Definition: Compensation management deals with every type of reward and its allocation in the most desirable way. It is an essential tool for managers in Human Resource Management. This is because it helps achieve equity, transparency and consistency across the organization.
Organizations can offer these compensations to employees directly or indirectly. They may pay directly in monetary form and indirectly in a non-monetary form which is discussed in detail further.
Compensation management can also be termed as:
- Wage and Salary Administration
- Remuneration Management
- Reward Management
Content: Compensation Management
Objectives
The objectives of compensation management are to:
- Administer wages and salary.
- Attract new and skilled employees.
- Retain current employees.
- Acknowledge and recognize good work.
- Control unnecessary costs.
- Blend individual goals with organizational goals.
- Adhere to the Government laws related to remuneration.
Internal and External Factors
A variety of internal and external factors affect the organisation’s compensation strategy.
Internal factors include:
- Employee
- Business Strategy
- Job Evaluation
- Performance Appraisal
External factors include:
- Labour Market
- Government Legislations
- Society
- Economy
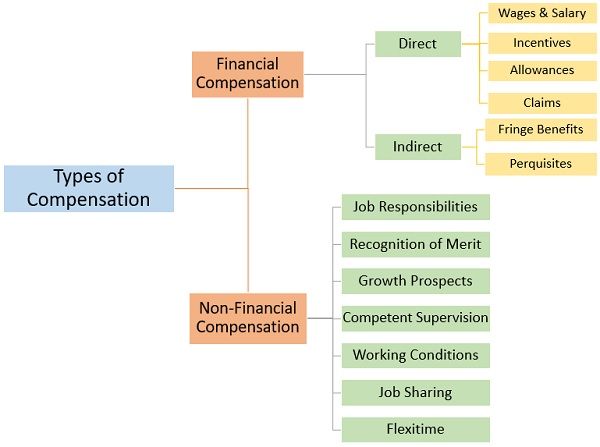
Types of Compensation Management
Employers can make use of different components for compensating their employees. These components or types of compensation are as follows:
- Financial Compensation
- Non-Financial Compensation
Financial Compensation
In this form of compensation, the payment of rewards takes place in monetary terms. It is further divided into:
- Direct Compensation
- Indirect Compensation
Direct Compensation
- Wages and Salary
The compensation paid daily for intra-day work is known as Wages. Whereas, Salary is the monthly payment for the work performed. - Incentives
It is the money received in addition to wages or salary based on individual performance. - Allowances
Apart from a basic salary, the employer pays a certain amount for a specific purpose or expenditure. Different types of allowances are part of compensation management like:- Dearness Allowance
- House Rent Allowance
- Conveyance Allowance
- Leave Travel Allowance, etc.
- Claims
Claims are the reimbursement of bills. Generally, employees claim their bills along with their monthly salary. These include:
-
- Telephone/Mobile Allowance
- Internet Allowance
- Medical Allowance, etc.
Indirect Compensation
- Fringe Benefits
These are the financial benefits received by the employees. Fringe Benefits include:- Provident Fund
- Gratuity
- Medical Care
- Accident Relief
- Insurances, etc.
- Perquisites
These are the benefits allowed to the executives above salary. Perquisites include:
-
- Company Car
- Club Membership
- Paid Holiday
- Furnished House
- Stock option schemes
Non-Financial Compensation
In this form of compensation, the employees receive non-monetary rewards. Non-Financial compensation consists of:
- Challenging Job Responsibilities
- Recognition of Merit
- Growth Prospects
- Competent Supervision
- Comfortable Working Conditions
- Job Sharing
- Flexitime, etc.
Compensation Management Process
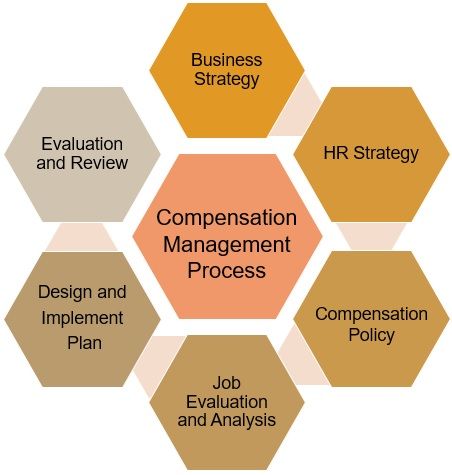
Step 1: Business Strategy
Companies adopt several strategies to fulfil their long-term goals. These strategies may include – expansion, contraction and widening, etc.
Thus, companies assess human resources requirements and their compensation based on these strategies.
Step 2: HR Strategy
HR managers use compensation as a motivational tool toward organizational objectives.
So, after analyzing the human resources requirements, managers develop an appropriate compensation strategy. They can choose from financial and non-financial incentives.
For instance, high risk and return rewards for encouraging employees.
Step 3: Compensation Policy
The compensation policies are developed in a flexible, performance-oriented and easy form. The entire compensation structure is designed considering internal and external factors.
Step 4: Job Evaluation and Analysis
The managers perform a detailed analysis of the job. The rewards or combinations of rewards are structured as per the job and its elements.
Step 5: Design and Implementation of Compensation Plan
The rewards are designed according to the need and different organisational levels. These rewards have a significant impact on the employer-employee relationship. Its implementation considers certain factors like:
- Performance
- Skill Development, etc.
Step 6: Evaluation and Review
The compensation designed and implemented requires periodic evaluation and review. The managers must ensure employee satisfaction at the end of the process.
Principles
- The company should pay compensation according to its ability to pay. If they spend more/less than their ability, they may suffer bankruptcy, or competitors may take advantage of it.
- Organizations must keep in mind internal and external equity while compensating.
- There should be a performance-based rewarding system. It will result in maintaining fairness and justice in the organization.
- Remuneration paid to employees should be non-discriminatory. It must be irrespective of factors like religion, gender, etc.
- Organizations must pay minimum wage to distinct categories specified by law.
- The compensation scheme should be flexible and simple. It should be easy to understand and update according to requirements.
Importance of Compensation Management
- It integrates employees’ efforts towards organizational goals.
- It helps in acquiring, maintaining, and creating a motivated workforce.
- Compensation is an essential tool for managers in human resource management.
- Helpful in attracting a talented workforce and creating organizational brand value.
- It enables enhancement in work efficiency and job satisfaction among employees.
- Compensation management helps in the creation of talent pools.
Theories of Compensation Management
Theories help to find out the most suitable components of compensation. Following are the theories of compensation management:
- Equity Theory
- Reinforcement Theory
- Agency Theory
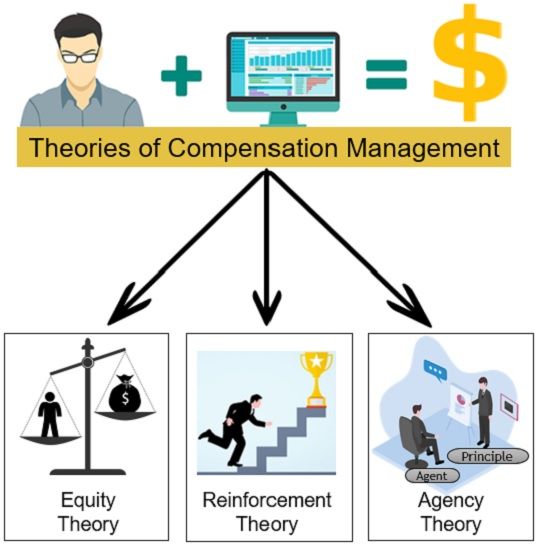
Equity Theory
This theory focuses on the equity in remuneration among employees. Adam’s equity theory suggests that the employee tries to gain equity who don’t find equity in their rewards.
Equity is of three types:
- Internal Equity
The fairness & difference in remuneration between different job roles & responsibilities within the organization. - External Equity
The fairness & difference in remuneration between the same job roles outside the organization. - Individual Equity
The fairness & difference in remuneration between the same job roles within the organization.
The following can be the results of the inequity in the organization:
- Decreased Productivity
- Increased Absenteeism
- Increased Employee Turnover
Reinforcement Theory
According to reinforcement theory, the employees are most likely to repeat their rewarding experience.
Suppose one employee received a bonus for high performance. After that, he would repeat the same in future. But, if he doesn’t receive financial rewards in the future, his performance may degrade.
Agency Theory
This theory aims to align individual interests and goals with organizational goals by using compensation.
The employer (principal) and employee (agent) are the two stakeholders of the organization. The rewards paid to the employees are agency costs.
The agent tries to maximise this cost while the principal attempts to minimise it. The principal chooses a contract scheme to align interests and goals. These contact can be either behaviour-oriented or outcome-oriented.
Example of Compensation Management
Microsoft Corporation is a technology-based multinational company. They provide a set of monetary and non-monetary benefits to their employees.

At Microsoft, they aim at a healthy life and investment in personnel’s future. They organize a specific set of programs, events, services and better human connections. Some of them are listed below:
- Flexibility to care for employees and their families.
- Paid leaves to the family caregiver and new parents.
- Promotes family support programs and organizes parenting classes.
- Work schedules flexibility for the employees.
- Microsoft focuses on the growth and career progress of employees.
- The company also provides a car lease policy.
- They offer competitive pay to their employees.
- Stock awards to employees based on their performance.
- Bonuses other than salary for different purposes.
Final Words
To sum up, compensation is the value offered to the employee for their efforts. Employees can receive it in monetary and non-monetary forms.
The managers design the compensation according to the job roles and responsibilities. Thereby providing fair wages and creating a motivated workforce.
Leave a Reply