Definition: Labour turnover can be defined as the overall change in the number of people employed in a business entity during a particular period. It takes into consideration the number of exiting personnel, new joinees and the total number of workers as listed in the payroll at the end of a given period.
A high labour turnover rate is considered to be unfavourable for the organization’s stability and can even result in a temporary shutdown or strike. The entities, therefore, take up human resource as an integral part of the business.
Content: Labour Turnover
Causes of Labour Turnover
When we talk about the reasons behind a high labour turnover, we come across the factors which are under control and others which are beyond the regulation of the organization.
Let us now go through the critical reasons behind the labour turnover:
Avoidable Causes
The factors that are related to the organizational facilities and working conditions, the ones which the management could modify to retain the workforce are considered as preventable causes.
Some of the significant issues are related to improper wages, lack of healthcare facilities, inappropriate fringe benefits, cold relations with the management and many others as listed below: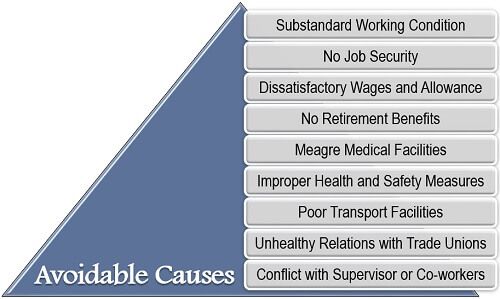
Unavoidable Causes
The workers are sometimes compelled to depart from the organization, for the inevitable reasons. Neither the organization nor the employee can take any step to avoid such circumstances.
Some of these causes include death, severe accident, marriage or retirement of the personnel. The various others are mentioned in the given image: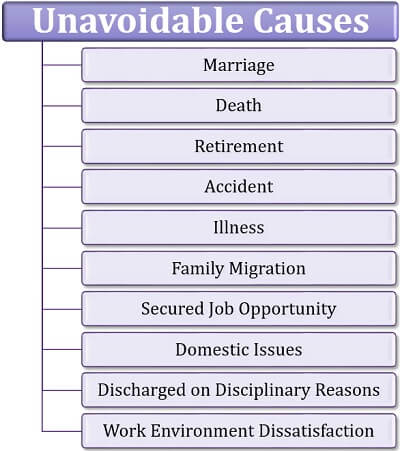
Labour Turnover Effects
When a worker departs from the organization, it impacts a part or sometimes overall working of the entity.
This impact could be both constructive and destructive for the organization at the same time. The effect is even more if the workers leave in groups, creating a dent in productivity.
Adverse Effects
Let us first discuss the negative impact of labour turnover in the organization:
- Hampers Productivity: When a worker quits the job, the production is temporarily ceased or slowed down until the new hire joins the organization.
- Decreases Morale: The co-workers feel demotivated when they notice that the exiting employee is moving out for a better opportunity.
- Hikes Production Cost: The training or learning phase of the new worker, increases expense due to slower productivity and high wastage.
- Training Expense: The wages paid to the trainee or new hire as well as the mentor for that unproductive training period, is a considerable cost for the organization.
- Replacement Cost: To fill the position of the exiting worker, recruitment of a new staff involves advertising, hiring and training expenses.
Positive Effects
Labour turnover also has some benefits to the organization, which are discussed in detail below:
- Improves Organizational Culture: Labour turnover means the entry of new people with different values, mindsets and beliefs to enrich the organizational culture.
- More Talented Personnel: New hires can be more efficient, knowledgeable, sharp and active than the existing workforce.
- Less Expensive Resource: With constant hikes and promotion, the existing workers cost more in comparison to the inexpensive trainees who replace them.
- Infusion of Fresh Ideas: The new resources bring with them innovative thoughts and ways of doing things, which is quite beneficial for organizations.
- Better Skills and Qualification: With evolving courses and skills training, the organization can get fresh graduates possessing better competence.
Types of Labour Turnover
The labour turnover can be distinguished based on the employees’ spontaneity and the effect it has on the organization. Given below are its four basic types: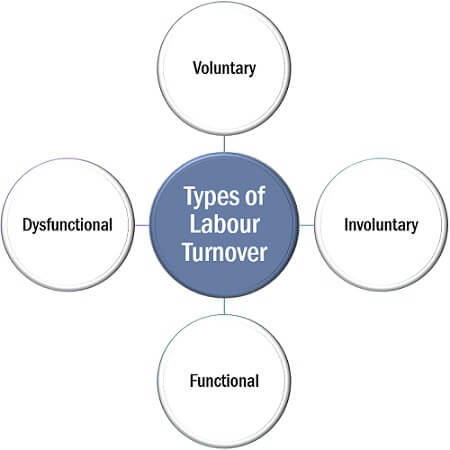
- Voluntary: When a worker willingly exits the organization, i.e., the person resigns from the job position due to any of the circumstances, it is termed as voluntary labour turnover.
- Involuntary: In the case of involuntary labour turnover, the worker is abolished from the duties by the management. It can be due to any of the reason like failing to comply with the norms.
- Functional: By saying functional, we mean to improve the organization’s efficiency, the under-performing workers are terminated from work.
- Dysfunctional: The dysfunctional labour turnover takes place when highly efficient and skilled personnel leaves the job by hampering the overall functioning of the organization.
Strategies to Reduce Labour Turnover
Labour turnover is an inescapable business aspect. However, it can be controlled by taking timely action and improving existing human resource policies.
Let us have a look at other ways of lowering the number of exits:
The management should make constant efforts to promote sound employee-superior relations in the organization. The wages and incentives plan should be reviewed and upgraded annually to ensure fair pay to the workers.
Another way is to modify the human resource policy as per the guidelines stated by the government and companies act. Not only fair wages but providing various other fringe benefits like an insurance plan, medical facility, transportation, etc. can retain employees.
Exit interviews provide the critical reasons for labour turnover, therefore to know what all to improve, go for it. The workplace facilities like ample ventilation, lighting, drinking water, cleanliness, etc. should be maintained.
The organization should not overlook labour welfare and implement suitable measures for empowering its human resources. A company’s reward and compensation plan should be progressive to motivate and value the high performing workers.
The ideas of the ground-level workers can prove to be conducive for the organization; therefore, they should be encouraged to share their views. Resolving the conflicts and addressing the complaints or problems of the workers in the workplace develops a healthy environment for everyone.
The managers and supervisors should be unbiased towards their subordinates to deepen their bond and understanding. Every worker looks forward to the growth prospects that the organization provides. Therefore, granting the workers with promotion opportunities is quite favourable.
Conclusion
Labour turnover is usually high in private organizations where a large number of workers are engaged in routine activities that do not require much expertise.
However, the skills-based organizations try to maintain low labour turnover rate. This is because they have to bear a considerably high cost of turnover if their valuable resources exit the company.
Though a small factor, if the employee orientation process is prominent, then the workers tend to stay with the organization for a more extended period.
NISAR HUSSAIN says
thank you for helping
Chisha sikazwe haggai says
This information is very much helpful, i really appreciate have learnt a lot on the labour turnover, thanks once more
Mukesh Motwani says
How to retain labor.
TATENDA NDEREMAH says
THESE NOTES ARE WELL UNDERSTANDABLE PLEASE SENT ME MORE NOTES UNDER HUMAN RESOURCES MANAGEMENT
Mutetwa Brenton T says
This content was really helpful. Thank you so much, 😊
Ugonma Njoku says
A very good outline, simple to understand by way of explanation and flow. The stages of sub topics make it better understood. Thanks for helping out.
keberku says
More helpful note and well organized to understsnd.
Tadiwanashe Manyara says
Thank you so much I appreciate