Definition: Debentures are the certificate or the creditorship securities issued by the company to the public when there is a need of capital for expansion and development, but the company don’t want to uplift their share capital. They are the liability of the company which has to be repaid in a specific time period; however, a feasible alternative of term loans for companies.
Content: Debentures
Features of debentures
Following are some of the features of Debentures:
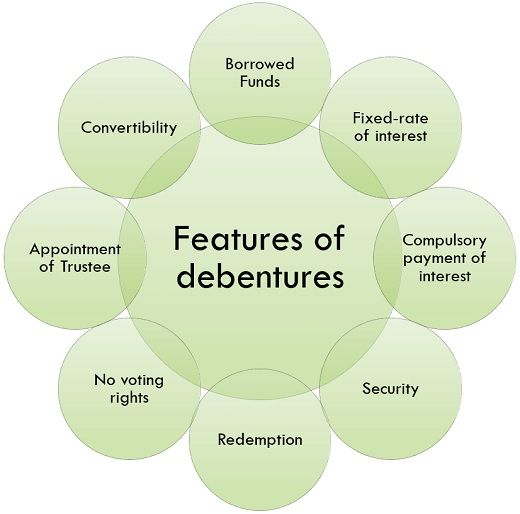
- Borrowed Funds: Debentures are the capital funds that are borrowed by the authority bodies from the public while seeking for a capital; however, the company needs to repay the capital to the investors within a stipulated period of time.
- Fixed-rate of interest: It is always issued with a fixed rate of interest which is payable once in every six months or annually to the investors as decided by the shareholders in the annual general meeting.
- Compulsory payment of interest: The company is obligated to the debenture holder interest payment in priority irrespective of the condition of profit or loss in their business.
- Security: Debentures can be secured against the assets of the companies even if the company becomes insolvent debenture holders will get their money by selling the assets of the company.
- Redemption: Redemption of debenture implies paying back of the sum to the debenture holders against the issued debentures as mentioned in the company’s prospectus on the completion of a fixed period of time or date at par, premium or discount.
- No voting rights: Debenture holders are the creditors of the company; thus, have no right to say or make a vote on any internal matters of the company untill their rights are being affected or the company asks their opinion in special circumstances.
- Appointment of Trustee: At the time of issuing of debentures to the public investing in your company, a deed is signed by the person appointed as trustee, the trustee is supposed to ensure that the borrowing firm fulfills its institution.
- Convertibility: Debentures has an option of convertibility, i.e., the company may issue convertible debentures at the option of debenture holders which are convertible into equity shares.
Types of Debentures
Based on various distinctive aspects there are numerous types of debentures; they are as follows:
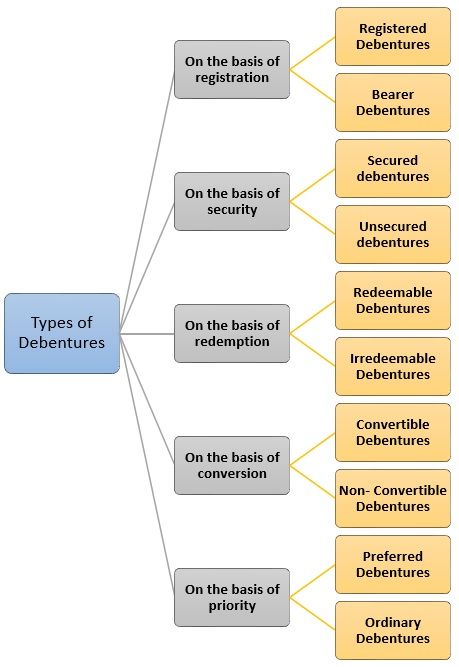
On the basis of registration
1. Registered Debentures: Debenture holders whose full details such as name, phone number, address are retained and registered under the company’s register can only claim for such debentures, transfer of such debentures also requires registration and are not transferable by simply delivering documents to one another.
2. Bearer Debentures: These debentures are the unregistered debentures of the company, and therefore the company does not retain any information about the investors in their register like registered debenture holders.
They are payable to the bearer or holder of the security and are easily transferable by the holder to any person with his consent of transferring.
On the basis of security
1. Secured debentures: Secured debentures are the debentures which are charged wholly or partly over the assets of the company, i.e., either floating or fixed charges where floating charges implies charges on all assets of the company and fixed charges indicates charges on the particular asset of the company; and
Such charges must be registered within 30 days from the date of issue of the debenture.
2. Unsecured debentures: Unsecured debentures are not secured wholly or partly over the assets of the company, hence can be mortgaged easily, and the holders of such debentures are unsecured creditors of the company; thus companies do not prefer to issue such debentures very frequently now-a-days.
On the basis of redemption
1. Redeemable Debentures: These debentures can be redeemed either at par, premium or discount after a certain period of time or on the expiry of the term as well as can be called for redemption by the company on demand of debenture holders on the lumpsum basis.
2. Irredeemable Debentures: Company has no constraint or is not bound to repay such debentures during its endurance as these debentures are not issued with any specific redemption date, and thus are perpetual in nature; they can either redeemed at the time of winding up of the company or on the occurrence of an any uncertain event.
On the basis of conversion
1. Convertible Debentures: These debentures are considered as long-term unsecured debts of the company.
However, it can be converted into equity or preference shares by the holders as and when required at the rate declared in the agreement signed at the time of the issue of debentures.
2. Non- Convertible Debentures: Non- Convertible Debentures will always remain the debt of the company, and cannot be converted into shares at any point as they are the fixed income instrument without any collateral against which the company pays a certain interest after a specific duration of time, i.e., on maturity.
On the basis of priority
1. Preferred Debentures: During the time of winding up of the company, the holders of the preference debentures have a first right or priority to get payment of their debentures.
2. Ordinary Debentures: The holder of such debentures gets payment after the payment of preference debenture holders at the time of winding up of a company.
Advantages of Debentures
Following are some of the advantages of the debentures:
- The company without giving ownership rights can raise long-term funds.
- Interest amount to be paid on debentures remains constant irrespective of any fluctuations in the profit of the company.
- At the time of liquidation, debenture holders are on top priority to claim on the assets of the company.
- Debentures are less risky than shares from an investors point of view as investing in debentures is the safest option of investment though it will always give a profit in return.
Disadvantages of Debentures
Following are some of the disadvantages of the debentures:
- They are the creditors of the company; thus don’t have any voting rights in the matters of the company.
- Interest on debenture is fully taxable on the company’s income.
- It becomes challenging to pay debenture capital when the economy faces crises like depression.
- It increases the cost of capital because of brokerage, commission, etc.
Methods of Issuing Debentures
Issue of Debentures for Cash
Various ways for issuing of debentures for cash are as follows:
- Issue of debentures at par: When the face value of the debenture is equal to its issue price, it is said to be debenture issued at par. It can be more precise with the journal entry passed for the issue of such debenture.
Example: Issue of 1,00,000 9% debentures of 100 each at par.
Journal entry for the issue of debentures at par:
| Date | Particulars | L.f. | Amount (Dr.) | Amount (Cr.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14/03/2020 | Bank A/c | 100000 | - | |
| To 9% Debentures | - | 100000 | ||
| (Being debentures issued at par) |
- Issue of debentures at a premium: Debentures are assertedly issued in premium when the issue price is higher than face value or nominal value.
Example: Issue of 1,00,000 9% debentures of a premium of 5%
Journal entry for the issue of debentures at a premium:
| Date | Particulars | L.f | Amount (Dr.) | Amount (Cr.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14/03/2020 | Bank a/c | 105000 | - | |
| To 9% Debentures | - | 100000 | ||
| To Security premium | - | 5000 | ||
| (Being debentures issued at premium) |
- Issue of debentures at a discount: When issue price is less than face value, it is said to be debentures issued at a discount.
Example: Issue of 1,00,000 9% debentures of a discount of 10%
Journal entry for the issue of debentures at a discount:
| Date | Particulars | L.f | Amount (Dr.) | Amount (Cr.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14/03/2020 | Bank a/c | 90000 | - | |
| Discount a/c | 10000 | |||
| To 9% Debentures | 100000 | |||
| (Being debentures issued at discount) |
Issue of Debentures other than cash
Debentures can also be issued for consideration other than cash for purchasing assets from the vendor’s company
Example: XYZ limited purchased a machine costing Rs.88000 Payable by the issue of 10% debentures of Rs.100 each at
Case1: At par
Solution:
Journal Entry 1
| Date | Particulars | L.f | Amount (Dr.) | Amount (Cr.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14/03/2020 | Machine a/c | 88000 | - | |
| To Vendor's a/c | - | 88000 | ||
| (Being machinery purchased) |
Journal Entry 2
| Date | Particulars | L.f | Amount (Dr.) | Amount (Cr.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14/03/2020 | Vendor's a/c | 88000 | - | |
| To 10% debentures | - | 88000 | ||
| (Being 880 debentures issued at par) |
Working note 1: No. of Debentures= 88000/100=880 debentures
Case 2: At a premium of 10%
Solution:
Journal Entry 1
| Date | Particulars | L.f | Amount (Dr.) | Amount (Cr.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14/03/2020 | Machine a/c | 88000 | - | |
| To Vendor's a/c | - | 88000 | ||
| (Being machinery purchased) |
Journal Entry 2
| Date | Particulars | L.f | Amount (Dr.) | Amount (Cr.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14/03/2020 | Vendor a/c | 88000 | - | |
| To 10% debentures | - | 80000 | ||
| To security premium | - | 8000 | ||
| (Being 800 debentures issued at premium of 10%) |
Working note 2: No. of Debentures= 88000/110=800 debentures
Case 3: At a discount of 10%
Solution:
Journal Entry 1
| Date | Particulars | L.f | Amount (Dr.) | Amount (Cr.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14/03/2020 | Machine a/c | 88000 | - | |
| To Vendor's a/c | - | 88000 | ||
| (Being machinery purchased) |
Journal Entry 2
| Date | Particular | L.f | Amount (Dr.) | Amount (Cr.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14/03/2020 | Vendor's a/c | 88000 | - | |
| Discount on issue a/c | 9778 | - | ||
| To 10% debentures | - | 97778 | ||
| (Being 978 debentures issued at a discount of 10%) |
Working note 3: No. of Debentures= 88000/90=978
Conclusion
Debentures are considered as the debt that is borrowed from the general public for the growth and development of the company against which the investor enjoys a certain amount as an interest paid by the company for a fixed period of time.
Leave a Reply