Definition: Decentralization refers to the assignment of authority along with the responsibility at each level of the organization. Distribution of the power of decision making along with the related responsibilities among the different managerial levels is necessary for better management.
Example; A bakery manufacturer and outlet owner opened two more retail outlets in his city. The owner was initially taking all the decisions solely and was able to manage both; the manufacturing and the retail outlet by himself.
But now he has to plan for decentralization of his organization. This is because he has to focus more on strategical decisions rather than on the day to day operations of the business.
The sole proprietor hired three managers for all the three outlets. He decided to manage the manufacturing unit by himself. He also appoints the other staff for cleaning and sales to work for each outlet.
Finally, he decides to delegate the authority to the managers for making decisions related to their respective outlet regarding stock, customer handling, order placement, worker’s leave and turnover and other operational activities.
This decentralization practice leads to better management of each outlet as well as the manufacturing unit. It also facilitated the owner to plan for organizational growth and development.
Content: Decentralization
Factors Influencing Decentralization
Decentralization is necessary for large organizations. Here, decision making is required at every step of the business operations. However, every organization need not necessarily go for decentralization.
The following factors affect the decision of decentralization of the organization: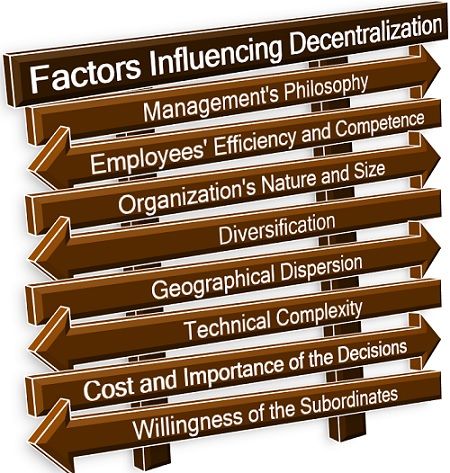
Management’s Philosophy: In the organizations where the top management wants its employees to take some of the decisions, a decentralized system is formed.
However, if the mindset of the administration is such that they solely prefer to make all the business-related decisions, they won’t go for decentralization.
Employees’ Efficiency and Competence: If the organization has efficient and skilled resources which it can rely on, it opts for decentralization. Whereas in the absence of capable managers, the top management prefers to retain the power of decision making.
Organization’s Nature and Size: If the organization is a sole proprietorship or partnership business, running on a narrow scale with a limited number of employees, there is no need for decentralization.
However, for the corporates running on a vast scale, a decentralized system is necessary for the smooth functioning of the business.
Diversification: For an organization which is engaged in the production of a whole range of different products, centralization becomes difficult. Thus, the delegation of authority and division of work is essential for the organizations involved in a diversified product line.
Geographical Dispersion: The organizations which expand over a vast geographic area, having branches in different locations need decentralization. Since the management cannot function and take all operational decisions solely in such cases.
Technical Complexity: While introducing new technology into the organization, the top management has to shift some authority and responsibility to the experts in the area, i.e. the managers. They know all the in and outs of the business operations and the new technology.
Cost and Importance of the Decisions: The top management analyzes the impact and importance of the decisions before delegating the authority of such decision making to the managers. Mostly, the decisions related to business operations are entrusted to the managers.
Willingness of the Subordinates: Decentralization is also influenced by the desire and initiative of the subordinates to take responsibility for their decisions, along with its authority.
Objectives of Decentralization
Decentralization is an important strategical decision. It changes the whole organizational structure right from the top management to the bottom level. Like other business strategies, decentralization is also purposeful.
Let us understand the various objectives for which organizations decentralize their operations: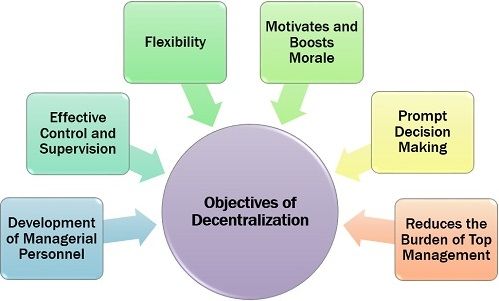
Development of Managerial Personnel
Decentralization provides for self-learning of the managers by facing the problem, finding the solutions themselves and taking the correct decisions. It adds on to the skills, experience and expertise of the managers in their respective departments.
Effective Control and Supervision
The managers exercise better control over the operations of the subordinates by taking disciplinary actions. They can make decisions related to production schedules, promotions and leaves taken by the subordinates.
Flexibility
Decentralization leads to flexibility in business operations. It also provides authority to the managers to handle unexpected situations independently. It allows them to manage their respective departments in the way they want to.
Motivates and Boosts Morale
It creates self-dependant managers and drives them to enhance their performance, take the initiative and develop a problem-solving attitude. Decision making also boosts their morale and confidence.
Prompt Decision Making
There are times when the managers have to take immediate and unplanned decisions at operational levels; it is only possible in decentralized organizations.
On the contrary, in a centralized organization, the decision-making process is quite lengthy and complicated, which is ineffective for handling unforeseen operational problems and issues.
Reduces the Burden of Top Management
The management has to take certain crucial strategical decisions which require a lot of analysis and planning. Decentralization releases the management from operational decision making, facilitating them to engage themselves in future strategic planning.
Limitations of Decentralization
As we have already seen that decentralization is a useful practice for the organization operating on a large scale. But there are certain shortcomings of decentralization too which makes it unsuitable for all type of organizations.
To know more about these limitations of decentralization, read below:
- Increases Administrative Expenses: To practice decentralization, the top management has to appoint well qualified and experienced managers. These managers need to be paid reasonably, thus increasing the administrative expenses of the organization.
- High Operational Cost: When different department are formed during decentralization, the organization incurs high cost on the day to day operations, resources, employees, etc.
- Managerial Inefficiency: At times, the managers are not efficient and skilled enough to take decisions on their own. The decisions made by such managers may sometimes prove to be disastrous for the organization.
- Not Suitable for Small Firms: The organizations which are small in size neither require decentralization nor departmentation. They can be efficiently managed by the owner or the management itself.
- Lacks Uniformity: Every manager in a decentralized organization will possess a different opinion, individual set of actions and a unique management style which brings in non-uniformity in the organization.
- Co-ordination Problem: Decentralization allows decision making at all levels. These decisions need to be taken in collaboration with other departments. Sometimes there is a coordination problem among the managers of the different departments creating loopholes in the business operations.
Conclusion
Decentralization is essential in the present business scenario where the organizations are becoming vast and diversifying into different product lines.
The top management needs to focus on other strategical issues. For this, they have to free themselves from the day to day operations. It is only possible through delegation of the authority and responsibility to the managerial level.
The top management may also plan for partial decentralization of the organization. Where the managers themselves can take certain less critical business decisions; the senior management is responsible for making crucial decisions.
Leave a Reply