Definition: Rectification of errors is a procedure of revising mistakes in the entries. These errors can be of two types, i.e, the errors committed on both sides in an entry that does not influence the trial balance and can be rectified by making a journal entry.
And another one is the errors that occur on one side of the trial balance and disturbs the trial balance are known as single-sided errors, which cannot be corrected by only passing journal entry, however, gets corrected by opening a suspense account. For understanding the rectification of errors, it is a must to understand the kinds of errors first. The kinds of errors can be understood below precisely.
Content: Rectification of Errors
- Kinds of Errors
- Rectification of Errors that do not influence Trial Balance
- Rectification of Errors which Influences the Trial Balance
- Conclusion
Kinds of Errors
Following are the kinds of errors that occur:
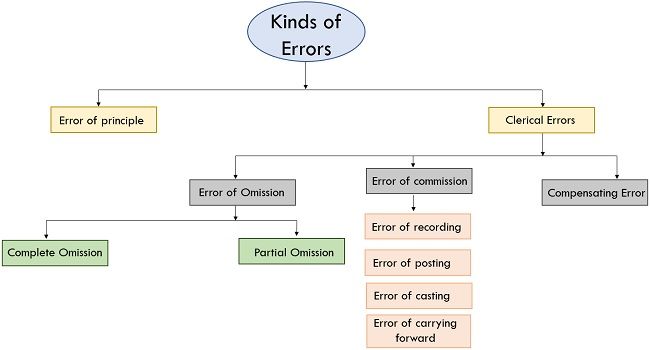
1. Error of principle
Transactions are reported by means of Generally accepted accounting principle (GAAP). In case, principles are opposed or neglected, errors of principle arise in such transactions, which will not alter the trial balance.
- Example 1: Credit sale of land reported in the sales book.
This is an error of principle as credit sale of assets doesn’t need to be reported in subsidiary books. It has to be reported in Journal Proper. Amount used up-on enhancement of fixed assets has to be considered as a capital expenditure and not revenue expenditure.
- Example 2: Spent ₹ 20000 for extra accessory to an existent machine.
Reporting as repairs a/c debit is an error of principle. Alternatively, the machine account is to be debited. A corresponding error will not affect the trial balance but will bluff the financial accounts because of this wrong allocation of capital and revenue expenditure.
2. Clerical Errors
These errors arise because of mistakes made by attentive accounting clerks, which can be more classified into subsequent categories:
1. Error of Omission
When an entry is overlooked in the books of accounts, this kind of error occurs. This may be more clearly defined as:
- Error of complete omission: When an entry of amount is completely overlooked for reporting in the books of accounts, this class of error arises.
- Example: Credit sale of ₹ 15000 to Ankit. If this transaction is neglected completely, such an error is known as an error of complete omission. This will not disturb the trial balance.
- Error of partial omission: When only one facet of the transaction is reported, this class of error arises. In the above, given example, one facet credit sales are reported duly in sales a/c, but the facet, Ankit’s account is neglected while reporting, thus the error of partial omission derives. This will influence the trial balance.
2. Error of Commission: This kind of error appears due to diversified factors like incorrect recording, incorrect posting, incorrect balancing, etc. This may be classified further as follows:
- Error of recording: This error occurs when an entry is wrongly reported in the books of the original entry.
- Example: Purchase of goods in credit from Nidhi for ₹ 14,500 reported in the books at 15,400.
- Error of posting: This error arises when facts reported in the books of original entry is recorded inappropriately in the ledger. This error may occur because of:
- Reporting the correct amount in the incorrect side of an appropriate account.
- Reporting the correct amount in the correct side of an inappropriate account.
- Recording the incorrect amount in the correct side of an appropriate account.
- Recording the incorrect amount in the incorrect side of an appropriate account.
- Recording the incorrect amount in the correct side of an inappropriate account.
- Reporting incorrect amount in the incorrect side of an inappropriate account.
- Error of casting: When an error is committed during the time of recording in a subsidiary book, this error occurs.
- Example: If the total sum of ₹ 15,000 in a subsidiary book is incorrectly added up and posted as ₹ 18,000. This is an over-casting error. If it is inappropriately added up as ₹ 11,000, it is an under-casting error.
- Error of carrying forward: When a sum of one page is recorded inappropriately on the adjacent page, the error of carrying forward arises.
- Example: Sum of cash book on page 114 of the ledger is ₹ 2,04,000. At the time of transmitting to the adjacent page 115, if it is reported as ₹ 2,40,000, this causes the relevant error.
3. Compensating Error
While two or more mistakes are committed, just like that the net outcome of these mistakes on the debits and credits of accounts is zero, these errors occur, which are termed as “compensatory errors”.
- Example: If the purchase book is over-casted by ₹8,000 which outcomes in a surplus debit of ₹ 8,000 because of which shortfall of debit in sales return account arise. These kinds of mistakes compensate one another. One surplus of ₹ 8,000 is compensated by another deficit of ₹ 8,000. The net result is zero. Therefore, these kinds of errors do not influence the trial balance.
Now, let’s understand how the rectification of error not influences the trial balance and how does it influence the trial balance.
Rectification of Errors that do not influence Trial Balance
By making corrected journal entry in the concerned accounts, these errors can be rectified, as these are the errors committed in two more accounts. The errors belonging to this category are:
- Errors of complete omission
- Errors of Principle
The process of rectifying such errors consist of the following steps:
- Reverse the entry for cancelling the effect of wrong debit or credit.
- Make a new entry with correct debit or credit.
The example of rectification of complete omission error by passing journal entry is shown below:
- Illustration 1
Credit sales to Anita ₹ 2,05,000 were not recorded in the sales book. Rectify the error.
- Solution
This type of error is known as the error of complete omission, the entry we have to make for rectifying such error will be:

The example of rectification of error of principle by passing journal entry is shown below:
- Illustration 2
Repairs to the building -1800, debited to building a/c treated as capital expenditure. Rectify the error.
- Solution
Repairs to the building is an expenditure of a revenue nature but mistakenly treated as capital expenditure. Thus, the correcting entry would be:

Rectification of Errors which Influences the Trial Balance
These kinds of errors do not get corrected by passing a single general entry, in addition with that the suspense account needs to be opened which is created to fill up the gap arrangement till error detected and rectified. When we use a suspense account, the following process is adopted to rectify errors.
- Identify the affected account due to error.
- Find the excess or shortage amount troubling the account.
- If the difference is derived because of “excess debit amount” or “short credit amount”, credit the account with the difference amount.
- If the difference is derived because of “excess credit amount” or “short debit amount”, debit the account with the difference amount.
- The entry gets completed by debiting or crediting the suspense account.
Conclusion
Rectification of errors is the method of correcting errors made in entries on either one side or on both sides of the transaction, which can be identified by making a trial balance after passing all the journal entries.
Leave a Reply