Definition: High-yield Bonds or Junk Bonds are publicly traded debt securities. It belongs to the noninvestment grade category in the credit rating list. It is a part of corporate finance which is risky but yields high returns, which is why it is named ‘High-yield Bonds‘.
The securities rated below BBB (S&P) or Baa3 (Moody’s) come under the noninvestment grade category.

It is known by a variety of names like:
- Junk Bonds
- Speculative Grade Bonds
- Low-rated Grade Bonds
These bonds are called ‘Junk‘ because they obtain low ratings from credit rating companies.
Investors buying these bonds benefit from higher yields or returns for investing in struggling companies. Usually, they can earn yields between 2% and above 10%. In addition, investors will get their invested amount back upon reaching maturity.
The companies issuing these bonds are riskier than the normal ones. There are high chances of loss in unfavourable market conditions.
Generally, the companies that issue Junk Bonds are either start-ups or struggling financially. They pay high interest and investor-friendly norms to compensate for the risk attached to these bonds.
Content: High-yield Bonds
- Terminology
- Understanding High-yield Bonds
- Credit Rating List
- Risk Involved
- High-yield Bonds List
- Why invest in High-yield Bonds?
- Advantages and Disadvantages
- Example
- Bottom Line
Terminology
- YTM: Yield to maturity refers to the total estimated return the bond will generate if an investor holds it till maturity.
- Coupon Rate: It implies the interest rate the bond issuer pays to the investor for investing in it.
- ROI: It is an abbreviation for Return on Investment. It is the return earned by investing money in relation to its cost.
- High-Grade Bonds: These are the securities that are less risky and get good credit ratings. Such securities get ratings above BBB & Baa3, securing their place in the investment grade.
- High-yield Government Bonds: It is the high-yield bonds issued by the government. These bonds are less prone to default than the corporate bonds.
- High-yield Corporate Bond: It is the speculative-grade bond issued by companies paying higher ROI.
- Fallen Angles: The companies once listed in the investment grade in the credit rating list were later downgraded to noninvestment grade.
Understanding High-yield Bonds
In general, bonds are the secured forms of debt instruments. It forms a debtor-and-creditor relationship between the issuer and investor. Both government and corporates issue it to raise loans from the public.
Investors purchase high-yield bonds post referring to the credit rating list. They take this risk to earn potentially high returns on their investments. On reaching maturity, they will get their principal amount back.
Bonds are generally considered safe instruments, but Junk bonds are risky. The reason being, the company is already facing some issues, which is why it couldn’t make it to investment grade. Moreover, it might also become default before reaching the maturity date.
Traditionally, these bonds were a source to finance a hostile takeover. Also, the fallen angels used to issue junk bonds after being downgraded.
Today, companies issue it for general corporate purposes like:
- Financing Capital Needs
- Paying Bank
- Lines of Credit, etc
Credit Rating List
The three popular rating agencies that the majority prefers are Fitch, Moody’s and S&P Global.
A sample of rating list issues by them is given below:
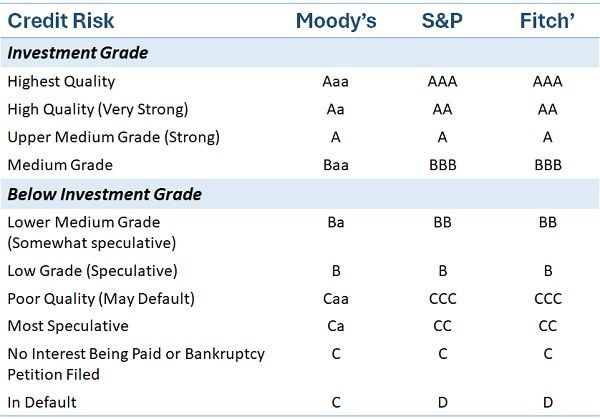
Players in Junk Bonds
The crucial players involved in the entire process are:
- Issuing Companies
- Underwriters
- Traders
- Investors
- Credit Rating Agencies
Risk Involved in High-yield Bonds
Unlike other bonds, junk bonds are highly volatile and have a higher default risk. During economic stress, the chances of default spike up. Therefore, it becomes more sensitive towards economic changes than other securities in the asset class.
However, it can generate fixed income and have some features of equity. Thus, it must be a part of the diversified portfolio and an intelligent asset allocation.
High-yield Bonds List
Some high-yield bonds in India are as follows:
- 12% Maa Kudargarhi Steels Private Limited
- 13% Eden Renewable Alma Private Limited
- 10% Pheonix Hitec City Private Limited
- 9% Bhadla Renewable Power Private Limited
- 12.75% IcI Fincorp Limited
Why invest in High-yield Bonds?
Besides the risk involved, junk bonds have amazing benefits that attract investors.
Investors mitigate the risk involved by widening their portfolios and tracking issuers’ financial health. They go for high-yield bonds due to following reasons:
- Earn Consistent Returns: It outlays consistent returns to the investors. Moreover, the return is more than the other bonds.
- Capital Appreciation: The company’s positive performance may even yield returns like equity. Therefore, investors might encounter a significant capital appreciation through Junk Bonds.
- Short Maturity: Often, high-yield bonds are issued for a shorter duration. In general, they have a maturity of 10 years or less.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The advantages of Junk Bonds are as follows:
- Better return on investment than good investment grade bonds.
- It is a security that has the potential to generate a fixed income.
- It helps create a diversified portfolio with stable returns.
- Junk Bond’s performance also indicates the market conditions.
Given below are the disadvantages of Junk Bonds:
- Speculative bonds are fully taxable. Thus, it is a tax-inefficient way to gain equity-like exposure.
- Hard to trust low-grade companies as they have a higher risk of default.
- Investors may even lose the principal amount if the market conditions are unfavourable.
- The high degree of fluctuations in bond price and value.
Example
Ford
In 2020, Ford slipped from a high grade to a speculative grade in the credit rating list. It happened due to the COVID-19 pandemic and the global economic crisis. It issued Junk Bonds, which is still traded at a premium due to the company’s goodwill.

Netflix
It is listed under the growth-oriented company category. Issuing Junk Bonds has been a part of its strategy for a long time. The company uses the generated fund to finance its activities like:
- Finance the TV and Inhouse Production
- Pay for New Content Creation
The value of its high-yield bond has increased over time and is traded at a premium.
Bottom Line
To sum up, these are the risker bonds yielding high returns backing low capital ratings. It is issued by corporations falling in the low investment grade category.
Moreover, investors can spot these bonds with the help of the grading list issued by independent rating agencies.
The ones who follow the market very often consider it an essential segment in the debt market. Investors must diversify their investments while investing in these bonds.
Leave a Reply