Definition: Production Function in Economics studies the mathematical relationship among the physical input and outputs of production under given technology at a certain period.
In other words, it expresses the technical relationship between input and output, i.e. the number of commodities produced and variables or factors used in production.
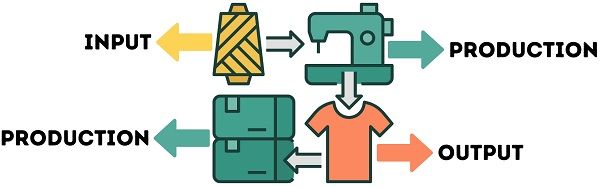
It addresses the allocative efficiency in commodities production and income distribution. Also, it determines the maximum output level the firms can produce using inputs.
It is the concept of Microeconomics, as it focuses on firms and production. However, it is also studied in Macroeconomics as Aggregate Production Function. It describes the functional relationship between Aggregate Output and Aggregate Inputs in the economy.
What is Production?
It is a process by which firms transform the inputs into outputs. Moreover, it adds value to outputs to meet human requirements and desires.
The resources used in the production of commodities are known as Inputs. The four most prominent forms of input are:
- Land
- Labour
- Capital
- Entrepreneurship
If we take the example of cloths, the fabric used in production will be the Input. Whereas, the finished product post-production will be the Output.
Besides inputs, the technology used in production also plays an essential role. As with the help of advanced technology, more amount of output can be produced with the same inputs.
Firms choose such techniques which maximize production with optimum resource utilization.
Content: Production Function
Production Function Formula
The formula for the production function is as follows:
Q = f (K, L)
where,
Q represents Output,
f stands for Function,
K indicates Capital Invested,
L indicates Labour
In words, this formula can be stated as follows: The output level generated depends on the unit of Capital and Labour invested during production.
Important Points
- It is expressed for a particular period of time, suppose for a day or month.
- It expresses a physical relationship as both factors are described in physical terms.
- The relationship is purely technological. This is because, the commodity produced from inputs depends upon the state of technology.
Types of Production Functions
Depending on the time period, two types of production functions can be seen:
- Short-run Production Function
- Long-run Production Function
Short-run Production Function
It is the type of production function that shows changes in output with the change in one variable. Here, the other factors remain constant.
There are two theories based on short-run production function:
- Law of Variable Proportion
- Return to Factor
Long-run Production Function
All the variables are changed in this production function but in the same proportion. Here, all the factors are variable, and the size operation can be increased or decreased as required.
The theory based on the long-run production function is ‘Return to Scale’.
Factors of Production
Understanding the factor of production is a must while studying production function. This is because it is vital in determining the output level and much more.
Broadly, factors are categorized under two main heads: Fixed Factors and Variable Factors.
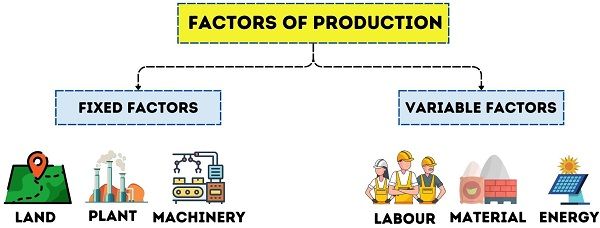
- Fixed Factors: That does not change with the change in the volume and level of output. Example, Land, Plant and Fixtures.
- Variable Factors: Its quantity changes with the change in volume and level of output. Example, Labour, Material and Energy.
What are Short-run and Long-run
The nature of the production function greatly depends upon the time period. This period is divided into two spans, i.e. Short-run and Long-run.
Short-run
It is the span wherein the firms don’t have sufficient time to increase output scale. During this period, fixed factors of production cannot be changed. Thus, firms can only increase the output by increasing the variable factors.
Example: Suppose XYZ Baker’s received an order to deliver 2000 Cakes and Cookies in 4 days.
In this scenario, the baker cannot immediately install additional ovens to fulfil the demand. But, it can increase the number of workers and make them work overtime to meet the demand.
Long-run
It is the duration wherein the firms can increase the scale of output. Also, all the factors of production can be changed as per the requirement. Therefore, firms can increase all the variables to increase the output level.
Example: In the above example, if the delivery date had been two months.
In this case, XYZ Baker’s had enough time to make the necessary arrangements to complete the order. It can increase its capacity and complete the order with the same number of workers.
Example
Suppose a vendor uses only two factors to produce plastic bottles, i.e. Plastic and Machinery.
The machine has the capacity to produce 100 bottles. Besides, to produce 1 bottle, he needs 10 grams of plastic. Here, the production function will specify the maximum number of bottles the vendor can produce with the machinery and plastic.
Final Words
To sum up, it explains the technical relationship between the input and output required in production. Here, technology and time are important as they affect the output level. For this reason, we can call it a technical problem rather than an economic problem.
It is also a base for many laws of economics, like the Law of Variable Proportion and Return to Scale.
Tope Oyemolade says
Thanks for a precise and concise explanation. I really love it , you can still put some calculations there for some of us that would like to have some calculated examples.