Definition: Marketing mix is a tool for ensuring a successful marketing process by analysing the consumer’s need, determining the cost to be incurred on the product or service, deciding a proper distribution channel, communicating the product idea and information to the customers, developing a strong marketing team, channelizing the marketing activities and adjusting to the market environment.
The marketing mix concept was first developed by Neil Borden, describing it into multiple components like product, packaging, branding, pricing, advertising, promotion, distribution, etc.
Later on, these components were combined by E. Jerome McCarthy to form 4 P’s model.
Content: Marketing Mix
4 P’s of Marketing Mix
The 4 P’s concept is a traditional model of marketing mix focusing only on the goods or products and not services. The four components of this model are the product, price, place and promotion.
These elements are discussed in detail under the 7 P’s marketing mix model.
7 P’s of Marketing Mix
The 7 P’s model was given by Booms and Bitner; they proposed the additional 3 P’s in support of the services offered to the customers. The three essential variables developed under this model were people, process and physical evidence.
The elements of the marketing mix are under the control of the marketing team and the organisation to capture the prospective market and generate long-term revenues.
These variables are described in detail below:
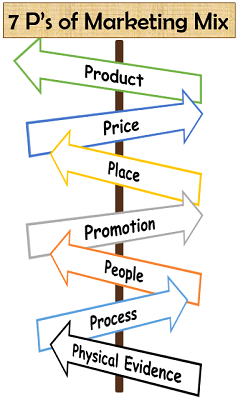
Product
The product can be anything sellable, whether tangible or intangible. Nature, quality, features, variety, design, packaging, brand, after-sale services, warranty and return policy of the product or service.
Price
The product or service needs to be priced competitively. Other additional benefits such as discounts, allowances, EMI options, credit facilities, etc. must be strategically planned and implemented while determining the pricing methods, to beat the competition.
Place
The product or service distribution must be such that it is conveniently approachable by the customers. For this purpose, decisions regarding supply chain management, target market, inventory management, transport medium and location of supply units are to be taken wisely.
Promotion
To communicate the product or service information to the customers, promotion strategies are to be framed. Promotional plans include direct marketing, sales, sales team, customer relationship management, advertising and publicity.
People
Selecting the right people to form a marketing team is essential. The focus is on the employee’s knowledge, experience, communication skills, training, development, etc. to understand customer’s needs and requirements.
Process
The marketing activities need to be aligned and planned in such a way that the consumers derive maximum satisfaction from the service offered to them. It considers factors like modes of payment, customer service, personalised touch, customisation, customer experience, etc.
Physical Evidence
The proof that the product or service is performing well in the market differentiating it from its competitors like its packaging, bills and invoices, brochures, pamphlets, web portals, appreciation, and awards, etc.
Example
Chinese smartphones brand ‘Xiaomi’ is the best example of a well-executed marketing mix.
The brand creates smartphones having the latest features competitive to those of an i-phone to meet customer’s needs. The products are priced almost half of the competitor’s products to provide high value to customers at a low price.
The most effective strategy of the brand was introducing products through its e-store as its primary market, selling the products online. Xiaomi used various communication tools like advertising through social media, creating a scarcity of the product, ‘Mi fans’ community, etc.
Thus, xiaomi became the leading brand for smartphones, manufacturing a competitive product at low cost and selling it at a low price made it popular among the consumers.
4 C’s of Marketing Mix
Robert F. Lauterborn gave the 4 C’s model. The 4 P’s model was the traditional concept of the marketing mix. Over the period, it was enhanced with the change in consumer preference and demands. Hence the 4 C’s model was developed.
Let us now know about the four components of the 4 C’s model:
- Consumer Needs: The marketers now focus on what precisely the consumers want, what are their expectations from a product or service.
- Cost: The cost here refers to the value that a product or service generates for the consumer and also its opportunity cost, i.e. the sacrifice made by not choosing its alternative.
- Convenience: The distribution strategies of a product or service must be such that it is easily accessible by the consumers.
- Communication: Effective communication in this context does not only refer to the promotion of products or services. But it is a two-way process where the consumer’s feedback to know their preference, ideas, views, experiences and queries are also openly welcomed by the marketers.
Nature of Marketing Mix
The marketing mix is concerned with the effective implementation of marketing strategies to derive maximum customer satisfaction and profitability.
Though the marketing mix seems to be a simple practice, it involves a lot of skills and tactics.
To better understand the concept, let us first study its nature:

- Needs Constant Review: With the change in market demand and preference, the marketing mix needs to be updated with all such fluctuations.
- Goal Achievement: Marketing mix is majorly concerned with the accomplishment of organisational goals.
- Customer Oriented: It is a customer-centric approach aiming at providing the highest possible value to customers against their purchase.
- The essence of Marketing Process: The whole marketing process depends upon the selection of a suitable marketing mix.
- Interlinked Variables: All the elements of the marketing mix are interconnected to each other. Thus, the marketing team has to make a proper combination of these variables.
- Flexibility: It is flexible enough to give importance to a particular element if the market conditions demand so.
Process of Marketing Mix
The marketing manager has to be wise and innovative to make crucial decisions and manage all the marketing activities efficiently.
The marketing mix is a systematic procedure involving the following standard steps:
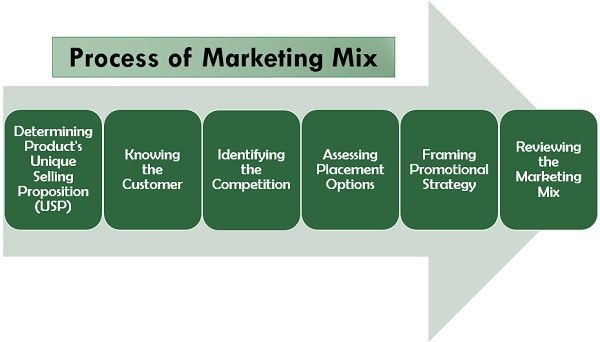
Determining Product’s Unique Selling Proposition (USP)
The USP distinguishes a product or service from its competitors. Thus, the marketing team has first to define the USP of the product or service.
Knowing the Customer
The marketing team must know its target market and value the product or service will create to the customers.
Identifying the Competition
Next step is the comparison of the product or service with that offered by the competitors to provide additional benefits or discounts and price the product or service accordingly.
Assessing Placement Options
Here, the placement refers to positioning the product or service in the market such that it is readily available to its prospective customers.
Framing Promotional Strategy
After determining the target market and price of the product or service, the marketing team frames the strategy to communicate the ideas and information to the consumer.
Reviewing the Marketing Mix
The last step is to continually check the elements of the marketing mix, whether they are aligned with the organisational objective, consumer’s preference and market conditions. If not, then make the alterations.
Conclusion
A well-planned marketing mix creates positive value for the consumer, generates good revenue for the business, helps in penetrating a competitive market and develops the economy as a whole.
Leave a Reply