Definition: Public-private partnership (PPP) is a model where the government associates with private companies to accomplish infrastructure projects. This alliance between both the parties, ensure financing, designing, flourishing and maintaining of the infrastructural amenities within the country.
The PPP approach initiates the efficient facilitation of public goods to the people. This is because, such projects are handed over to the relevant private entities, who hold expertise and knowledge in their field.
Content: Public-Private Partnership (PPP)
Features of Public-Private Partnership
To understand the PPP concept, we must know its fundamental characteristics. Some of these are discussed in detail below: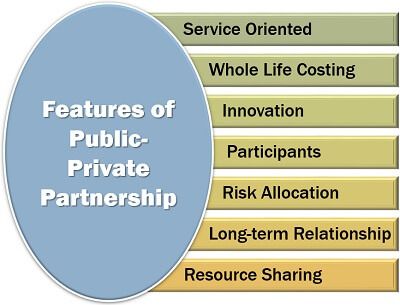
- Service-Oriented: The PPP approach deals with the facilitation of long-term public services. It includes roads for transportation, dams for electricity and water supply and street lights for lighting.
- Whole Life Costing: In the PPP model, the project’s total cost is computed at once for its entire life span. Thus, taking into consideration the initial capital expenditure, repair and maintenance expenses, modification expense and the eventual disposition cost.
- Innovation: With the involvement of the private firms, the PPP approach also initiates the implications of creativity and new technology to the infrastructure projects.
- Participants: The two parties involved in the public-private alliance are; the government and the respective private company.
- Risk Allocation: Infrastructure projects involve high risk; thus, PPP helps the government to transfer this risk to private firms.
- Long-term Relationship: These projects are usually for years; therefore, the government authority and the private entity remains associated for an extended period.
- Resource Sharing: The capital, financial, design and other resources required, are shared between the government and the firm for successful project accomplished.
Types of Public-Private Partnership (PPP)
When we talk about the public-private partnership, we come across various ways in which this approach functions. To understand some of the frequently adopted PPP structures, read below: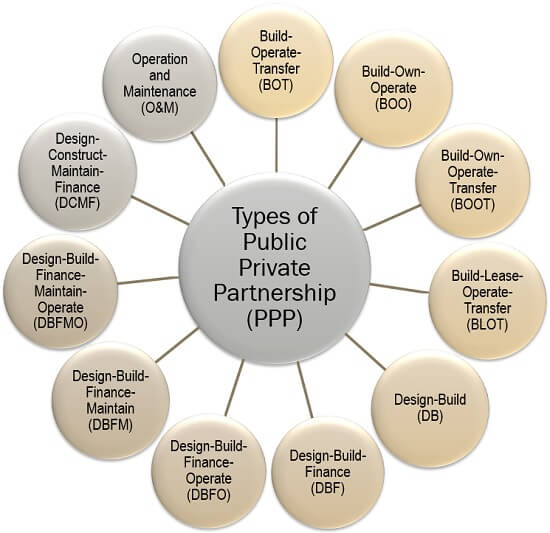
Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT)
The toll road construction projects are illustrated under this conventional model. The private company construct the road, collect toll or revenue (for the contract period) and then pass its possession to the government.
Build-Own-Operate (BOO)
It is though very similar to the BOT model; here, the possession of the facility remains with the private entity itself.
Build-Own-Operate-Transfer (BOOT)
To recover the cost of construction and incur gains, the private firm, after development, keeps the possession of the facility up to the contract period. After which it passes on the ownership to the public sector.
Build-Lease-Operate-Transfer (BLOT)
The private company uses a leased public property to develop a facility. It functions on this property for the lease period to recover cost and earn revenue. Later as the lease expires, the land is handed over, back to the government.
Design-Build (DB)
This is the basic form of P3 where the private company layouts and constructs the facility as per the government requirements, after complete risk assessment. In return, it takes a fixed amount as its charges.
Design-Build-Finance (DBF)
The private sector firm undertakes a project to design the layout, build the facility and meet the capital cost involved in such designing and construction.
Design-Build-Finance-Operate (DBFO)
In the DBFO model, the private company is responsible for planning the project layout, facility construction, arranging the required capital and operating it till the grant period. The facility operations revenue meets the cost incurred and generates profit to the company.
Design-Build-Finance-Maintain (DBFM)
This model can also be termed as a management contract. Here, the public sector entity remains associated with the project from the beginning to the end.
The process starts right from designing of the layout, to construction, funding and lifetime maintenance of the facility. The firm either charges a fixed sum or shares profit; also, it is involved in the project’s managerial decision making.
Design-Build-Finance-Maintain-Operate (DBFMO)
It is an extended version of DBFO. Here, the private firm prepares the blueprint, builds up the facility, invest the required sum and carry out the operations to generate revenue. Since the company undertakes the project for a long-term, it has to take care of the maintenance work too.
Design-Construct-Maintain-Finance (DCMF)
In the DCMF model, the private entity understands the government specifications and accordingly designs, develops, upkeeps and invest in a facility. This facility is then leased out to the government body itself.
Operation and Maintenance(O&M)
This model involves assigning of a sub-contract to the private companies for running and up keeping a facility.
The firms which undertake such projects are experts in maintenance work. Also, the possession of the facility remains with the government body. The revenue for private entities is commonly generated through a performance-based fee. In some cases, the companies charge a lump sum and fixed price for their services.
Advantages of Public-Private Partnership (PPP)
The PPP approach is highly beneficial for the government, the country, the economy, the private organizations and the public. Given below are some of the prominent pros of this concept: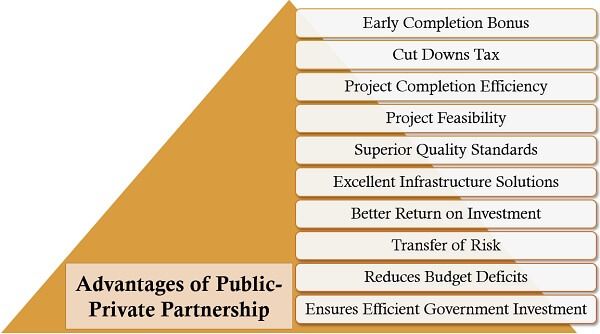
- Early Completion Bonus: To improve efficiency, the private companies are motivated through bonus if they complete the project before time.
- Cut Downs Tax: The cost-efficient infrastructure projects help the government to save funds and thus, provides for a reduction in the tax rates.
- Project Completion Efficiency: When the standard time for completing a project is estimated, its execution and fulfilment become more competent.
- Project Feasibility: As the project’s risk involvement and practical implementation are well-analyzed, the chances of failure reduces remarkably.
- Superior Quality Standards: PPP approach initiates benchmarking for the desired quality of the project and ensuring the same during the project’s life cycle.
- Excellent Infrastructure Solutions: This has been possible since, the proficient private companies work in collaboration with the government, where each of them contributes their best.
- Better Return on Investment: The ROI of the P3 infrastructure projects might be reasonably high in the long run. The reason being it has been monitored and accomplished by both parties together.
- Transfer of Risk: The government hands over the associated risk along with the project to the private firms who have relevant experience and knowledge in the area.
- Reduces Budget Deficits: In the PPP approach, the private companies determine the cost and performs the capital budgeting to avoid any shortage of funds in future.
- Ensures Efficient Government Investment: Since P3 initially let the private companies invest their funds in the infrastructure projects, the government can utilize its capital for socio-economic welfare.
Disadvantages of Public-Private Partnership (PPP)
On the one hand, it helps to improve the infrastructure conditions in a country. Whereas, on the other hand, it has the following limitations: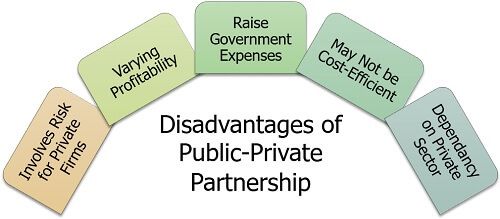
- Involves Risk for Private Firms: The public-private partnership provides for the transfer of risk to the private entities, overburdening them with the responsibility of failure.
- Varying Profitability: The complexity, competition level, associated risk, nature, size and impact of the project determines its profitability.
- Raise Government Expenses: Due to the project’s high-risk involvement, the companies usually demand huge compensation, leading to a hike in government expenses.
- May Not be Cost-Efficient: At times, the government lacks sufficient knowledge of the project cost. When the private company holds the complete cost information; the public sector may be misled.
- Dependancy on Private Sector: The most significant limitation of the PPP approach is that the government majorly relies on the private sector for project undertaking and accomplishment.
Public-Private Partnership (PPP) Example
The public relations officer noticed the problem of conveyance between the two villages in her area, which were separated by a river. The only means of reaching the other village was through boats. Therefore, she proposed the bridge construction project in front of the government; to establish connectivity between the villages.
The task being highly complicated, the government decided to go for a PPP approach for this project.
Public-Private Partnership Process
Let us now understand how the project in the above illustration will proceed, through the following significant steps involved in it: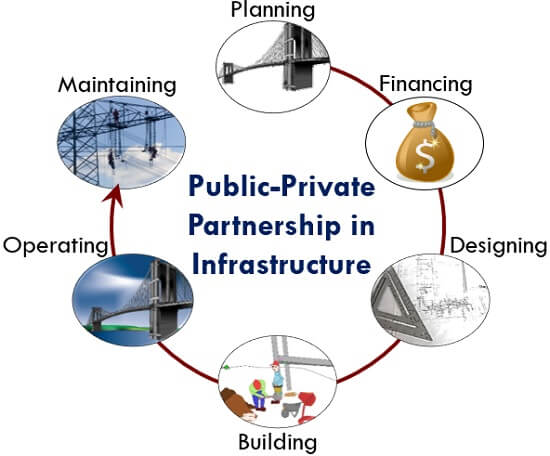
- Planning: The government initiates the basic plan of the bridge and select a suitable private company providing the best offer to undertake the project.
- Financing: Now, comes the role of the private entity. It first analyzes the whole life costing of the bridge and accordingly finances the project. This cost can be recovered from the government later on.
- Designing: The experts and engineers then draft the final layout of the bridge, and both the parties give their input for the purpose. Also, a time frame is ascertained for project accomplishment through the Critical Path Method.
- Building: The company engages an experienced contractor and the labourers to construct the bridge. The project completes efficiently within the estimated duration.
- Operating: After the proper testing and quality check, the bridge is opened for the public to use. Thus, facilitating the connectivity and conveyance for the natives.
- Maintaining: As estimated in the whole life costing, after five years of use, the bridge requires some repairing. Such maintenance cost is also borne by the private company which has undertaken the project.
Conclusion
Collaboration is inevitable when it comes to substantial infrastructure projects requiring high investment and expertise.
Therefore, the government prefers to take the assistance of professionals in the field. Here, comes the role of private companies for the accomplishment of such projects.
BERUK says
presented in interactive approach
Roy Kirinda says
Thx
Juneja bist says
Easy to understand 😊
Chinenye says
Thank you so much. This piece helped a lot. Your piece was very clear and very easy to understand.
Le Le Hlaing says
minutes reading.
It is useful for us.
thank you so much for this