Definition: Indexation is relief on long-term investments. A long-term investor can claim it merely by showing that, the value of their assets raised is not a real gain, but it rises only due to inflation. It is the inevitable link between monetary constraints and price level. It diminishes the cost of inflation and is enforced on interest, taxes and wages. For instance, employers are compelled to index wages across prices to reduce the divergence among money income and real income.
The interest of long-term loans is so driven that the debtors would have to repay the borrowings in absolute terms. In lack of Indexation, unanticipated inflation, by destroying the actual value of loan deviates the belongings from a money lender to debtors and disturbs the credit structure, and for that reason the capital market. For instance, NSC (National Saving Certificates) are index associated. The purchasing power parity theory of rate change measurement in international economics is again a model of Indexation. The Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Of nations is further restrained on the basis of purchasing power parity(PPP).
Indexation of wages is essential, and the prevailing system in various countries where wages agreements are abiding agreements and inflation survive to endure. In those situations, compensating employees for the trouble of their real income as a result of inflation becomes inescapable and two approaches are accepted primarily; they are as follows:
- Link wages to cost of living index.
- Create a regular set-up of wages increase, later CPI escalates by a definite percentage point.
As per CBDT (Central Board of Direct Taxes), an investor can claim Indexation by simply comprising their asset with the cost of Inflation Index (CII).
Content: Indexation
- Formula for calculating Indexation
- What is the Price Index?
- What is Base Year?
- Cost inflation index (CII) from the financial year 2001-2002 to 2020-21
- Effect of Indexation on Debt Funds
- Benefit of Indexation
- How can an investor maximize Indexation?
- Conclusion
Formula for calculating Indexation
What is the Price Index?
Price index shows the relative change in the price level, by comparing the price index of two years the government or various index preparing agencies can see that what has happened in general to the price level. If the price level index has increased, it means that there is an increase in the price level. Thus, it can be said that index is a specialized average and is mainly used to measure the relative change in a price level, through price index, we measure inflation.
For that, we need to understand how price level index is constructed but to construct the price level index first; we need to understand the concept of a base year.
What is Base Year?
Base year is nothing but a particular normal year which the government took to measure the price level and fix that year as a base year. While selecting base year one needs to keep in mind, it should be a normal year (prices should be normal in average years) and not an abnormal year (prices are not too high or now too low in that year). According to every commodity and its prices of the base year will be set as a base price and with that price only we will compare. Thus, we need a base year to compare the relative change in the price level.
Base year is mainly used for constructing the price index. To construct price index what government or agencies preparing indexes normally does is, if they want to create the present year price index, they check it with the following formula:
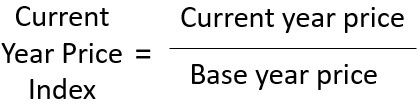
And inflation is calculated in relation to the price index of the previous year and formula for calculating Inflation rate is as follows:
Cost inflation index (CII) from the financial year 2001-2002 to 2020-21
| Financial Year | Cost of Inflation Index (CII) | Financial Year | Cost of Inflation Index (CII) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2001-2002 | 100 | 2011-2012 | 184 |
| 2002-2003 | 105 | 2012-2013 | 200 |
| 2003-2004 | 109 | 2013-2014 | 220 |
| 2004-2005 | 113 | 2014-2015 | 240 |
| 2005-2006 | 117 | 2015-2016 | 254 |
| 2006-2007 | 122 | 2016-2017 | 264 |
| 2007-2008 | 129 | 2017-2018 | 272 |
| 2008-2009 | 137 | 2018-2019 | 280 |
| 2009-2010 | 148 | 2019-2020 | 289 |
| 2010-2011 | 167 | 2020-2021 | 301 |
Effect of Indexation on Debt Funds
Now let us understand the effect of indexation on the debt funds of investors with an example:
Situation
Mr. A (Investor) purchase a debenture of ₹ 100 in 2016 and sold at ₹ 140 in 2019. Cost inflation index (CII) for the year 2016 was ₹ 825 and Cost inflation index (CII) for the year 2019 is ₹ 979.
Analysis
Based on the above-given data, we can notice a long-term capital gain of ₹ 40 on which the investor has to pay tax under long-term capital gain. Now, let’s see what’s the real gain of an investor with the benefit of Indexation.
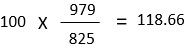
- After Indexation gain

Thus, it is noticed that investor has to pay tax on long term capital gain of ₹ 40, and after Indexation, he has to pay tax on the only long-term capital gain of ₹ 21.34. Therefore, an investor gets benefited with the Indexation in the long-term.
Benefit of Indexation
Indexation deals with calculating the purchase price, after regulating for inflation index, as issued by the Income Tax Department. As the purchase price is regulated for inflation, the amount of capital gain decreases. In case, long-term capital gain for non-equity funds, the financier can use the indexation benefit.
How can an investor maximize Indexation?
Indexation can be doubled or maximized with the help of the following trick or process:
- Acquire an asset at the beginning of any financial year and sell it at the beginning of another financial year. In this way, the one will get benefited with the Indexation of both the years, i.e., the current year as well as the previous year.
Conclusion
Indexation is a process by which prices and wages partly or entirely reimbursed for adjustment in the general price level. Therefore, it is not a procedure for regulating inflation. It is the process of adjusting monetary incomes so as to reduce the excessive gains and deficits in real incomes of inflation. Its main purpose is to oversee social dissatisfaction and to make inflation obvious to live with it.

Leave a Reply