in companies profits. - Employee Recruitment and Retention
The companies can retain their employees as they are also the stakeholders. - Disputes Settlement
Companies often go for Employee Stock Ownership Plans(ESOPS) for dispute settlement. If it is not resolved on time with labours leading to firm failure. - Loyalty
The employees of employee-owned companies are loyal. Also, they own a part of the business, so they work with more dedication and commitment.
Merits of Employee Ownership
The employee-owned business has several advantages over the conventional business model. The merits of employee ownership within and outside the organization are as follows:

Internal Business Environment/ Within the Organization
- Lower Turnover Ratios
The employee-owned companies often show a lower turnover ratio. As the employees are more engaged and loyal to the organization. - Goodwill
The companies can create their worth in the market through this model. Every business element works together towards the common goal and takes it to new heights. - Employee Commitment
The organization’s profits and losses are shared with the employees too. Thus, they are self-motivated and work with more commitment. - Profit Maximization
The company maximizes its profits by applying this model. Because the company receives tax relief and enhanced workforce productivity. - Job Security
The employees get job security in the long run by becoming an essential part of the company’s ownership. Therefore, during layoffs, the employees who hold shares are secured. - Improved Adaptability
Companies with shared ownership are more adaptive to economic changes. - Motivated Workforce
The monetary and non-monetary benefits gained through employee ownership are an excellent source of motivation for the organization.
External Business Environment/ Outside the Organization
- Economic Growth
The applicability of shared ownership in businesses results in overall economic growth. To encourage enterprises, the government provides tax benefits. - Reliable Business Model
It is a reliable business model as many companies practice this model locally and globally, generating satisfactory results. - Firm Survival
A firm with employee-owners can survive in economic downturns longer in the dynamic business environment. - Social Responsibility
The concept of employee ownership develops influential community and social responsibility.
Demerits of Employee ownership
Following are the demerits or disadvantages of employee ownership:
- Employees can feel stressed.
- The companies can generate more capital through trading in financial markets.
- Sometimes employees may feel pressurised. This is because they are also part of the crucial decision-making process.
- Along with the profits, employees have to bear the company’s losses if it doesn’t perform well.
- Employees may not leave the organization easily.
Theory of Ownership
The theory of ownership implies that the stake in the company’s ownership affects employees positively. It stimulates various factors within the organization like:
- Job Satisfaction
- Motivation
- Reduced Personnel Turnover,
The right in the company’s decision-making and information about critical issues develops psychological ownership in the employees. Psychological ownership promotes enhanced employee performance, behaviour and increased commitment.
Example of Employee-Owned Organization
The two employee-owned organizations are listed below:
Parsons Corporation
It is an American company founded by Ralph M. Parsons in 1944, headquartered in Centreville at Virginia. It provides solutions digitally for defence, intelligence and infrastructure.
Parsons uses ESOP as a retirement plan for its employees. Also, it offers Employee Stock Purchase Plan(ESPP) as additional financial security.
Houchens Industries
Houchens Industries is a 100% employee-owned company listed by Forbes based in Bowling Green, Kentucky. It is a private American company belonging to the Grocery store and Insurance Industry.
It was founded as Houchens Foods by Ervin G. Houchens in Glasgow, Kentucky.
Final Words
Employee ownership is a concept in which the employee becomes the company owner by holding a full or partial stake in the company.
There are different ways of implementing employee ownership in the organization. Companies can select the form of ownership according to profitability and degree of control.
Leave a Reply