The Sinking Fund Method of Depreciation involves the creation of a contingency fund that assures the availability of funds for asset replacement upon completing its useful life.
It is also known by a variety of names like:
- Depreciation Fund Method
- Amortisation Fund Method

Every fixed asset has a specific useful life, after which it needs replacement. With each passing year, the asset’s value keeps on decreasing for various reasons. This decrease in the asset value is referred to as Depreciation.
For replacement, companies create a separate reserve called Depreciation Fund.
The amount charged as depreciation is invested in securities at a certain interest rate. However, Sinking Fund Tables or Annuity Tables determine the annual depreciation amount.
Periodic investments equivalent to depreciation amount (charged annually) are made outside the business. The company invest these funds in readily saleable securities. Moreover, the interest earned from these investments is also invested (compound interest).
Therefore, we can also call it an Interest Earning Asset Replacement Fund.
Before investing, the company must ensure that the investment must have the following qualities:
- Safety of Funds
- Regularity of Income
- Liquidity of Funds
Mostly, companies prefer to invest in government securities. This is because they are safe in comparison to other marketable securities.
Content: Sinking Fund Method
- Sinking Fund in General
- Formula
- When to use the sinking fund method?
- Working
- Accounting Treatment
- Advantages
- Disadvantages
- Example
- Similar Terms
- Final Words
Sinking Fund in General
It refers to a fund created from the company’s profit for a certain period to replace an asset or repay the long-term liability.
The amount accumulated within this fund is invested in the securities and realized when required. The object behind creating this fund is to generate enough funds for repayment or replacement.
Thus, there are two types of sinking funds:
- Sinking Fund for Fixed Asset Replacement
- Sinking Fund for long-term Liability or Loan Repayment
Sinking Fund Formula
The total money accumulated in the sinking fund (A) can be calculated with the help of the formula given below:
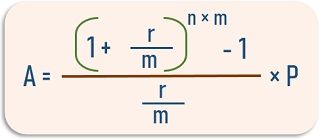
Where,
r is the rate of interest,
m depicts the number of payments per year,
n depicts the number of years,
and P indicates the periodic contribution
When to use the sinking fund method?
Usually, companies opt for this method when the cost of the concerned asset is high. This is because the amount required to replace these assets is huge. Besides, it is suitable for assets to be recorded at the original cost.
For Example, Long- term leases, Heavy Machinery, etc.
Points to Remember
- Transfer the debit balance of Depreciation A/c to the Profit & Loss A/c.
- To simplify calculations, round up the interest and depreciation amount to the nearest number.
- Two entries must be passed if the interest is received twice a year.
- The annual depreciation amount must be uniform every year.
Working of Sinking Fund Method
First, you need to determine the amount of depreciation to be charged on the asset. For this purpose, you can use the Sinking Fund or Annuity Table.
After that, ascertain the depreciation to be paid annually by using the formula given below:

Further, invest this amount of annual depreciation outside business each year except last year. The investments must preferably be made in readily saleable securities like government securities.
In the end, replace the asset post-completion of its useful life. Generate cash by liquidating the purchased investments.
Sinking Fund Accounting Treatment – Journal Entries
Now let’s see the accounting treatment of the sinking fund method of depreciation.
The accounting will revolve around the following accounts:
- Depreciation Fund A/c
- Depreciation Fund Investment A/c
- Concerned Asset A/c
- Depreciation A/c
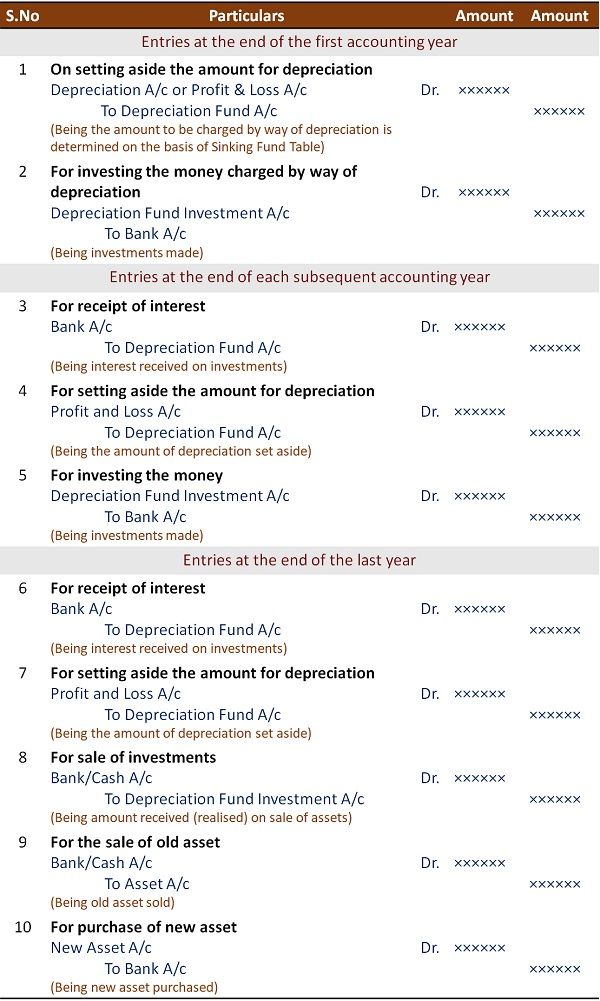
- The profit or loss on sale is transferred to the depreciation fund account.
- The balance in the depreciation fund account will be transferred to a respective asset account.
- The sale process of sinking fund investments will be utilized in a new asset purchase.
Advantages
The advantages of adopting the depreciation fund method are as follows:
- Funds Availability: This method ensures the availability of funds during the replacement of the concerned asset.
- Investment Outside Business: The depreciation amount charged against profit is invested in the stock market. Thus, the money is not locked up within the business.
- Complete Record: One can retrieve entire data from the depreciation fund account.
- Unaffected Working Capital: The asset replacement doesn’t affect the working capital. This is because cash is accumulated by liquidating sinking fund investments.
- Assets Original Price: Unlike other methods, assets appear at their original price on the balance sheet.
Disadvantages
Given below are some of the disadvantages associated with the Depreciation Fund Method:
- Inaccurate Selling Price: As the assets appear at the original value, it is difficult to ascertain their selling price.
- Money Outflow: Here, the money is mobilized outside the business. Consequently, it cannot be used for other purposes within the company.
- Market Risk: The investments are affected by stock market fluctuations. Thus, the risk is always associated with the purchased securities.
- Complex Method: This depreciation method is complicated as it involves a large number of calculations.
- Burden on Profit & loss A/c: In this method, the amount of depreciation is fixed and invested outside the business. But, with time, the repair amount increases as the asset grows older.
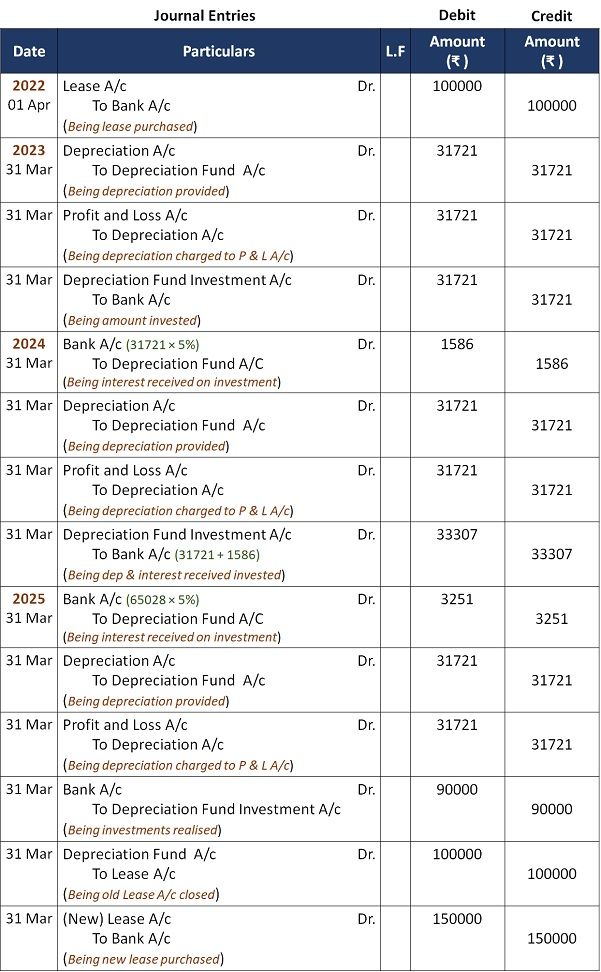
Example
Dolly ltd. purchased a lease for ₹ 1,00,000 on 1st April 2022 for 3 years. And the company established a depreciation fund for the lease renewal after 3rd year. Besides, the investment of depreciation fund money will realize up to 5%.
At the end of March 2025, the sale proceeds from debenture fund investments were ₹ 90,000. The company’s bank account previously showed a balance of ₹ 80,000. In addition, the company acquired a new lease for ₹ 1,50,000.
Record necessary journal entries.
Solution:
Annual Depreciation = ₹ 1,00,000 × 0.317208 = ₹ 31721 (Nearest Rupee)
Similar Terms
Following are some of the terms similar to the sinking fund:
Sinking Fund Investments
The investments are periodically purchased out of sinking funds to be liquidated for loan repayment or asset replacement. Since these investments are purchased for a specific purpose, the interest earned is also reinvested.
Sinking Fund Reserve
It refers to a specific reserve created for a definite purpose. Unlike general reserve, the accumulated fund is only utilized for the very purpose for which it was established.
Sinking Fund for Redemption of Debentures
It is similar to the depreciation fund method we have discussed so far. But, the difference is that here we create the sinking fund to pay off the debenture holders.
In other words, the funds are made available to redeem debentures at maturity.
Sinking Fund Bonds
Sinking Fund Bonds are the ones that are backed by a sinking fund, especially for the repayments. It requires the issuer to create a sinking fund that will ensure the availability of funds during maturity.
We can also understand it as a specific reserve created against any default in the payment to bondholders.
Final Words
It is a great method for calculating depreciation, but it involves many critical calculations. Consequently, it increases the complexity during Book Keeping and leaves room for errors. Besides, the manufacturers might use this method. As they install expensive plants and machinery.
Leave a Reply