Definition: The Master Production Schedule (MPS) is the master level product-wise schedule made for the individual end-products or sub-parts of the products in order to get detailed information about the overall manufacturing.
Moreover, we can also understand it as the Disaggregation of the Aggregate plan. As it creates separate schedules for every single item of the aggregate plan.

Besides, it also provides an insight into all the items listed in the Bills of Material (BoM).
MPS is an integral part of the Resource Management System. It determines the current and future resource requirements in the manufacturing unit. Also, it states:
- When the product will be demanded?
- In what quantity the product will be demanded?
It is one of the operational tools for production management. Therefore, the success and failure of MPS affect the firm’s profitability.
Generally, the planning horizon of these types of schedules is small. The firms prepare it for an Hour, Day, Week or Month as required.
Usually, firms prepare MPS for a horizon of 3 to 18 months.
It is helpful for firms in transforming the aggregate plan into product-wise plans. It acts as a base for Income Planning post-critical analysis.
MPS also helps organizations to sync their efforts, become profitable and boost efficiency. Consequently, it demands collaboration from different departments and their approval.
Master Production Schedule Specifies:
- Product Specification
- Variants & Sizes
- Materials, etc
Some part of the MPS is kept constant, called as Frozen Zone. This zone helps in maintaining consistency and facilitates comparative analysis.
Note: Today, the manufacturing units prepare the MPS online over software.
Content: Master Production Schedule
- Master Schedule, Master Production Scheduling and Scheduler
- Master Production Schedule Principles
- Goals
- Uses
- Importance
- Functions
- Inputs for MPS
- Output for MPS
- Master Production Schedule Working
- Areas of concern
- Example
- Conclusion
What are Master Schedule, Master Production Scheduling and Scheduler?
Master Schedule provides information about the product’s quantity and delivery timings. However, it does not cover any information regarding the production plan.
The activity of preparing Master Production Schedules is known as Master Production Scheduling. And the person who prepares these schedules is known as Master Production Scheduler.
Master Production Schedule Principles
The scheduler must follow the principles given below while framing the MPS:
- Should be capable of matching the Production plan volumes as stated by the Top-management via Sales plan.
- The schedule must cater to the demands of internal and external customers.
- Formation of a simple MPS by making the operational environment lean and simple.
- Thoughtful use of the option of postponement. And during that span, align your structure, processes and schedules.
- Try to carry out production as per the Finish-to-order strategy.
- The control must remain with the managers during scheduling. They must only use computers as helping aid.
Goals
The goals behind creating the Master Production Schedules are as follows:
- Schedule and deliver the end products as per the end-users requirement.
- Extracting the best out of available resources.
- Making attainable delivery targets and meeting these targets.
- Fulfilling the objectives set by the Sales and Operations Teams.
- Save the company from lower production and losses.
Uses
The manufacturers use MPS to:
- Quantity Production
- Identify Bottlenecks
- Anticipate Requirements
- Achieve Production Targets
Importance
The Master Production Schedule (MPS) benefits manufacturing firms in the following ways:
- It bridges Material Resource Planning (MRP II) and Final Assembly Schedule (FAS).
- MPS is a type of detailed plan that clearly defines the priority plan.
- It facilitates the ascertainment of resource requirements and availability.
- The organizations can provide and achieve promised deliveries.
- MPS also clarify the changes and reason for changes in the production schedules.
- These schedules are the roadmap for different departments related to production.
- Assess the requirement and availability of machines for production and their sub-parts.
- Helpful in achieving the firms’ aggregate goals.
Functions
MPS performs the following functions in the manufacturing unit:
- Transformation of the Macro plans into Micro plans.
- Formation and analysis of the alternative schedules.
- Ascertain material and capacity requirements.
- Best utilization of available facility and its capacity.
- Creation of alternative plans as per the requirements.
Inputs for MPS
The scheduler retrieves data from different sources to frame the master production schedule. So, we refer to the sources of data collection as Inputs.
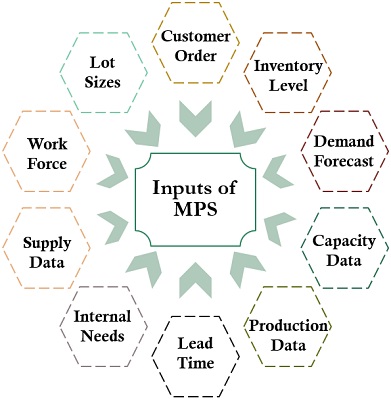
Following are some of the sources that can be taken as Input for the MPS:
- Orders from Customers and Dealers
- Inventory levels, Money and Progress
- Demand Forecasts
- Lot Sizes
- Capacity Data
- Production Data and Costs
- Lead Time
- Internal Requirements
- Supply Data
- Work Force and Work Centers
Output of MPS
Besides, after implying these Inputs, the MPS generates some Outputs listed below:
- Amounts to be produced
- Staffing Levels
- Quantities available-to-promise
- Projected available Balance
- Build Schedule Report
- Tracking Schedule
- Financial Planning
- Material Requirements Planning (MRP)
The output generated through MPS becomes the input for the Material Requirements Planning (MRP).
Master Production Schedule Working
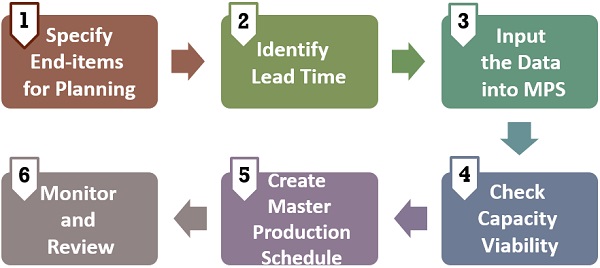
Stage 1: Specify the End-items for planning
At first, you need to segregate the product lines and categories. It will help in listing the items to be included in the MPS.
Stage 2: Identify Lead Time
The next step is to identify the lead time of the listed products. You can obtain this information from the Aggregate Production Plan.
Stage 3: Input the necessary Data into MPS
After that, Input the data required to frame the MPS. You can take the Input data from the list of sources given above.
Stage 4: Check capacity viability
Before making the schedule, you must analyze the capacity of the facility. Thus, you can use Rough-cut Capacity Planning.
Stage 5: Create a Master Production Schedule
If you have enough capacity, you can go ahead and create a product-wise MPS. However, prepare an alternative plan when the current capacity does not fulfil the demand.
Stage 6: Monitor and Review
Lastly, you must review the output generated by the MPS. Also, you need to track the actual performance with the created schedule. In the end, take necessary corrective actions in case of delay.
Areas of concern in the MPS
- Creation of a Rolling Plan based on the previous MPS analysis.
- The Planning Horizon for the preparation of the schedule.
- The part of the plan to be kept as the Freezing Zone.
- Thoughtful division of the Time Bucket and Time Fences.
Master Production Schedule Example
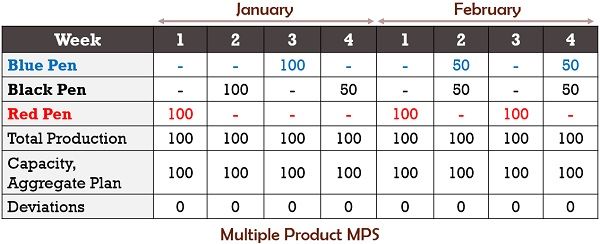
Multiple Products Example:
Given below is an example of the Master Production Schedule. It depicts a week-wise plan for January & February for three products.
Also, it shows the projected demand along with the Aggregate Production Plan.
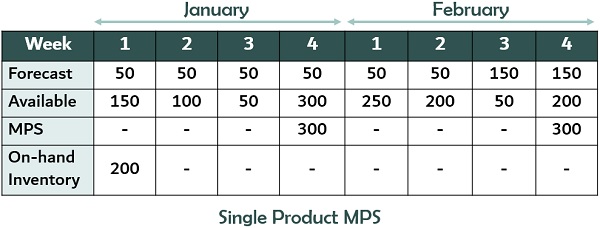
Single Product Example:
An example of a week-wise MPS for a single product for January & February is given below:
Conclusion
To conclude, MPS is a product-wise detailed plan created out of an Aggregate Plan. In addition, it provides a weekly schedule for the production with clarity.
Today, firms use ERP systems for planning and control. So, they create MPS over these systems. They just input the required data and generate the schedule. But the main emphasis is to be given to its practical application.
Leave a Reply