Definition: Management By Objectives (MBO) is the process of setting achievable goals for the managers and employees at all the levels to be accomplished within a stipulated period. It streamlines the plan of action of the workforce and establishes their roles and responsibilities.
The concept of MBO was introduced by Peter Drucker in his book ‘Practice of Management’ in the year 1954. In general terms, it is also called as MBR (Management By Results) or PRIDE (Performance, Result and Individual Development Evolution).
Content: Management By Objectives (MBO)
Elements of MBO
MBO includes multiple components which constitute the organizational goals and vision. These elements are as follows:
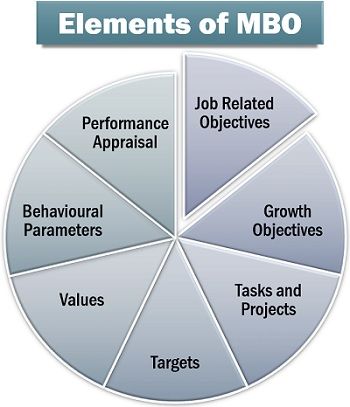
- Job-Related Objectives: In MBO, employees are briefed out on the common organizational goals along with their individual goals and expectations of the organization.
- Growth Objectives: Here, the emphasis is on the long-term organizational goals and the expected growth in future. Also, individual growth is linked to organization growth.
- Tasks and Projects: This is the part where the roles, responsibilities, duties and projects to be handled by each individual are chalked out.
- Targets: The vision of the organization, in the long run, is well-defined, and the individuals are directed to aim at these set objectives.
- Values: Another crucial element of MBO is the organizational values, perception, beliefs and business ethics.
- Behavioural Parameters: The management also defines the individual’s code of conduct, attitude and response to a particular situation.
- Performance Appraisal: MBO also includes the evaluation of individual performance concerning the efforts and contribution made by each employee for the growth of the organization.
Characteristics of MBO
Some may say that MBO is just about framing the business goals and objectives, but it is much more than that. Following features of MBO will broadly enlighten the above statement:

Resource Optimization: MBO ensures the proper utilization of the available resource (i.e., human resources) eliminating the wastage of these resources in terms of time and efforts.
Goal Orientation: The initial step in MBO is the goal formation, and all the efforts are directed towards the accomplishment of these set objectives.
Multiple Accountability: In MBO, goals are formed for the employees, and therefore, everyone has their course of action for which they are individually accountable.
Universally Applicable: The concept of MBO can be applied to almost all the organizations, whether business entities or non-profit organizations.
Systems Approach: It is applied to the whole system and thus integrates the efforts of the individual, the organization and its environments in a single direction.
Simple and Comprehensive: Since MBO is a non-technical process, it can be easily understood by all types of managers and employees.
Operational: It is practically applicable to the day to day business operations, and the performance can be evaluated periodically by comparing the actual result to the desired outcome.
Employee Management Participation: The top management does not just set the goals in MBO but involves the active participation of the employees and the managers too.
Key Result Areas (KRA): The priority zones in the organization which require special attention and are considered to be crucial for the growth and development of the business are termed as KRA. Thus, MBO focuses on this KRA for enhancing the overall performance.
MBO Process
MBO is not a process; instead, it functions as a cycle where the continuous process of goal formation and its accomplishment repeat after short intervals.
The process of MBO includes the following six steps:
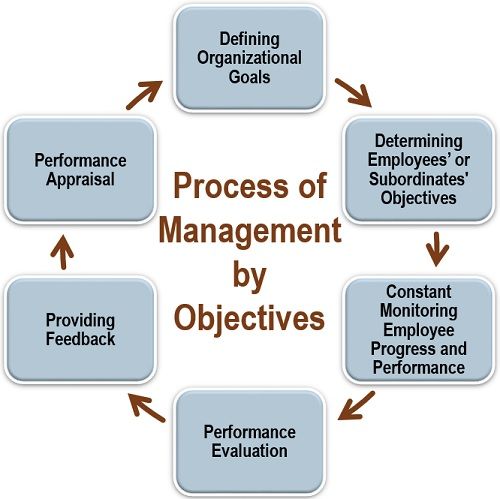
- Defining Organizational Goals: The initial step is to establish the short-term and long-term organizational goals and objectives which evolves from the mission and vision of the company.
- Determining Employees’ or Subordinates’ Objectives: The next step is to define the individual goals and objectives. For this, opinion is taken from the employees on their ability of goal accomplishment and targets which they will set for themselves.
- Constant Monitoring Employee Progress and Performance: The managers need to continuously monitor the performance of each employee to identify any loopholes or hurdles in business operations.
- Performance Evaluation: After monitoring the work, the managers need to evaluate and review the performance of every individual to spot any scope for improvement.
- Providing Feedback: With the help of the above evaluation, the managers now need to give valuable feedback to every individual to motivate them. And, at the same time making them aware of their weaknesses and potential for improvement.
- Performance Appraisal: The last step is reviewing the performance of the employees regularly to bring in efficiency in their workstream.
As these goals are usually set for short-term, the process can be repeated again and again.
Suggestions for Successful Implementation of MBO
To successfully apply this technique to the business organization, one must consider the following tips or points:
- The goals should be simple, smart and attainable.
- There should be a high degree of commitment from the top management too.
- The short term goals should be established (like monthly or quarterly) to reduce monotony.
Advantages of Management By Objectives
In the 1960s and 1970s, the theory of Management By Objectives was applied by many well-known companies like Google, Microsoft, Hp, Xerox, etc. to improve their business strategies.
MBO has been beneficial to the organizations, superiors and subordinates in many ways. Let us now discuss these in detail below:
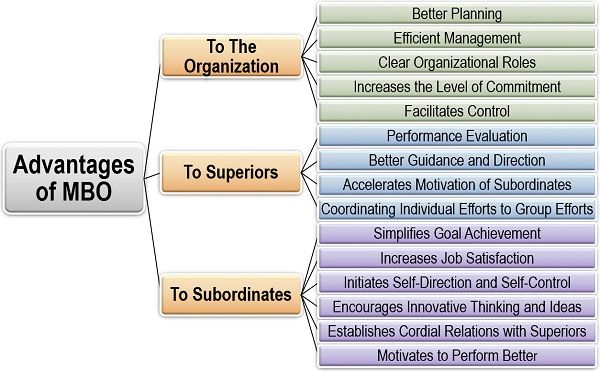
Advantages to the Organization
MBO is a strategical approach adopted to streamline the business activities and direct the individual and group efforts towards the attainment of the organizational goals.
Following are some of the other benefits of MBO to the business entities:
- Better Planning: When the organization knows what it wants to achieve, i.e., its goals, it becomes quite easy to plan in that direction.
- Efficient Management: MBO increases the efficiency of the organization to achieve its goals or objectives within a pre-determined time frame.
- Clear Organizational Roles: MBO provides a goal, target and objective for each employee. It also defines their individual and group roles clearly, to avoid any confusion or doubt.
- Increases Level of Commitment: When the employees have a clear goal or target, with a well-defined course of action, their level of commitment to give the desired results enhances.
- Facilitates Control: It becomes easy for the management to review and control the activities of the employees because of MBO.
Advantages to Superiors
Superiors control the functioning of the subordinates and monitor their performance. There are many benefits of MBO to the superiors; some of these are explained below:
- Performance Evaluation: MBO establishes a framework for every employee, thus providing a basis for the evaluation of individual performance.
- Better Guidance and Direction: When the subordinates know what they have to do, it becomes easy for the superiors to guide and mentor them in the same direction.
- Accelerates Motivation of Subordinates: Since MBO increases the level of commitment and enthusiasm of the employees towards their work, the superiors do not need to put in extra efforts on subordinates’ motivation.
- Coordinating Individual Efforts to Group Efforts: MBO emphasizes on achieving the organizational goals which will ultimately lead to the accomplishment of the individual goals as well. Thus, the superior can also direct the personal objectives and efforts of all the employees, towards the attainment of the organizational objectives.
Advantages to Subordinates
The subordinates are responsible for implementing MBO in their workstream. Following are the multiple benefits of MBO to the employees:
- Simplifies Goal Achievement: The subordinates are assigned with individual roles, responsibilities and tasks in the direction of achieving organizational goals which simplify their work.
- Increases Job Satisfaction: When the employees realize the level of efforts made by the management and the superiors to simplify their work, they feel valued and satisfied with their job.
- Initiates Self-Direction and Self-Control: With the help of the well-defined workstream, roles, goals and responsibilities, the subordinates do not need to ask everything from the superiors and can monitor their activities by themselves.
- Encourages Innovative Thinking and Ideas: MBO promotes two-way communication in the organization. Here, the subordinates are also open up to speak out their ideas, thoughts and suggestions; and the management values their innovation and creativity.
- Establishes Cordial Relations with Superiors: When the subordinates are free to communicate with the superiors in a highly motivated and positive work environment, a cordial relationship is formed among the two.
- Motivates to Perform Better: As we already know that MBO acts as a motivator for the subordinates by setting targets for them, they tend to perform better than before.
Limitations of MBO
Despite its numerous advantages, MBO has some shortcomings too, which may sometimes lead to poor results and a downturn in performance.
Let us now go through these drawbacks in detail below:

- Lack of Proper Objective: Due to the changing environment and competitiveness, the organizational objective seems to be vague at times.
- Issues in Goal Setting: Many times, companies set unrealistic goals which are too high to be attainment, thus hindering the MBO process.
- Co-ordination Problem: Eventually, everyone knows their work and are engaged in completing the individual task without interacting with each other. Thus, there may arise a coordination issue in business operations.
- Time Consuming: MBO takes a lot of time, sometimes years to give the desired results.
- Reward-Punishment Approach: It functions on the concept that reward the performer and punish the no-performer; this approach brings in negativity and resistance in the employees.
- Develops Organizational Problems: Sometimes superiors become lenient and carefree about the operations which may lead to substantial organizational problems on non-compliance of the assigned tasks.
- Sometimes Lack Appreciation: It is said that in MBO, appreciation and appraisals are based on individual’s performance. But in reality, in some organizations, promotions are based on favouritism.
Conclusion
When we talk about MBO, it seems a complicated approach. However, it is a strategy which simplifies the business operations, gives the right direction to the employees and the management and also provides the parameters to evaluate performance.
Leave a Reply