Definition: Flexible budget is the one that changes with the level of Activity/Output rather than for any specified activity level. It includes the preparation of multiple budgets that depict budgeted costs for various activity levels.
The flexible budget supersedes the limitations of a fixed budget. Because it is a practical approach that is suitable for dealing with real-life situations.
It analyses the costs with respect to the variations in the output levels. Consequently, the categorization of cost takes place under Fixed, Variable and Semi-variable.
The accuracy of the budget largely depends upon the efficient classification of the costs.
It is also known by multiple names like:
- Dynamic Budget
- Variable Budget
- Sliding Scale Budget
- Step Budget
- Expense Control Budget
- Capacity Budget
Content: Flexible Budget
- Flexible Budget Variance
- Need for a Flexible Budget
- Importance
- Uses
- Methods for Flexible Budgeting
- Advantages
- Disadvantages
- Points to Remember
- Difference Between Fixed and Flexible Budgets
- Example
- Conclusion
Flexible Budget Variance
Generally, the term variance refers to any kind of difference existing between two components.
Flexible Budget Variance is the disparity between the actual and budgeted output, costs and standards. The reason is that budgets are the forecasts for future activities. And the actual output may be more or less than the budgeted ones.
The variance can be either:
- Favourable Variance
- Unfavourable Variance
For Example, A company has prepared a flexible budget and expects an output of 500 units. But post-production, the company produced an output of 450 units. Hence, we can conclude that there exists an unfavourable variance.
Need for a Flexible Budget
The need for preparing flexible budgets arises due to following reasons:
- When the firms are uncertain about the supply of the required sources of production.
- In case of the changes in demand due to psycho-graphic factors like Taste and Fashion.
- Where the firms face difficulty in demand forecasting for new business and products.
- Firms can prepare in response to the changes in the activity resulting from new government policies.
- It is helpful for the firms that are mainly into exports.
- In the case of the firms that carry out production as per the orders received.
- Highlights the changes in the demands.
Importance
- Analytical Tool: This type of budget provides information about costs, profits, etc. Therefore, it helps in performing comparisons and analyses like Marginal Analysis.
- Comparative Analysis: Through flexible budgeting, managers can perform comparative analysis. The analysis may include actual and budgeted costs and comparisons between different costs.
- Cost Reduction and Control: The managers prepare multiple budgets, which helps in selecting the most cost-effective option.
- Practical Approach: The market in which the companies operate is dynamic. So, flexible budgets are a blessing in such situations. As it helps in the forecasting of different output levels.
Uses
- It is a tool for performing the controlling function.
- Aids cost ascertainment.
- A logical comparison between the costs helps in price fixation.
- Helps in cost ascertainment for varied activity levels.
- It also plays a vital in allocating responsibilities in Responsibility Accounting.
Methods for Flexible Budgeting
The organization prepares a flexible budget showing expenses for output levels beforehand. So that they can refer to it as a guide during actual production.
There are two ways of preparing a flexible budget:
- Multi-Activity Level Method
- Flexible Budget Equation Method
Multi-activity Level Method
In this, one prepares different budgets for varied activity levels. Among all, the one closer to the actual activity is to be considered. After that, one needs to analyze the performance and cost analysis by comparing both.
Besides, a major demerit of this method is that multiple budgets are prepared for a single activity. Consequently, consuming extra time and costs.
However, it is suitable when there is a probability of fluctuations in fixed costs.
Flexible Budget Equation Method
It is a scientific approach for creating a flexible budget.
At first, you need to analyze the range under which the activity is expected to fluctuate. Also, anticipate the costs that may incur in this range.
Secondly, categorize these costs under Fixed, Variable and Semi-variable costs.
In addition, distribute the semi-variable costs under Fixed and Variable components. For this, you can use the below-mentioned techniques:
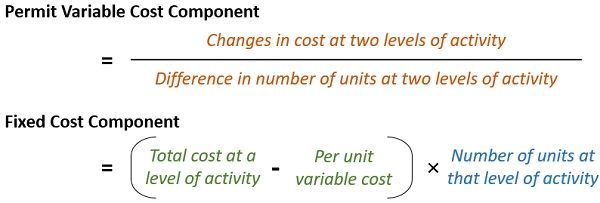
Subsequently, every cost element fits into a flexible budget equation. This equation is expressed as –
y= a + bx
Where,
y shows cost,
a depicts Fixed Cost components,
b indicates the Variable Cost per unit,
x represents the Number of Units
Taking the above equation as a base you can get the flexible budget formula.
Flexible Budget Formula
Flexible Budget= Fixed Cost + (Variable Cost per unit of Activity × Actual Unit of Activity)
Thereafter, prepare a flexible budget for single or multiple activity levels.
Advantages
Following are the advantages of preparing a flexible budget:
- Helps in estimating budgeted costs for each level of activities.
- Significant for budgetary control.
- Facilitates performance analysis of departmental head.
- Provides sufficient data for creating and sending quotations.
- Enables profit planning.
- More practical approach than controlling.
Disadvantages
Besides the above advantages, flexible budgeting possesses the following disadvantages:
- It is a little complex to prepare and therefore requires expert guidance.
- The fallacy in cost classification under fixed and variable heads.
- Can produce misleading results due to errors in cost assortment.
Points to Remember
- Particulars will be in the first column. And the additional columns will be as per the output levels.
- The semi variables will appear in the middle section of the budget.
- In semi-variable costs, variable and fixed costs must appear separately.
- Fixed cost is constant in all activity levels, therefore it must appear in all columns.
Difference Between Fixed and Flexible Budgets
| Basis | Fixed Budget | Flexible Budget |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | As the name suggests, it is the budget that doesn’t change with the actual output. It is prepared for a fixed level of activity | In contrast, it changes with the changes in the activity levels. Hence it is known as a flexible budget |
| Flexibility | It is rigid or inflexible. It remains constant & doesn’t vary with output volume | However, this type of budget is flexible. And it can fluctuate as per the changes in the output volume |
| Budget | Preparation of a Single budget for a fixed level of output | Preparation of Multiple budgets for different output levels |
| Comparison of actual and budgeted costs | There is no scope for comparison | One can make comparisons between actual and budgeted costs for further analysis |
| Cost control | Its application is limited. Thus, it cannot control the costs | In contrast, it facilitates control over costs |
| Classification of Cost | While preparing fixed budget classification of cost isn’t required | During flexible budgeting, the expenses are segregated under Fixed, Variable and Semi-Variable costs |
| Forecasting | Result forecasting is difficult | One can perform future forecasts with the help of business operational aspects |
| Applicability | It has limited applicability | It has a broad scope and applies to everyone |
Example
In a factory, the production budget of expenses for 5000 units is as follows:
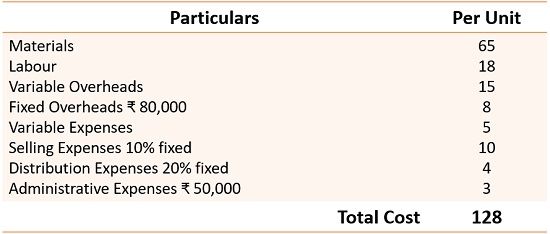
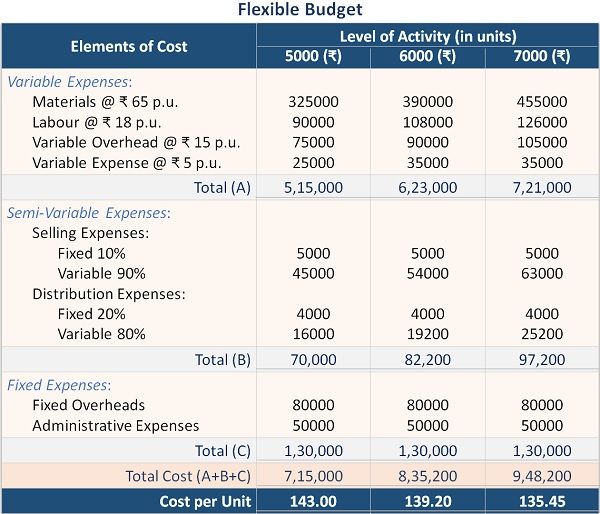
Prepare alternate budgets for producing 6000 and 7000 units.
Solution:
Conclusion
In conclusion, the budget that companies can prepare for multiple output levels is a Flexible Budget. Practically, managers widely use this type of budget as it is the most realistic one.
Besides, it provides guidelines and a base for comparing actual and budgeted costs.
Leave a Reply