Definition: Performance appraisal is a process of evaluating the employee’s performance in a workplace covering all qualitative and quantitative aspects of the job. It can be considered as an efficient method of evaluating personnel’s capabilities and their work-related conduct to assess his/her future growth possibilities. It also builds an effective communication channel between the employer and the employees of the organization.
Performance appraisal can alternatively be said as a method that ascertains and conveys to the personnel that how well they are performing in their workplace by constituting new plans and making improvements in the old ones. It is always considered as one of the crucial area of any organization as companies generally provide increments and bonuses on the basis of the annual performance appraisal report of the employees. On the contrary, in case of negative report employees becomes answerable to the organization why their report is negative.
Content: Performance Appraisal
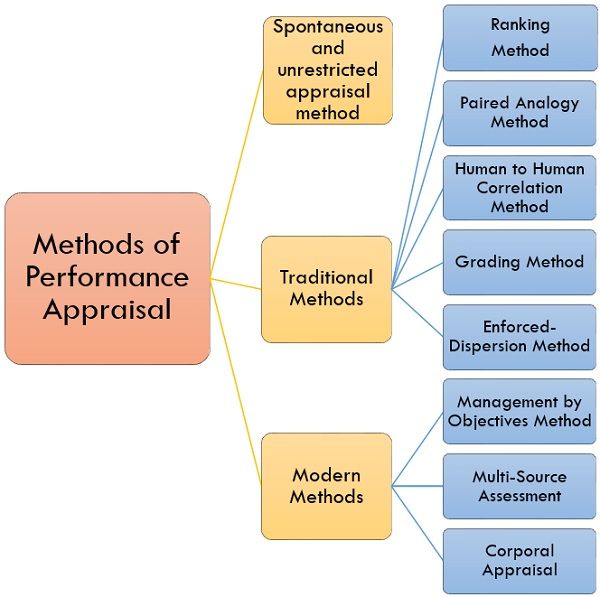
Methods of Performance Appraisal
Various performance appraisal methods have been developed in order to accomplish the targets. It is very tough to search for a suitable performance appraisal method. The selection of procedure relies upon the ideology of the company, its targets, technology, size and its products, etc. Some primary methods are discussed below:
1. Spontaneous and Unrestricted Appraisal Method
This approach is the oldest performance appraisal approach commonly used by all companies. This approach gives more importance in calculating personnel’s worth as an individual, although it does not assess all other performances; thus, there are more chances of human bias in this approach.
2. Traditional Methods
Some of the traditional methods are as follows:
- Ranking Method
Traditional method is the simplest performance appraisal method in which all the employees are compared, and ranking is provided to them according to their worth, which helps to differentiate efficient and inefficient personnel. But it has some shortcomings as well; they are as follows:
- Every individual has distinct attributes and characteristics; thus, it is not enviable to correlate one personnel from another.
- Comparing one personnel from another may tell us that one is better than another, but it cannot measure the percentage of betterment.
- Providing ranking to its employees becomes possible for small companies; in large companies, it’s very difficult to rank their employees according to their worth.
This approach does not have any precise method to assess the worth of the corresponding personnel.
- Paired-Analogy Method
Paired-Analogy method correlates the performance of every worker with the other worker in its section, and this method was made to beat the glitches of the ranking method. Comparison of two employees is made at a time, and from them, one employee gets selected. For example, there are 6 employees in a company vis: A, B, C, D, E, and F, then employee A’s performance will be compared with employee B, and the better performer will get selected. Then the selected employee will again be compared with C and D, and the same process will be followed by all the employees in a company. The formula used for deciding a number of total comparisons is as follows:
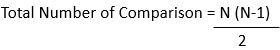
Where,
N= Number of employees to be compared.
In the above-given example, 8 decisions will be taken for 6 employees.
- Human to Human Correlation
In the human to human correlation method, definite elements are selected for investigation purposes such as action, fidelity, responsibility, vision and leadership, and after selecting all elements, the scale is outlined for every element. Specific employees are used to presenting images of these degrees, two individuals representing two ends of the scales are picked, the most efficient and least efficient employees will be selected for the two ends. Then an average individual will be chosen to show the medium point, and after choosing the medium point, make one point above the medium point and another one below the medium point. In this way, a scale of five points is determined, and in place of comparing all employees to all individuals, employees are correlated to the key person, one element at a time.
- Grading System
Some divisions of worth are entrenched well in advance under this system, such as division are entrenched as outstanding, fair, average, inadequate and worst, etc. The employee’s performance gets compared, and grade will be provided to them accordingly, I.e., the best performing personnel will get the best grade.
- Enforced-Dispersion
This approach is a modified version of the grading system approach, in which a fixed percentage is set for each grade. An ideal dispersion is as follows:

Thus, in this method, one cannot judge all employees in the same category. Here, the rating is given 10% to the superior employees, 20% to the good employees, 40 % to the average employees, 20% to the bad employees and 10% to the poor employees.
3. Modern Methods
Modern methods are more improvised methods than traditional methods of performance appraisal. The following are some of the methods that come under modern methods:
- Management by Objectives Method
To overcome the problems faced in a traditional method, Peter. F. Drucker introduced the management by objectives concept in 1954. Management by objectives specifies the significant targets and time to time analysis of the work progress. It gives prominence to a collaborated but joint decision of success in annual performance appraisal interviews and targets.
Primary stages of management by objectives consist of:
- Establishing the targets.
- Performance Reviews.
- Providing Feedback.
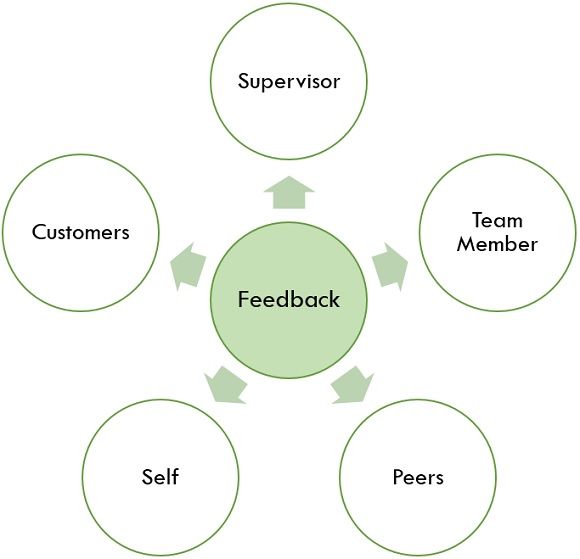
- Multi-Source Assessment
Multi-Source Assessment can be described as feedback collected from the shareholders individually or from a group of shareholders based on their performances. The main objective of this method is to provide a performance report to every employee of the company, which helps the employee to understand his efficiency level in a company, and it is mainly concentrated on top-level employees of the company. The mode for multi-level source assessment will look like this:
- Corporal Appraisal
This appraisal is regulated to calculate the personnel’s future capabilities for which companies appoint psychologists to assess the future capability of their employees. Psychologists perform psychological tests for it, which covers personnel’s reasoning ability, academic ability, emotional strength, forecasting ability, etc.
Conclusion
The term performance appraisal is made up of two split terms Performance + Appraisal, in which Performance denotes what is likely to be conveyed by a person, and Appraisal denotes the progression of worth or quality.
Leave a Reply