Definition: The term “Indirect Investing” describes the process of investing money in a portfolio of bundled securities through an intermediary. In simple words, these are third-party investments made through intermediaries.
Investors who resist investing directly in the stock market opt for this type of investing. They prefer investing in funds owned and managed by financial intermediaries.
These intermediaries are investment companies who invest directly in the exchange. Here, the returns depend upon the fund manager’s efficiency in managing funds.
The investor opts for indirect investment when they are:
- Not willing to take the high risk
- Don’t have knowledge about the exchange
- Expects minimum returns from their investment
- Cannot spend time studying stock market trends
- Needs professional help
Investors pay their share of the company’s expenses and fees on a pro-rata basis to the company. Whereas, the company pays the pro-rata share of the return generated to the investor.
In this form of investment, intermediaries take investment decisions. And there is no direct link between the investor and the investee. Thus, they do not take the buying and selling decisions.
The most common form of indirect investment is Mutual Fund and Pension Fund. Besides these, one can also invest in the real-estate sector without actually owning the asset.
Content: Indirect Investing
- Example
- Investment
- Types of Investment Companies
- Direct Investing vs Indirect Investing
- Advantages and Disadvantages
- Final
Example of Indirect Investing
Joy, a marketing professional, recently got a 30% hike in his salary. He is planning to invest some of this surplus money.
But, he fears the share market and fixed deposits yield fewer returns. So, he decided to invest indirectly through the Mutual Fund of a renowned AMC.
The fund manager looks after the fund’s performance, and Joy enjoys his returns.
Some top investment companies in the world are listed below:
- BlackRock
- JPMorgan Chase
- The Vanguard Group
- Allianz
- Fidelity Investments
Investment Companies
It is a financial organization that creates, invests and manages a portfolio of securities. It is a pure intermediary that accepts investors’ funds and generates returns on their behalf.
Investment companies create a portfolio of diversified securities considering the risk & return profile. The portfolio is created by the pool of funds accumulated by various individual investors.
Besides investment, these organizations offer some benefits to investors furnished below:
- Diversification
- Professional Assistance
- Liquidity
These organizations are not guaranteed by any authority or financial institution. Moreover, their funds are also subjected to market risks. They often convey this through their promotional campaigns and documents. Thus, the investors may even suffer losses.
Types of Investment Companies
There are four different types of investment companies as follows:
- Unit Investment Trusts (UIT)
- Exchange-traded Funds (ETF)
- Open-ended Funds (Mutual Funds)
- Closed-ended Funds
Unit Investment Trusts (UIT)
It is a financial institution that provides fixed portfolios of stocks and bonds. These portfolios are basically for capital appreciation and income generation. An independent trustee handles these funds.
Example: Equity Investor Funds
Exchange-Traded Fund (ETF)
It is the latest form of investment company comprising an unmanaged portfolio. Here, the stock basket targets a particular segment like – investment style, geographical area or market.
Like close-ended funds and other stocks, ETFs are also traded on the exchange.
Examples: Bond ETFs, Currency ETFs, Commodity ETFs, Sector/Industry ETFs, Foreign Market ETFs, etc.
Closed-ended Funds
It is the oldest form of investment company. The close-ended fund contains a fixed number of shares traded on the exchange. Also, these funds have a fixed market capitalization.
Example: Municipal Bond Funds
Open Ended Funds – Mutual Funds
It is the most common type of investment company. It is basically a mutual fund that can issue unlimited shares.
In open-ended funds capitalization of shares keeps on changing. This is because, new investors buy shares, and existing ones may sell the shares back to the company.
Examples: Mutual Funds, Hedge Funds, etc.
Direct Investing vs Indirect Investing
Both forms of investments generate returns for the investors. But, the primary difference is that the investment company stands between the investor and the portfolio of securities.
Let’s explore the differences between direct and indirect investment based on the below points.
- Ownership: The investor actually owns the complete or a part of the asset in direct investing. Whereas, in indirect investing, they are only exposed to risk and return associated with the asset/securities.
- Selection Risk: Direct investing involves high selection risk compared to indirect investing.
- Mode of Investment: Investors invest directly through financial markets. However, they invest indirectly through financial intermediaries.
- Market Monitoring: Constant market monitoring is necessary for direct investing to generate good returns. In contrast, fund managers track the market for investors in indirect investing.
- Portfolio: Investors create their own portfolio of investments in direct investing. But, in the indirect form of investing, intermediaries create portfolios in which the investors invest their money.
Advantages and Disadvantages
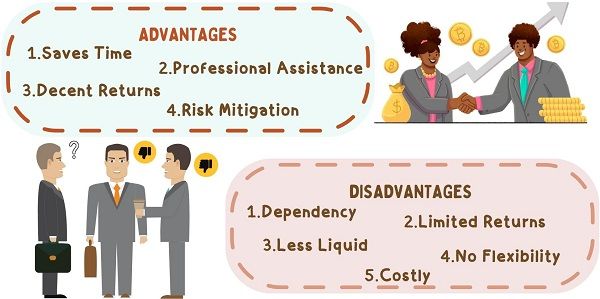
Indirect investing has the following advantages:
- Saves Time: It is a time-efficient alternative. As it saves investors time in the decision-making and monitoring of the fund’s performance.
- Professional Assistance: Investors may not have adequate know-how about investing. Therefore, investment companies manage funds on their behalf.
- Decent Returns: The stock market is volatile and full of uncertainties. Investment companies create a pool of funds and generate decent returns for all individual investors.
- Risk Mitigation: This investment alternative is less risky. This is because, the fund managers diversify investments and keep some secured investments.
The following are the disadvantages of Indirect Investing:
- Dependency: Individual investors are completely dependent on the fund managers. The reason being they maintain the portfolio and takes necessary decisions.
- Limited Returns: The generated returns are less compared to direct investments. As they invest in different securities to generate minimum returns.
- Less Liquid: Here, the investments are less liquid as compared to direct investments.
- No Flexibility: They only have the authority to switch or liquidate the fund rest of everything is managed by the fund manager.
- Costly: The investors owe many fees besides brokerage to the investment company.
Final Words
The investor must choose between direct and indirect investments wisely. Both alternatives have some advantages and disadvantages attached to them. Also, they must consider investment-related market risks.
Leave a Reply