Definition: Market Segmentation implies a process of fragmenting the diversified market containing similar attributes or needs. It is the first stage of the STP decision process (Segmentation, Targeting and Positioning). It is a tool to achieve stability and fight competition in a highly competitive market in the long run.
Classification of market segments depends on certain variables. These variables include geographic, demographic, psychographic and behavioural aspects.
Marketers use market segments to spot their target market and achieve a compelling marketing mix for the product. It provides a specialised understanding of the customer’s requirements, tastes, preferences, etc.
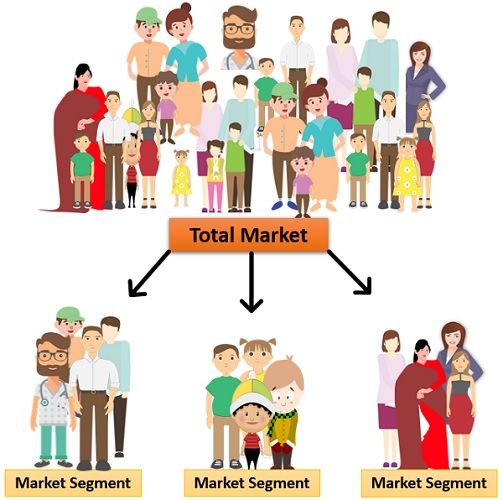
Segmentation is a base for creating marketing plans and strategic decision-making. One such example is Niche Marketing. Also, it identifies the scope of product development to cater unique demands of the potential customers.
For example, the clothing market is a vast and potential market for companies. Marketers divide this huge market based on demographic variables into segments like:
- Men
- Women
- Kids
- Infants
Further, it is sub-divided according to psychological variables like:
- Traditional Wear
- Western Wear
- Casual Wear
- Sports Wear, etc.
Companies can choose specific categories and formulate marketing schemes accordingly. Besides, they focus on satisfying their target audience in the best possible manner.
Content: Segmentation
Types of Segmentation
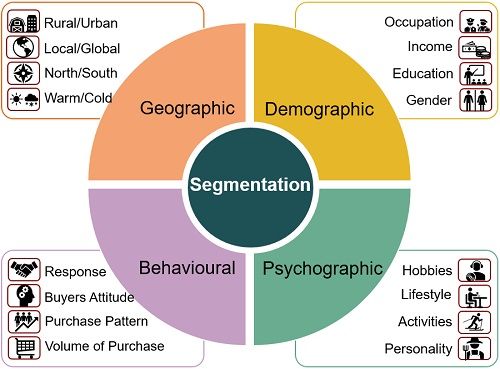
The market can be segmented on the basis of four major groups. These are also called the Basis or Methods of Segmentation. However, companies can also use a combination of these variables during segmentation.
Following are the four types of segmentation discussed in length below:
- Geographic
- Demographic
- Psychographic
- Behavioural
Geographic Segmentation
Consumer needs differ according to the geographic regions. So, we can categorise the consumer market based on these regions. This is the most common form of segmentation adopted by companies.
Some factors of geographic segmentation are listed below:
- Rural or Urban
- Local or Global
- North or South
- Warm or Cold Regions
- Metro or Non-Metro
- High Humid or Dry Areas
For Example, People in cold cities like Manali prefer warm garments or winter wear. In contrast, people in Rajasthan prefer summer wear.
Demographic Segmentation
The segmentation of the market also depends upon demographic attributes. These attributes enable marketers to choose the most suitable products and target markets.
Demographic variables depend upon the customer’s choice and preferences based on their:
- Occupation
- Income
- Education
- Gender
- Age
- Generation
- Family Size
- Religion
For Example, the customers belonging to the high-income group prefer to buy an A.C., whereas the mid-income group generally opts for a Cooler. The ones who belong to the low-income group can only afford to buy a Fan.
Psychographic Segmentation
Customers may belong to the same segment but may not possess similar habits or interests. Thus, to be more specific, marketers conduct a thorough analysis of demographic factors. This analysis results in a more striking marketing campaign by the company.
Psychographic variables include:
- Hobbies or Interests
- Lifestyle
- Activities
- Personality
- Opinions
For Example, Coca-Cola launched Diet Coke (Sugar-free and no-calories) for health-conscious customers.
Behavioural Segmentation
In behavioural segmentation, the market is grouped according to the response towards the product. Besides, the marketer analyses the customer’s behaviour to find out the target group.
The basis of segmentation may be customers:
- Response
- Buyers Attitude
- Purchase Pattern
- Volume of Purchase
- Product Knowledge
- Usage, etc.
For Example, Companies like Surf Excel use different packaging, such as 1 kg, 4 kg, 10 kg packets, etc.
Process of Segmentation
Segmentation can be done in three stages, as mentioned by Kotler and Turner. The procedure adopted by the marketers for segmentation is as follows:-
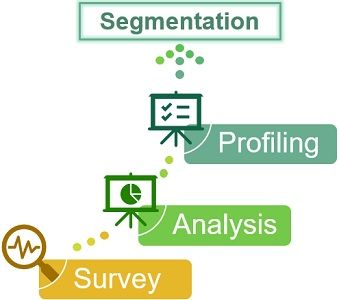
- Survey: In the first stage, markets conduct interviews and discussions with the customers. They identify focus groups and develop a questionnaire for data collection.
- Analysis: After that, marketers perform factor analysis on the collected data. Also, they segregate customers into groups based on these factors.
- Profiling: In this stage, the groups are placed under different bases, as discussed above. It is further segregated according to distinguished attributes to reach the target market.
Criteria
The following criteria must be satisfied during the segmentation process:
- There should be a means of identification of segments.
- The segment should be responsive to the changes in the marketing mix.
- The target group should be accessible in terms of promotion and distribution.
- The size of the segment must be significant to gain profitability.
- Categorisation must depend up on the demand from that sector.
- The market segment should be measurable to ascertain the size of the market.
- Marketers should conduct an in-depth competitive analysis to survive in the long run.
Importance of Market Segmentation
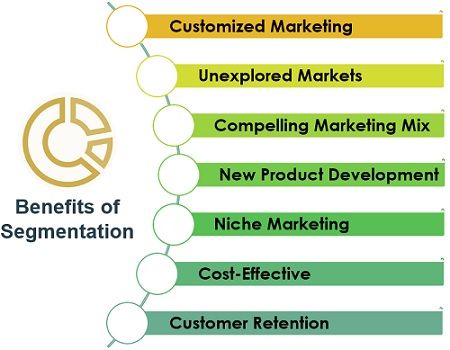
- Customised Marketing: Segmentation focuses on a particular group of people. It provides clarity about the customer’s needs and preferences. Hence, it is easy to make customised marketing strategies.
- Unexplored Markets: The process of segmentation helps marketers to identify unexplored markets. It provides an opportunity to serve these untapped markets and become profitable.
- Compelling Marketing Mix: The segments enable marketers to create a product-based marketing mix.
- New Product Development: It provides the scope for developing a new product and exploring potential markets.
- Niche Marketing: By segmenting the markets, marketers can identify the unique needs of the target audience. These unique needs are the base for Niche marketing.
- Cost-Effective: Through segmentation, the marketers get clarity about the requirements of target customers. Thus, they can run cost-effective marketing campaigns.
- Customer Retention: Segmentation is a customer-centric approach. It provides more customer satisfaction which ultimately results in customer retention.
Strategic approaches for segmentation
Following are the strategic approaches that help marketers during segmentation:
- Undifferentiated Strategy
As per this approach, the marketer launches products catering to a large consumer base. So, they drop the segmentation idea and form a mass marketing strategy. - Focus Strategy
Here, the complete focus is on the single defined target market. Thus, the marketers form a focused marketing strategy catering unique needs of that segment. - Differentiated Strategy
In this approach, marketers target more than one market segment. Therefore, they form differentiated marketing strategies for each segment. - Hypersegmentation
Hypersegmentation involves the creation of multiple segments. So, the marketers need to prepare customised marketing strategies.
Market Segmentation Examples
Following are real-life examples of successful application segmentation:
Lefty’s: It is a U.S. based company specialised in products for left-handed people. The company fragmented the total market of its products by focusing on a particular segment of left-handed people.
Lefty’s offers a wide range of products. Some of them are listed below:-
- Stationery
- Cooking Utensils
- Scissors
- Knives
- Mugs, etc
Kinder Joy: It is an Italian company owned by Ferro. The company has divided its chocolate market into groups. Kinder Joy is a part of Ferrero which focuses mainly on the kid’s sector.
It attracts kids by offering:-
- Surprise gifts inside the chocolate
- Blue and Pink colour packaging for boys and girls respectively.
Final Words
Market Segmentation is a process of dividing the vast diversified market into small groups. Division of the market is based on similar traits belonging to that group. Marketers narrow down their consumer base into small segments. Therefore, creating focused marketing strategies and effective campaigns.
Leave a Reply