Definition: Consumer Price Index or CPI is the universal measure used for estimating the general price level of the goods and services produced in any nation. Every month the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) computes and report the Consumer Price Index. It is a calculation of the accepted price paid by the metropolitan as well as rural users for a market basket of consumer goods and services.
When the prices in the given nation flaunt an extended rising trend, it is termed as “Inflation”, i.e., a steady increase in CPI is called inflation and the annual change in the CPI is used to measure annual inflation.
Content: Consumer Price Index (CPI)
- Formula
- Important Elements
- How to calculate
- Consumer Price Index Chart of India from 2010-2019
- Categories of Consumer Price Index (CPI) in India
- Importance of Consumer Price Index (CPI)
- Difference Between CPI and WPI
- Conclusion
Formula for computing Consumer Price Index
Important Elements of Consumer Price Index (CPI)
For understanding CPI, it is necessary to understand the following terms:
1. Market Basket
Market basket is nothing but the group of goods and services used to analyze the changes in their prices year to year. The flow of prices in a nation is restrained in accordance with a basket of products. i.e., all goods created that a standard family of urban wage earners buys at the time of one month. For example Milk, rent, clothes, gas cylinder, medicines, etc. The real basket includes these products and various other products. The price that we have to pay to buy all the goods in the basket is known as “basket price”.
2. Index
Let us understand it with an example:
The index controls the basket price outset on a base date. In the figure below the index is denoted as 100 points, and the subsequent figures are larger or smaller depending upon related to the initial figures. The basket price on the base date is ₹3500. This price associate with 100 points although on the base date the index also equals 100 points.
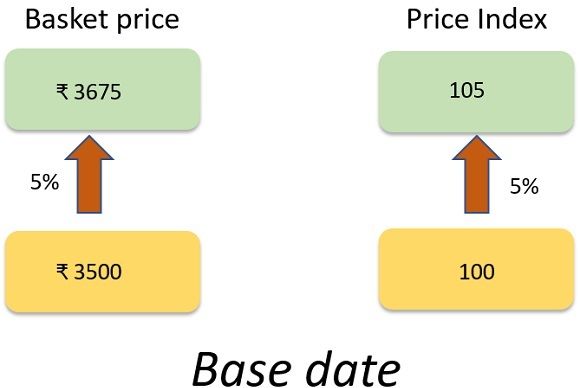
After taking the base date, the basket price rose by 5%, i.e., from 3500 to 3675 ₹. The increase in the basket price reflects a parallel rise in the index. The index will therefore rise in the same proportion from 100 to 105 points. The CPI measures the average change over time in the price of the basket of products consumed by an average household.
How to calculate the Consumer Price Index (CPI)?
When the Bureau of Labor Statistics computes the CPI and the inflation rate, it desires data on the prices of thousands of goods and services. The table below shows the five steps that BLS adopt
| Step 1 Evaluate consumers to ascertain a fixed basket of goods | ||
| Basket = 4 kg Wheat, 2 Kg Rice | ||
| Step 2 Identify the price of every good in each year. | ||
| Year | Price of Wheat | Price of Rice |
| 2017 | 25/ kg | 30/kg |
| 2018 | 27/kg | 34/kg |
| 2019 | 29/kg | 38/kg |
| Step 3 Calculate the cost of the basket of goods in each year. | ||
| 2017 | (25 ₹/kg * 4 kg) + (30 ₹/kg * 2 kg) = | 160 ₹/ basket |
| 2018 | (27 ₹/kg * 4 kg) + (34 ₹/kg * 2 kg) = | 176 ₹/ basket |
| 2019 | (29 ₹/kg * 4 kg) + (38 ₹/kg * 2 kg) = | 192 ₹/ basket |
| Step 4 Pick one year as a base year (2017) and calculate the CPI in each year. | ||
| 2017 | ( 160 ₹/ 160 ₹) *100 = | 100 |
| 2018 | ( 176 ₹/ 160 ₹) *100 = | 110 |
| 2019 | ( 192 ₹/ 160 ₹) *100 = | 120 |
| Step 5 Use the CPI to calculate the inflation rate from the previous year. | ||
| 2018 | (110-100)/100 * 100 = | 10% |
| 2019 | (120-110)/110 * 100 = | 20% |
Let us understand all the steps mentioned in an above table in a precise manner:
- Fix the Basket
Ascertain which prices are most relevant to the usual consumer. If the regular consumer buys more wheat than rice, then the price of wheat is more relevant than the price of rice and therefore, must be given higher weightage in mapping the cost of living. The BLS fixes this weightage by examining consumers to locate the basket of goods and services by the usual consumers. In the example table shown above, the usual consumer buys a basket of 4 kg wheat and 2 kg rice.
- Identify the prices
Detect the prices of every goods and service in the basket at any moment. The above table displays the prices of wheat and rice for three distinct years.
- Estimate the basket’s cost
Utilize the data on the amount to compute the price paid for the basket of goods and services at various times. The above table shows this computation for all of the three years. It should be noted that only the prices in this computation change by balancing the basket of identical goods (4 kg wheat and 2 kg rice). We are disconnecting the effects of price reversal from the effect of any quantity transformation that perhaps materialize at the same time.
- Select a base year and calculate the index
Stipulate one year as the base year, the reference point counter to which other years are compared. The selection of base year is irrational, as the index is used to evaluate changes in the cost of living. In the example table above, 2017 is taken as the base year, and the CPI is measure by the above-mentioned formula of CPI. i.e., the cost of the basket of goods and services in each year divided by the cost of the basket of a base year multiply by 100. The derived number is the Consumer Price Index.
- Calculate the inflation rate
Take the Consumer Price Index to compute the inflation rate, which is the proportion of change in the price index from the previous period, i.e., the inflation rate among two successive years is calculated as follows:

As shown in the last step of the table, the inflation rate in our illustration is 10% in 2018 and 20% in 2019.
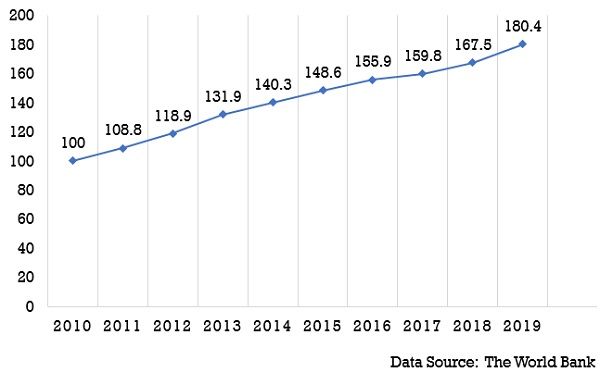
Consumer Price Index Chart of India from 2010-2019
Categories of Consumer Price Index (CPI) in India
Categories of CPI of India is primarily divided into two parts; they are as follows:
1. According to the workforce
CPI of India, according to the workforce, can be divided into subsequent categories:
- CPI for Agricultural Labour.
- CPI for Rural Labour.
- CPI for Industrial workers.
- CPI for Urban Non-Manual Employees.
2. According to time
CPI of India, according to the time is as follows:
- Average Annual Inflation Rate.
- Point to point Inflation Rate.
Importance of Consumer Price Index (CPI)
CPI of India is an essential factor in calculating the inflation of the country. Importance of CPI can be understood with subsequent points:
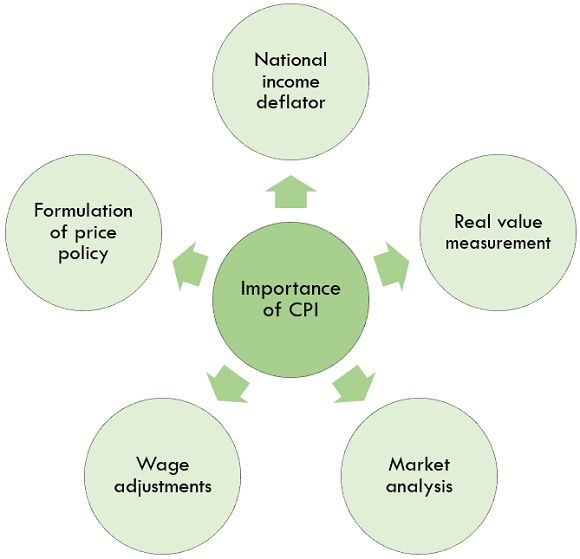
- Formulation of price policy: It acts as a helpful tool for the government for the formulation of price policies.
- Wage adjustments: Consumer Price Index helps in making agreements or contracts regarding the wages of the workers of the organization.
- Real value measurement: Consumer Price Index aids in measuring real income or national income.
- Market analysis: CPI helps in analyzing the market of specific commodities by measuring its demand and supply.
- National income deflator: It shows the real change in estimating the national income of the nation.
Difference between CPI and WPI
| Basis for Comparison | CPI | WPI |
|---|---|---|
| Full Form | Consumer Price Index | Wholesale Price Index |
| Definition | CPI is a price index which displays the average cost of a basket of goods and services over time. | WPI is a barometer of a price variations in the wholesale market.It determines the amount paid by the wholesalers and manufacturers in the market. |
| Released By | Central Statistics Office (Ministry of statistics and program implementation). | Office of Economic Advisor (Ministry of Commerce and Industry). |
| Cost Evaluation | It evaluates the cost of both goods and services. | It evaluates the cost of goods only. |
| Inflation Analysis | CPI analyzes inflation at the last step. | WPI analyzes inflation at first step. |
| Goods and Services covered | CPI includes transport, food, education, housing and medical care. | WPI comprise power, fuel and manufacturing goods. |
| Base year | A calendar year is taken as the base year. | A financial year is considered as base year in WPI. |
| Price bearer | The consumer confronts prices in CPI. | Manufacturer and wholesaler bears the price in WPI. |
| Used By | 175 countries of the world use CPI. | WPI is used only by some countries. |
Conclusion
Consumer Price Index is a method to measure inflation that is commonly used throughout the world. Each country examines different sets of goods but uses a similar approach. The CPI is determined by variations in the cost of goods and services in the market basket.

Leave a Reply