Definition: Exchange-traded funds are the stocks which track the performance of a particular index, which comprises a set of different securities, allowing the investor to diversify his limited funds into multiple investment options. It provides small investors with exposure to the whole sector in which they are interested in pooling their funds.
Just like mutual funds, exchange-traded funds benefit only if the investor puts in money with a long-term perspective.
Content: Exchange-Traded Funds (ETF)
Types of Exchange-Traded Funds
Exchange-traded funds can be distinguished into different categories based on the kind of security it is invested into, the level of risk involved and the nature of return it yields.
To understand each type of ETF in detail, read below: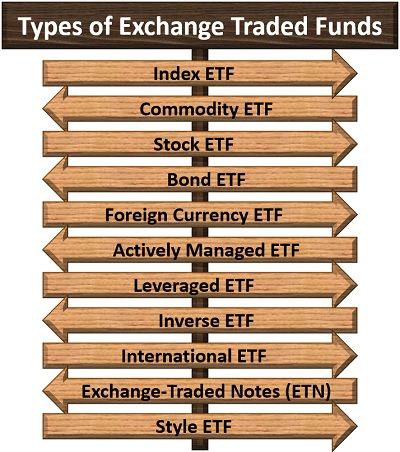
Index ETF
The index fund is the replica of a particular market index or the index of a subset of the market, providing the investors with an opportunity to invest in the whole or partial market with the limited capital investment.
Commodity ETF
An investor who is interested in trading of commodities like gold, shares, bonds, real estate and even cash can go for commodity ETFs.
A commodity ETF depends upon and fluctuates as per the price of that particular commodity in the market. Another option is a commodity stock ETF which is investing in the combined share of all the producers of that specific commodity.
Stock ETF
Stock ETFs are also known as Equity ETFs. These ETFs usually track the performance of index comprising of a combination of different equities.
Bond ETF
The investor’s objective of investing in a stable portfolio can be achieved through a bond ETF. It is an ETF share comprising of various fixed income securities or bonds like government bonds, yielding a fixed revenue to the investors.
Foreign Currency ETF
One of the most crucial exchange-traded funds is foreign currency ETF. In this ETF, individual investors also get a chance to invest in and track a particular foreign currency or a combination of various foreign currencies. It helps to make returns from currency fluctuations in the short run or long run.
Actively Managed ETF
These ETFs are made up of the securities chosen by the fund manager. The shares of an actively managed ETFs are listed in the National Securities Exchange (NSE). It is to facilitate day to day buying and selling of the shares.
All such ETFs are registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).
Leveraged ETF
To make high returns in the short run, the investors put their sum in leveraged ETFs. These are those funds which focus on increasing profits on the underlying index, through derivatives and debts.
Inverse ETF
An inverse ETF acts opposite to the stock ETF, i.e., if the index of a stock ETF keeps on falling, its inverse ETF will be rising accordingly. Thus allowing the investor to make good returns in the short position.
International ETF
The international ETF provides the investor with a chance to invest in the economies across the globe. It tracks the index of different countries to make a profit out of the economic growth of some other country.
Exchange-Traded Notes (ETN)
The exchange-traded notes are partially secured investment option for individual investors. These are issued by banks as a senior debt note which promises to pay the investors a sum equivalent to index value after deducting the management fees.
Style ETF
These type of ETFs follows a specific investment style or market cap. They usually track growth and development index to attain the desired investment objective.
Advantages of Exchange-Traded Funds
ETF acts as an opportunity for those who dream of investing in the whole sector or industry comprising of hundreds of different stocks.
Some of the significant benefits of investing in an exchange-traded fund are mentioned below: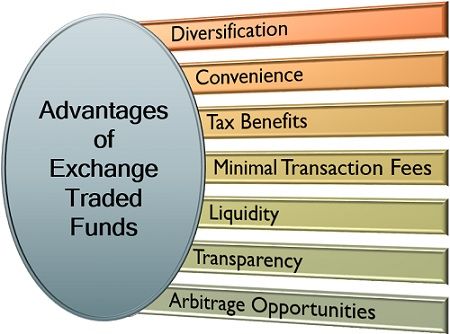
Diversification: ETF provides an opportunity for the investor to allocate his capital to a wide range of securities, eliminating the risk of loss from a particular stock. It can also be seen as a stock hedging strategy.
Convenience: The listing of ETFs on well-regulated trading portals have made the tracking of a particular ETF performance more convenient. For the new or unfamiliar investors, the exchange portals also have the option of investing in the index funds.
Tax Benefits: The investors need not pay any tax on the investment on ETFs made for more than a year. However, 10% is charged as a short-term capital gain tax on the ETFs redeemed before 12 months. Also securities transaction tax @ 0.25% is charged on redemption of ETFs.
Minimal Transaction Fees: The cost involved in the trading of ETF is comparatively less than the other investment options, which makes it more suitable for the low budget investors.
Liquidity: Unlike mutual funds, the ETFs can be traded on a day to day basis, just like the share trading is done. Thus, along with generating a fair return, the liquidity of the funds can also be maintained.
Transparency: The performance of ETFs can be traced with the help of index and trading portals. This provides for active management of the funds through the availability of clear data and figures.
Arbitrage Opportunities: The investors can also make a profit out of the price variation between the ETF and other investment options indexed for an exchange like futures. This is possible because of the index tracking facility and can be seen as a hedging strategy of the investor.
Risks Involved in Exchange-Traded Funds
Investment is always backed by some amount of risk. Though providing for diversification of funds, exchange-traded funds also involve various kinds of risk. These risks are classified as follows: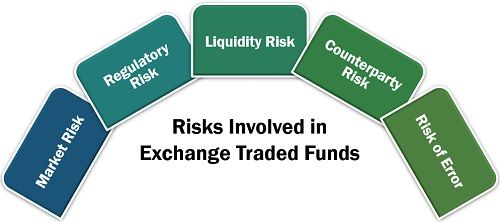
- Market Risk: In the recession, the ETF manager sometimes fails to secure a defensive position, even if he uses various strategies of exchange trade funds to achieve the desired objectives.
- Regulatory Risk: The ETFs lack compliance with regulations of FSB, BIS and IMF due to its complex structure and inadequate disclosure.
- Liquidy Risk: The trading of ETFs are backed by some of the market creators who lack active trading in the market, making it irregular.
- Counterparty Risk: The parties involved in the trading have to meet the obligation of the contract and deal is based on the monetary deposit of the exchanging parties, which involves risk.
- Risk of Error: The errors related to the valuation after the deductions like transaction fees and other expenses on ETF may arise.
Conclusion
ETF is one of the most suitable options for the ones who look forward to investing in many securities at once but have a limited sum for investment.
There are various ETF options available in the securities market, out of which the investor can choose the one that meets his investment goals in the best possible manner.
Alok kochiary says
Wow excellent