Definition: Inventory valuation or stock valuation is the method of identifying the actual value of the inventories at the end of the year. The foremost step of valuation is to ascertain the physical inventories of the company, i.e., raw material, work in progress goods, and finished goods. The main objective behind the valuation of inventory is to determine the true income and true financial position of the company.
Content: Inventory Valuation
Steps Involved in Inventory valuation
Following steps are involved in the valuation of inventory of any organization:
- Determine the cost of goods for every segment of the organization.
- Find out their net realizable value.
- Then value the inventory on the basis of the cost of goods or net realizable value, whichever is less.
Methods of Inventory Valuation
Some of the methods used for the valuation of inventory are as follows: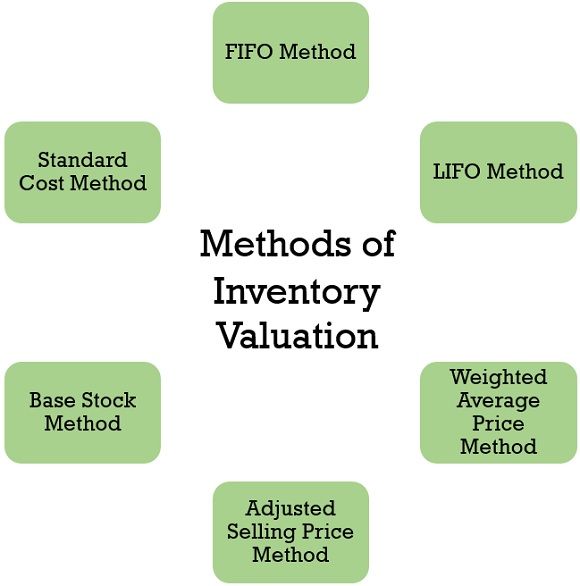
1. FIFO Method
This method of inventory valuation is the most appropriate method, as suggested by Accounting Standard – 2 (Revised). It is based on the approach of first in first out, i.e., the inventory which is purchased first should be used first, and the further purchased goods should be used, at last, i.e., the inventories used at last should be the most recent purchased goods. However, this method gets criticism as it leads to improper cost and revenue match as this method gives the cost of remaining inventories on the recent prices whereas the cost of goods sold is calculated on the basis of old prices. As this method is the most recommended method, let us understand with an example:
- Illustration
A company has an opening stock of 200 units @ 10 each for the month of June and has the following receipts and issues for the month:
| Receipts | Issues |
|---|---|
| 02/06 = 300 units @ 20/- | 05/06 = 200 units |
| 15/06 = 250 units @ 15/- | 17/06 = 150 units |
| 21/06 = 350 units @ 12/- | 25/06 = 350 units |
Prepare store ledger based on the FIFO Method.
- Solution:
Store Ledger
| Date | Receipt | Issue | Balance | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quantity | Rate | Amount | Quantity | Rate | Amount | Quantity | Rate | Amount | |
| 01/06 (Opening Stock) | 200 ------ | 10 ------ | 2000 ------ |
||||||
| 200 | 10 | 2000 | |||||||
| 02/06 | 300 | 20 | 6000 | 300 ------ | 20 ------ | 6000 ------ |
|||
| 05/06 | 200 | 10 | 2000 | 300 ------ | 20 ------ | 6000 ------ |
|||
| 300 | 20 | 6000 | |||||||
| 15/06 | 250 | 15 | 3750 | 250 ------ | 15 ------ | 3750 ------ |
|||
| 17/06 | 150 | 20 | 3000 | 150 | 20 | 3000 | |||
| 250 ------ | 15 ------ | 3750 ------ |
|||||||
| 21/06 | 350 | 12 | 4200 | 350 | 12 | 4200 |
|||
| 26/06 | 150 | 20 | 3000 | 50 | 15 | 750 | |||
| 200 | 15 | 3000 | 350 | 12 | 4200 | ||||
| --------- 13950 --------- (Total Purchases) | --------- 11000 --------- (Cost of Goods Sold) | --------- 4950 --------- (Value of Closing Stock) |
2. LIFO Method
LIFO Method works on the principle of last in first out, which means the stock purchased at last will be used first for the valuation of the stock. In this method, the recent cost of goods sold is matched with the recent sales revenue, which helps in determining correct income, and there will be no unrealized profit/loss as it is the cost-based method. However, this method is not suggested by Accounting Standard – 2 (Revised).
3. Weighted Average Price Method
This method is based on the assumption that all the goods available for sale are identical, and the cost of every unit is computed based on the weighted average of the identical opening goods and the purchased goods during the period. Weighted average price method can be effectively used in the process industries and averages out the price fluctuations effects. The formula applied for inventory valuation by this method is: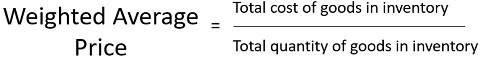
4. Adjusted Selling Price Method
As per AS-2 adjusted selling price method, also termed as retail inventory method is used in retail businesses for measuring similar margin inventories of expeditiously changing products or goods of the company.
5. Base Stock Method
This method is based on the assumption that the base stock should always be maintained for running any business appropriately. It is advantageous for the company as unrealized profits are eliminated, and the net income figure is reliable from a long-run point of view.
6. Standard Cost Method
Under this method of inventory valuation, the definite cost of every product is set, which serves as a base price for issued material pricing. This method reduces the repeated cost computation made on every new receipt of a new material lot, and it helps in making material price variance and material usage variance account to find out the purchase-related efficiency of activities.
Objectives of Inventory Valuation
The following are some of the objectives of inventory valuation:
- Ascertaining the Exact Income
For determining the accurate or exact income of the company, the cost incurred should match with the proceeds during the year for which proper valuation of inventories is essential to ascertain the gross profit. The cost of goods sold makes a huge impact on the sales revenue of the company since the cost of goods sold is computed by adding the opening stock and purchases of inventories during the year and deducting the closing stock of the inventories from it. Thus, proper inventory valuation is essential. If it is not done properly, it may affect the profit of the company. Thus, proper inventory valuation fulfils the objective of ascertaining the exact income of the company.
- Disclosing true and fair financial position
Financial statement of the company discloses the true and fair financial position of the company at the end of the year. The inventory plays a most important role in the company’s financial statement; being the most prominent asset it should be appropriately valued for disclosing the company’s fair position.
Significance of Inventory Valuation
Inventory valuation plays a prominent role in evaluating the profitability of a business. Let us understand it with some more points:
- Inventory acts as a backbone for any business enterprise as the enterprise’s current assets involve more than 75% of inventories. Thus inventory valuation plays a significant role in measuring the assets of the business.
- Inventory valuation is mandatory to find out the liquidity position of an enterprise as creditors always have an eye on the liquidity position of the business.
- Inventory valuation also plays a vital role in evaluating the gross profit of any business as without proper valuation of stock; true profit cannot be ascertained.
Conclusion
Inventory valuation comes under the Accounting Standard – 2, and it defines the value of the most important asset of the company, i.e., inventory, which is held by the company for the purpose of production of goods for sale in the form of raw material, work-in-progress and finished goods. Inventory valuation is mandatory for all the entities to show the true and fair financial position of the company.
Leave a Reply